Ferroptosis Target Information
General Information of the Ferroptosis Target (ID: TAR10053)
| Target Name | Solute carrier family 40 member 1 (SLC40A1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ferroportin-1; Iron-regulated transporter 1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene Name | SLC40A1 | ||||
| Sequence |
MTRAGDHNRQRGCCGSLADYLTSAKFLLYLGHSLSTWGDRMWHFAVSVFLVELYGNSLLL
TAVYGLVVAGSVLVLGAIIGDWVDKNARLKVAQTSLVVQNVSVILCGIILMMVFLHKHEL LTMYHGWVLTSCYILIITIANIANLASTATAITIQRDWIVVVAGEDRSKLANMNATIRRI DQLTNILAPMAVGQIMTFGSPVIGCGFISGWNLVSMCVEYVLLWKVYQKTPALAVKAGLK EEETELKQLNLHKDTEPKPLEGTHLMGVKDSNIHELEHEQEPTCASQMAEPFRTFRDGWV SYYNQPVFLAGMGLAFLYMTVLGFDCITTGYAYTQGLSGSILSILMGASAITGIMGTVAF TWLRRKCGLVRTGLISGLAQLSCLILCVISVFMPGSPLDLSVSPFEDIRSRFIQGESITP TKIPEITTEIYMSNGSNSANIVPETSPESVPIISVSLLFAGVIAARIGLWSFDLTVTQLL QENVIESERGIINGVQNSMNYLLDLLHFIMVILAPNPEAFGLLVLISVSFVAMGHIMYFR FAQNTLGNKLFACGPDAKEVRKENQANTSVV Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Family | Ferroportin family | ||||
| Function |
Transports Fe(2+) from the inside of a cell to the outside of the cell, playing a key role for maintaining systemic iron homeostasis. Transports iron from intestinal, splenic, hepatic cells, macrophages and erythrocytes into the blood to provide iron to other tissues. Controls therefore dietary iron uptake, iron recycling by macrophages and erythrocytes, and release of iron stores in hepatocytes. When iron is in excess in serum, circulating HAMP/hepcidin levels increase resulting in a degradation of SLC40A1, thus limiting the iron efflux to plasma.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene ID | 30061 | ||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Target Type | Driver Suppressor Marker | ||||
| Mechanism Diagram | Click to View the Original Diagram | ||||
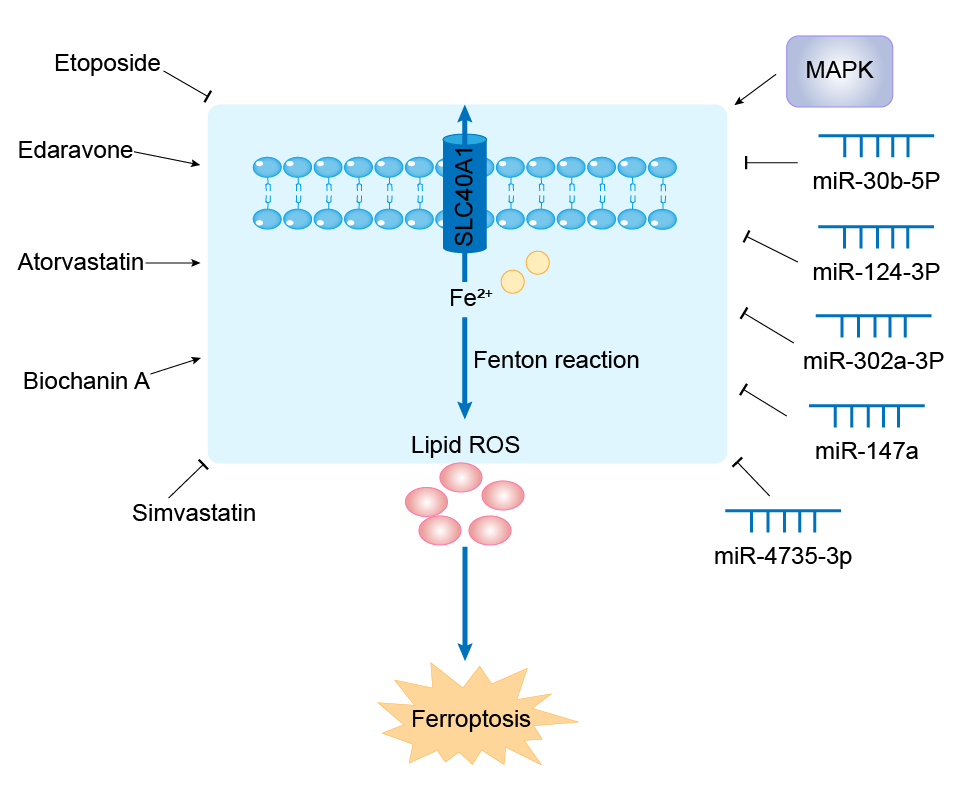
|
|||||
Full List of Regulator(s) of This Ferroptosis Target and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
SLC40A1 can be involved in and affect the ferroptosis by the following regulators, and result in corresponding disease/drug response(s). You can browse corresponding disease or drug response(s) resulting from the regulation of certain regulators.
Browse Regulator related Disease
Browse Regulator related Drug
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 (MAPK14)
Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [1] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Artesunate | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
In Vitro Model |
U-251MG cells | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0021 | |
| In Vivo Model |
The xenografts were established via the subcutaneous inoculation of U251 cells (1 x 107 cells/per mouse) into the armpit of one mouse. After two weeks of growth, the cancer tissues were cut into pieces with the dimensions of 1.5 x 1.5 x 1.5 mm3 and inoculated subcutaneously into the right armpit of the mice with a puncture needle. When tumor volume reached approximately 80 mm3, mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 5): Vehicle control, ART (20 mg/kg), ART (40 mg/kg), and TMZ (40 mg/kg). TMZ was used as the positive control. Drugs and vehicle were given by intraperitoneal injection daily for 21 days. Tumor volume and body weight were measured every three days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Artesunate triggers ferroptosis in glioblastoma in vitro and in vivo through regulation of iron metabolism and p38 ( MAPK14) and ERK signaling pathways. Meanwhile, ART reduced the protein level of GPX4 and FPN1, increased the protein level of DMT1, TfR, ferritin and NCOA4. | ||||
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK1)
Corpus uteri cancer [ICD-11: 2C76]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [2] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Drug | Simvastatin | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
In Vitro Model |
Ishikawa cells | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2529 |
| Response Description | Simvastatin has the potential to be a targeted drug for endometrial cancer (EC) treatment. Besides, the inhibition to the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway allows simvastatin to induce ferroptosis through up-regulating the level of ROS, MDA, Fe2+, and TRF1 (TF) and reducing the level of GSH, SLC7A11, and FPN in cells. | |||
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 35 (USP35)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [3] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
In Vitro Model |
BEAS-2B cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| HBE1 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0287 | ||
| A-549 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | ||
| NCI-H358 cells | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1559 | ||
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 | ||
| NCI-H1299 cells | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | ||
| H1650-ER1 cells | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4V01 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
BALB/c nude mice (4-5 weeks old) were obtained from HFK Bioscience Co., Ltd (Beijing, China) and maintained in a SPF barrier system. H460, H1299 or H1650 cell lines at a dose of 1 x 106 with or without USP35 manipulation were subcutaneously injected into the right dorsal flank of the nude mice.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | USP35 was abundant in human lung cancer tissues and cell lines. USP35 knockdown promoted ferroptosis, and inhibited cell growth, colony formation, and tumor progression in lung cancer cells. Further studies determined that USP35 directly interacted with ferroportin (FPN) and functioned as a deubiquitinase to maintain its protein stability. | ||||
Transcription regulator protein BACH1 (BACH1)
Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [4] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| Cell metastasis | |||||
In Vitro Model |
mEFs (Mouse embryonic fibroblasts) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
The generation of Bach1-/-mice on the C57BL/6J background was described previously. Mice 13 weeks of age were analyzed for models of AMI. The mice were subjected to ligation of the proximal LAD to induce AMI. They were randomly assigned to sham or AMI, DMSO, or DFX groups.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | BACH1 accelerates ferroptosis by suppressing labile iron metabolism. And ferritin genes (Fth1 and Ftl1) and the ferroportin gene (Slc40a1) were dramatically up-regulated in Bach1-/- MEFs. BACH1 controls the threshold of ferroptosis induction and may represent a therapeutic target for alleviating ferroptosis-related diseases, including myocardial infarction. | ||||
Serine-protein kinase ATM (ATM)
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [5] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| RCC4 cells | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0498 | |
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HT-1080 cells | Fibrosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0317 | |
| Response Description | ATM inhibition enhanced the nuclear translocation of metal-regulatory transcription factor 1 (MTF1), responsible for regulating expression of Ferritin/FPN1 and ferroptosis protection in breast adenocarcinoma. | |||
Paired box protein Pax-3 (PAX3)
Preeclampsia [ICD-11: JA24]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [6] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
HTR-8/SVneo cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7162 | |
| hETCs (Human first-trimester extravillous trophoblast cells) | |||||
| In Vivo Model |
Pregnant SD rats were randomly dived into four groups: sham group (n = 8), PE group (n = 8), PE + ferrostatin-1 group ( n= 8), and PE + miR-30b-5p inhibition group (n = 8). On day 14 of pregnancy, PE rat model was established through reduced uterine perfusion pressure (RUPP) surgery, wherein constrictive silver clips were placed on the aorta (0.203-mm clips) superior to the iliac bifurcation and on the ovarian vessels (0.100-mm clips), according to a previous description. Sham rats were operated on in a fashion similar to that of RUPP rats, but without clipping. Mini-pumps were also intraperitoneally inserted into rats on day 14 of pregnancy. The mini-pump in each rat delivered the ferrostatin-1 at a dose of 10 umol/kg/day for 5 days. An miR-30b-5p antagonist (GenePharma) was injected from the tail veins on day 13 of gestation, at a rate of 100 uL/day for 6 days. The blood pressure was measured on days 14, 16, and 19 of gestation using catheters inserted into the carotid artery and jugular vein.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Abnormally up-regulated miR-30b-5p triggered the ferroptosis in trophoblasts under hypoxic conditions by down-regulating SLC7A11, Pax3, and Pax3-downstream target, FPN1. Blockage of miR-30b-5p up-regulation or direct inhibition of ferroptosis attenuated preeclampsia (PE) symptoms in the rat model, making miR-30b-5p a potential therapeutic target for preeclampsia. | ||||
Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p100 subunit (NFKB2)
Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [7] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
Royan N9 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_9455 | |
| Royan N33 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_9417 | ||
| T98 cells | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B368 | ||
| U87 MG-Red-Fluc cells | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5J12 | ||
| U-251MG cells | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0021 | ||
| LN-229 cells | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | ||
| A-172 cells | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | ||
| U118 cells | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0633 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Four-to five-week-old female BALB/c nude mice were obtained from the Laboratory Animal Center, Southern Medical University. To study the role of IRP1 in TMZ resistance, the mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 6 per group) (U87TR, U87TR + TMZ, U87TR-lvIRP1, U87TR-lvIRP1 + TMZ). To establish the GBM models, IRP1 overexpress or control U87TR cells (5 x 105 cells per mice in 3 uL PBS) transfected with luciferase lentivirus were injected into the mice brain under the guidance of a stereotactic instrument at coordinates relative to bregma: 2.0 mm posterior, 2.0 mm lateral, and 3.0 mm ventral.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Amplifying IRP1 signals can reverse TMZ resistance and suppress tumor growthin vivovia inhibiting NFKB2 in the noncanonical NF-kB signaling pathway. In addition, NFKB2 affected TMZ sensitivity of glioblastoma by modulating the expression of LCN2 and FPN1. | ||||
NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-2 (SIRT2)
Neuropathic pain [ICD-11: 8E43]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [8] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
About 70 adult male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 200-250 g were used in the animal model. Rats were anesthetized with 5% isoflurane by a small animal anesthesia machine and maintained with 2-3% isoflurane. The rats were placed in a left decubitus position; approximately 1 cm below the right iliac bone, the three branches of the sciatic nerve were exposed: the tibial nerve, common peroneal nerve, and sural nerve.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | An intrathecal injection of SIRT2 overexpressed recombinant adenovirus, which upregulated the expression of SIRT2, attenuated mechanical allodynia, enhanced the level of FPN1, inhibited intracellular iron accumulation, and reduced oxidant stress levels, thereby reversing the changes to ACSL4 and GPX4 expression in the SNI rats. This evidence suggests that SIRT2-targeted therapeutics may help relieve the symptoms of chronic neuropathic pain (NP). | ||||
mmu-miR-124-3p (miRNA)
Intracerebral hemorrhage [ICD-11: 8B00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [9] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
In Vitro Model |
HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| hBCs (Brain cells) | |||||
| In Vivo Model |
Fpn-floxed (Fpnflox/flox) mice were obtained from Dr. N.C. Andrews and transferred into a C57bl/6 background. Mice were treated with a mixture of ketamine (100 mg/kg) and dexmedetomidine (0.5 mg/kg) and immobilized on a stereotaxic apparatus (RWD Life Science Co., Shenzhen). All experimental mice received a total of 20 ul autologous blood injected successively into the caudate nucleus (bregma 0: 0.8 mm anterior, 2 mm left lateral and 3.5 mm deep).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Both apoptosis and ferroptosis, but not necroptosis, were regulated by miR-124/Fpn signaling manipulation. Thus, Fpn upregulation or miR-124 inhibition might be promising therapeutic approachs for intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). | ||||
Metal regulatory transcription factor 1 (MTF1)
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [5] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| RCC4 cells | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0498 | |
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| HT-1080 cells | Fibrosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0317 | |
| Response Description | ATM inhibition enhanced the nuclear translocation of metal-regulatory transcription factor 1 (MTF1), responsible for regulating expression of Ferritin/FPN1 and ferroptosis protection in breast adenocarcinoma. | |||
hsa-miR-4735-3p (miRNA)
Hereditary Leiomyomatosis [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [10] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In Vitro Model |
786-O cells | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1051 |
| A-498 cells | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1056 | |
| HK-2 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0302 | |
| Response Description | The miR-4735-3p mimic increased, while the miR-4735-3p inhibitor decreased oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, iron overload, and ferroptosis of human Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) cell lines. Mechanistic studies identified SLC40A1 as a direct target of miR-4735-3p. | |||
hsa-miR-30b-5p (miRNA)
Preeclampsia [ICD-11: JA24]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [6] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
HTR-8/SVneo cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7162 | |
| hETCs (Human first-trimester extravillous trophoblast cells) | |||||
| In Vivo Model |
Pregnant SD rats were randomly dived into four groups: sham group (n = 8), PE group (n = 8), PE + ferrostatin-1 group ( n= 8), and PE + miR-30b-5p inhibition group (n = 8). On day 14 of pregnancy, PE rat model was established through reduced uterine perfusion pressure (RUPP) surgery, wherein constrictive silver clips were placed on the aorta (0.203-mm clips) superior to the iliac bifurcation and on the ovarian vessels (0.100-mm clips), according to a previous description. Sham rats were operated on in a fashion similar to that of RUPP rats, but without clipping. Mini-pumps were also intraperitoneally inserted into rats on day 14 of pregnancy. The mini-pump in each rat delivered the ferrostatin-1 at a dose of 10 umol/kg/day for 5 days. An miR-30b-5p antagonist (GenePharma) was injected from the tail veins on day 13 of gestation, at a rate of 100 uL/day for 6 days. The blood pressure was measured on days 14, 16, and 19 of gestation using catheters inserted into the carotid artery and jugular vein.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Abnormally up-regulated miR-30b-5p triggered the ferroptosis in trophoblasts under hypoxic conditions by down-regulating SLC7A11, Pax3, and Pax3-downstream target, FPN1. Blockage of miR-30b-5p up-regulation or direct inhibition of ferroptosis attenuated preeclampsia (PE) symptoms in the rat model, making miR-30b-5p a potential therapeutic target for preeclampsia. | ||||
hsa-miR-302a-3p (miRNA)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [11] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
In Vitro Model |
A-549 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H358 cells | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1559 | |
| NCI-H1299 cells | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| H1650-ER1 cells | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4V01 | |
| BEAS-2B cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | |
| HBE1 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0287 | |
| Response Description | The miR-302a-3p mimic directly bound to the 3-UTR of FPN and decreased its protein expression, thereby causing intracellular iron overload and ferroptotic cell death, while the miR-302a-3p inhibitor significantly prevented erastin/RSL3-induced ferroptosis and tumor suppression. miR-302a-3p functions as a tumor inhibitor, via targeting ferroportin to induce ferroptosis of non-small cell lung cancer. | |||
hsa-miR-147a (miRNA)
Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [12] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
In Vitro Model |
U-87MG cells | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_GP63 |
| A-172 cells | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| hMGCs (Human normal brain astroglia cells) | ||||
| SVG p12 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3797 | |
| Response Description | miR-147a targets SLC40A1 to induce ferroptosis in human glioblastoma in vitro. Mechanistically, miR-147a directly bound to the 3'-untranslated region of SLC40A1 and inhibited SLC40A1-mediated iron export, thereby facilitating iron overload, lipid peroxidation, and ferroptosis. | |||
hsa-miR-10a-5p (miRNA)
Intervertebral disc degeneration [ICD-11: FA80]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [13] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
hCDs (Chondrocytes) | |||
| Response Description | Inflammatory cytokine IL-6 appeared in Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) aggravates its degeneration by inducing cartilage cell ferroptosis. This is caused partially by inhibiting miR-10a-5p and subsequently derepressing IL-6R signaling pathway. The ferroptosis-inhibitory effect exhibited by overexpressing miR-10a-5p was achieved by promoting GPX4 and ferroportin-1 (FPN1) but suppressing divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) expression in IL-6-treated cartilage cells. | |||
Glutaredoxin-related protein 5, mitochondrial (GLRX5)
Head neck squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2D60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [14] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
AMC-HN-3 cells | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5961 | |
| HN3R (Human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell) | |||||
| HN4 cells | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_IS30 | ||
| HN4R (Human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell) | |||||
| In Vivo Model |
Five-week-old athymic BALB/c male nude mice (nu/nu) were purchased from Central Lab Animal Inc. (Seoul, Republic of Korea). HN4R cells with vector control or shGLRX5 were subcutaneously injected into the bilateral flank of nude mice. From the day when gross nodules were detected in tumor implants, mice were subjected to different treatments: vehicle or SAS (250 mg/kg daily per intraperitoneal route). Each group included seven mice.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Inhibition of GLRX5 predisposes therapy-resistant head and neck cancer (HNC) cells to ferroptosis. Increased IRP and TfR and decreased Fpn and FTH boosted up intracellular free iron, resulting in lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis in vitro and in vivo. | ||||
CD82 antigen (CD82)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [15] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
In Vitro Model |
MIA PaCa-2 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 |
| Response Description | High expression of the KAI1 (CD82) gene promoted the occurrence of ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells through its extensive effect on FPN and GPX4. KAI1induced ferroptosis did not significantly inhibit the proliferation of PC cells. | |||
Carbonic anhydrase 9 (CA9)
Pleural mesothelioma [ICD-11: 2C26]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [16] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| Cell migration | ||||
In Vitro Model |
ACC-MESO1 cells | Pleural mesothelioma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5113 |
| NCI-H2373 cells | Pleural mesothelioma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_A533 | |
| NCI-H2052 cells | Pleural mesothelioma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1518 | |
| MET-5A cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3749 | |
| Response Description | CA9 suppression by inhibitors (S4 and U104) decreased viability and migration of MM cells, accompanied by overexpression of TFRC, IREB1/2 and FPN1(SLC40A1) and by downregulation of FTH/FTL in Pleural mesothelioma. | |||
Unspecific Regulator
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 3 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [17] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Siramesine | Terminated | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| SK-BR-3 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| ZR-75-1 cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 | |
| Response Description | Overexpression FPN resulted in decreased ROS and cell death whereas knockdown of FPN increased cell death after siramesine and lapatinib treatment. This indicates a novel induction of ferroptosis through altered iron regulation by treating breast cancer cells with a lysosome disruptor and a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [17] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Lapatinib | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| SK-BR-3 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| ZR-75-1 cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 | |
| Response Description | Overexpression FPN resulted in decreased ROS and cell death whereas knockdown of FPN increased cell death after siramesine and lapatinib treatment. This indicates a novel induction of ferroptosis through altered iron regulation by treating breast cancer cells with a lysosome disruptor and a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [18] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Etoposide | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 |
| MCF-10A cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| Response Description | The combined treatment of etoposide and erastin synergistically induced oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, while suppressing glutathione peroxidase activity in breast cancer cells. More importantly, the combination treatment synergistically increased iron accumulation, which was associated with altered expression of IREB2/FPN1. Additionally, ferroptosis-regulating proteins ACSF2 and GPX4 were altered more potently by the combination treatment, compared to untreated cells and erastin treatment alone (p<0.05). | |||
Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [19] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Epigallocatechin Gallate | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Response Description | Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) pretreatment counteracted 6-OHDA-induced increased expression of divalent metal transporter-1 (DMT1) and hepcidin and decreased expression of the iron-export protein ferroportin 1 (Fpn1), leading to a 28% reduction in Fe2+ uptake. EGCG inhibits iron overload, decreased LPO, and increased GSH levels in Parkinson disease models, which are the three major hallmarks of ferroptosis. | |||
Alzheimer disease [ICD-11: 8A20]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [20] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Thioctic acid | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
In Vitro Model |
hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
The P301S transgenic mice [B6C3-Tg (Prnp-MAPT*P301S) PS19 Vle/J], originally obtained from the Jackson laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME, USA), were used as a model of tauopathy. The female mice at the age of 5 months were randomly allocated to three treatment groups (7 mice/group) corresponding to vehicle control, 3 mg/kg LA (T5625, Sigma, St. Louis, MO; the dosage was calculated everyday based on weight), and 10 mg/kg LA. LA was administered by intraperitoneal injection once per day (no injection was administered one day every three days), and vehicle control mice received physiological saline.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease and is characterized by neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) composed of Tau protein. a-Lipoic acid (LA) plays a role in inhibiting Tau hyperphosphorylation and neuronal loss, including ferroptosis. After LA administration, TFR expression level was downregulated while Fpn1 level was upregulated, thereby reducing the iron overload. | ||||
Temporal lobe epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A61]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [21] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Klotho | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
rHTs (Rat hippocampal tissues) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Adult male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats aged between 6 and 8 weeks old and weighing between 280 and 320 g were purchased from Hunan slake jingda laboratory animal company (Changsha, China) and used in this study. Under a 12 h light/dark cycle, rats had free access to water and food and were maintained in a room with controlled temperature, humidity. These rats were adapted to the environment for at least 2 week before we began to enter the experimental procedure.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Klotho overexpression inhibits ferroptosis in temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) with cognitive deficits and has a neuroprotective effect. Moreover, for the first time, we found that klotho overexpression inhibits ferroptosis and iron overload in TLE with cognitive deficits. In addition, klotho overexpression down-regulated the expression of DMT1 and up-regulated FPN expression which regulated iron metabolism balance. | ||||
Cerebral ischemia [ICD-11: 8B10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [22] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Edaravone | Approved | |||
| Pathway Response | Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Seventy-three specific-pathogen-free (SPF)grade healthy male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats, weighing 240 ± 20 g, were purchased from Hunan Slake Jingda Experimental Animal Co., Ltd., China (animal certificate number SCXK (Xiang) 2013-0004). The animals were reared in an SPF animal laboratory, and the ambient temperature was maintained at 23 ± 1 . All protocols followed the ARRIVE guidelines in terms of study design, sample size, randomization, outcome measures, data analysis, experimental procedures, and reporting of results. This study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Hunan University of Chinese Medicine.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Edaravone inhibits ferroptosis to attenuate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, probably through the activation of the Nrf2/FPN pathway. | ||||
Cardiomyopathy [ICD-11: BC43]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [23] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Atorvastatin | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
CHO-S/H9C2 cells | Normal | Cricetulus griseus | CVCL_A0TS | |
| In Vivo Model |
A total of 18 Wistar rats (250~300 g) were purchased from Hunan slake Jingda experimental animal Co., Ltd. The rats were randomly divided into the Sham group, I/R group, and I/R + ATV group (n = 6/group).They received standard diet and water before myocardial I/R. Rats in the I/R + ATV group were orally treated with ATV (10 mg/kg/d) for 2 weeks before myocardial I/R (9).The Sham and I/R model rats were constructed as follows: The rats were anesthetized with sodium pentobarbital (50 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection), ligation of the left anterior descending branch with 4-0 silk thread for 30 min, and then reperfusion for 180 min. In the sham control group, the entire procedure was performed with silk thread passing below the coronary artery, but the LAD coronary artery was not ligated. At the end of reperfusion, the rats were given excessive isoflurane for 10 min and sacrificed by bloodletting. Then the rat myocardial tissues were isolated for subsequent detection.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Atorvastatin (ATV) intervention blocked erastin or H/R-induced ferroptosis in H9C2 cells by activating SMAD7 expression and thereby down-regulating the hepcidin/FPN1 pathway. The in vivo study also demonstrated that ATV inhibited ferroptosis in ischemia-reperfusion rat myocardium through the SMAD7/hepcidin pathway. | ||||
Cardiovascular diseases [ICD-11: BE2Z]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [24] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Sesamin | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
rHTs (Rat hippocampal tissues) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Forty specific pathogen-free normal Sprague Dawley (SD) rats (7 weeks old and 251-275 g in weight) were supplied by Charles River Laboratories. The SD rats were randomly allocated into five groups (n = 8). In the PM2.5 exposure group, the rats were treated with 0.5% CMC (10 mL per kg b.w.) for 21 days. The SD rats were anesthetized with isoflurane and administered with PM2.5 suspension by intratracheal instillation (10 mg per kg b.w.) every other day for a total of three times. In the saline control group, the SD rats were treated with 0.5% CMC (10 mL per kg b.w.) for 21 days. The SD rats were anesthetized with isoflurane and intratracheally instilled with 0.9% saline (1 mL per kg b.w.) every other day for a total of three times. In the Ses pretreatment groups, the SD rats were gavaged with low (L-Ses, 40 mg per kg b.w), medium (M-Ses, 80 mg per kg b.w.), and high (H-Ses, 160 mg per kg b.w.) doses of Ses. The SD rats were anesthetized with isoflurane and administered with PM2.5 suspension by intratracheal instillation (10 mg per kg b.w.) every other day for a total of three times.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Sesamin pretreatment upregulated the expression levels of GPX4, SLC7A11, TFRC, and FPN1 and inhibited the expression levels of FTH1 and FTL. Ses pretreatment could ameliorate PM2.5-induced cardiovascular injuries perhaps by inhibiting ferroptosis. | ||||
Pulmonary fibrosis [ICD-11: CB03]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [25] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Bleomycin | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
In Vitro Model |
MLE-12 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_3751 | |
| In Vivo Model |
C57BL/6 J mice (8-week old) from SLAC Laboratory Animal Co. LTD (Shanghai, China) were housed in a specific pathogen-free (SPF) barrier system at 20 with 12-h light/dark cycles. They were randomly grouped as follows: (1) intratracheal saline (control group); (2) intraperitoneal deferoxamine (DFO, Sigma-Aldrich; DFO group); (3) intratracheal bleomycin (BLM, Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd.; BLM group); and (4) intratracheal BLM plus intraperitoneal deferoxamine (BLM + DFO group). They were intratracheally injected with 50 ul of BLM (5 mg/kg) on day 0. For the preventive anti-fibrotic treatment, DFO (50 mg/kg2 day-1) was administered from day 0 to day 20. Lung samples were collected at day 21.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Bleomycin (BLM) can induce the inhibition of cellular GPX4, leading to the generation of lipid ROS. Besides, BLM treatment significantly increased the expression levels of TfR1 and DMT1 in a concentration- and time-dependent manner but similarly decreased those of FPN. TfR1 expression was significantly increased by BLM treatment but decreased by BLM + DFO treatment. These findings indicate that iron metabolism disorder, iron deposition, and ferroptosis in ATII cells may be involved in the pathogenesis of BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis. | ||||
Knee osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA01]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [26] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Biochanin A | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
hCDs (Chondrocytes) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Male mice were purchased from Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine's Experimental Animal Center C57BL/6 mice (7-week-old, 20 g) (Guangzhou, China). After one week of adaptively feeding with chow meals and sterilized water, the animals were separated into five groups of ten mice randomly assigned to the negative control (NC); model, positive control (PC); model group; high dosage of BCA treatment (BCA-H) group; and low dosage of BCA treatment (BCA-L) group. The iron overload mice model was designed based on earlier research. Except for the NC group, mice were administered ID intraperitoneally (500 mg/kg) once a week for eight weeks. In the right knee joints, OA was induced with the initial injection of iron dextran two weeks after the injection by destabilizing the medial meniscus (DMM) using a microscope. After the operation, the positive control group was administered with NAC intragastrically (100 mg/kg) for eight weeks. BCA-H and BCA-L groups were administered 20 mg/kg and 40 mg/kg of BCA separately for eight weeks according to previous studies.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Biochanin A (BCA) could directly reduce intracellular iron concentration by inhibiting TfR1 and promoting FPN but also target the Nrf2/system xc-/GPX4 signaling pathway to scavenge free radicals and prevent lipid peroxidation. The results of this research indicate that BCA regulates iron homeostasis during the progression of osteoarthritis, which can open a new field of treatment for knee osteoarthritis. | ||||
Male infertility [ICD-11: GB04]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [27] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Busulfan | Approved | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
mTTs (Mouse testicular tissues) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Eight-week-old healthy ICR male mice, weighted 20-24 g, were provided by Experimental Animal Center of Nantong University (Nantong, China). For the first animal study, eight-week-old ICR male mice were randomly assigned to four groups: control, busulfan, busulfan plus Fer-1 and busulfan plus DFO groups (n = 6 per group). Mice were anesthetized and then given testicular injection of busulfan on both sides at the dose of 4 mg/kg body weight. The solution containing busulfan was directly injected from the scrotum into testicular transverse diameter. Fer-1 and DFO were administered by intraperitoneal injectionat concentrations of 1 mg/kg and 30 mg/kg respectively three times a week after busulfan injection. Four weeks later, the epididymal spermatozoa and testes from all mice were collected for assessment.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Busulfan treatment induced spermatogenic cells ferroptosis by down-regulating nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) expressions, and decreasing iron efflux through reduction of ferroportin 1 (FPN1) expression. Targeting ferroptosis serves as a potential strategy for prevention of busulfan-induced damage and male infertility. | ||||
Traumatic brain injury [ICD-11: NA07]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [28] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Hepcidin | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were introduced into research, for the present SAH model a total of 383 rats, weighing 250-300 g, were purchased from the Animal Center of Chongqing Medical University. The adult male SD rats assigned to SAH model procedures were randomly divided into several groups. The rats assigned to SAH model procedures were randomly divided into the groups, first to determine the expression of hepcidin, DMT1, FPN1, and GPX4, the main regulator of ferroptosis, and to subsequently select the most suitable timing for drug injections. Second, adult male SD rats were randomly divided into the groups to determine the significant preoperative doses of ebselen, heparin and OSM in terms of their effects on hepcidin, DMT1, FPN1, and GPX4 for further study. Lastly, male SD rats were randomly divided into the groups to determine the effects of hepcidin and DMT1 on iron metabolism, ferroptosis, and EBI, by using heparin, ebselen and OSM as the experimental interventions.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Inhibition of DMT1 by ebselen could suppress iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation, and thereby alleviate ferroptosis and early brain injury (EBI) in SAH rats. Heparin downregulated the expression of hepcidin and DMT1, increased FPN1, and exerted protective effects that were equivalent to those of ebselen on ferroptosis and EBI. In addition, OSM increased the expression of hepcidin and DMT1, decreased FPN1, and aggravated ferroptosis and EBI, while the effect on ferroptosis was reversed by ebselen. | ||||
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 (MAPK14)
Artesunate
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [1] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00] | ||||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | U-251MG cells | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0021 | |
| In Vivo Model |
The xenografts were established via the subcutaneous inoculation of U251 cells (1 x 107 cells/per mouse) into the armpit of one mouse. After two weeks of growth, the cancer tissues were cut into pieces with the dimensions of 1.5 x 1.5 x 1.5 mm3 and inoculated subcutaneously into the right armpit of the mice with a puncture needle. When tumor volume reached approximately 80 mm3, mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 5): Vehicle control, ART (20 mg/kg), ART (40 mg/kg), and TMZ (40 mg/kg). TMZ was used as the positive control. Drugs and vehicle were given by intraperitoneal injection daily for 21 days. Tumor volume and body weight were measured every three days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Artesunate triggers ferroptosis in glioblastoma in vitro and in vivo through regulation of iron metabolism and p38 ( MAPK14) and ERK signaling pathways. Meanwhile, ART reduced the protein level of GPX4 and FPN1, increased the protein level of DMT1, TfR, ferritin and NCOA4. | ||||
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK1)
Simvastatin
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [2] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Corpus uteri cancer [ICD-11: 2C76] | |||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| In Vitro Model | Ishikawa cells | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2529 |
| Response Description | Simvastatin has the potential to be a targeted drug for endometrial cancer (EC) treatment. Besides, the inhibition to the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway allows simvastatin to induce ferroptosis through up-regulating the level of ROS, MDA, Fe2+, and TRF1 (TF) and reducing the level of GSH, SLC7A11, and FPN in cells. | |||
Unspecific Regulator
Siramesine
[Terminated]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [17] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| SK-BR-3 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| ZR-75-1 cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 | |
| Response Description | Overexpression FPN resulted in decreased ROS and cell death whereas knockdown of FPN increased cell death after siramesine and lapatinib treatment. This indicates a novel induction of ferroptosis through altered iron regulation by treating breast cancer cells with a lysosome disruptor and a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. | |||
Lapatinib
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [17] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| SK-BR-3 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0033 | |
| MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| ZR-75-1 cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0588 | |
| Response Description | Overexpression FPN resulted in decreased ROS and cell death whereas knockdown of FPN increased cell death after siramesine and lapatinib treatment. This indicates a novel induction of ferroptosis through altered iron regulation by treating breast cancer cells with a lysosome disruptor and a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. | |||
Etoposide
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [18] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 |
| MCF-10A cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| Response Description | The combined treatment of etoposide and erastin synergistically induced oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, while suppressing glutathione peroxidase activity in breast cancer cells. More importantly, the combination treatment synergistically increased iron accumulation, which was associated with altered expression of IREB2/FPN1. Additionally, ferroptosis-regulating proteins ACSF2 and GPX4 were altered more potently by the combination treatment, compared to untreated cells and erastin treatment alone (p<0.05). | |||
Epigallocatechin Gallate
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [19] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00] | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Response Description | Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) pretreatment counteracted 6-OHDA-induced increased expression of divalent metal transporter-1 (DMT1) and hepcidin and decreased expression of the iron-export protein ferroportin 1 (Fpn1), leading to a 28% reduction in Fe2+ uptake. EGCG inhibits iron overload, decreased LPO, and increased GSH levels in Parkinson disease models, which are the three major hallmarks of ferroptosis. | |||
Thioctic acid
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [20] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Alzheimer disease [ICD-11: 8A20] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
The P301S transgenic mice [B6C3-Tg (Prnp-MAPT*P301S) PS19 Vle/J], originally obtained from the Jackson laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME, USA), were used as a model of tauopathy. The female mice at the age of 5 months were randomly allocated to three treatment groups (7 mice/group) corresponding to vehicle control, 3 mg/kg LA (T5625, Sigma, St. Louis, MO; the dosage was calculated everyday based on weight), and 10 mg/kg LA. LA was administered by intraperitoneal injection once per day (no injection was administered one day every three days), and vehicle control mice received physiological saline.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease and is characterized by neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) composed of Tau protein. a-Lipoic acid (LA) plays a role in inhibiting Tau hyperphosphorylation and neuronal loss, including ferroptosis. After LA administration, TFR expression level was downregulated while Fpn1 level was upregulated, thereby reducing the iron overload. | ||||
Klotho
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [21] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Temporal lobe epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A61] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | rHTs (Rat hippocampal tissues) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Adult male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats aged between 6 and 8 weeks old and weighing between 280 and 320 g were purchased from Hunan slake jingda laboratory animal company (Changsha, China) and used in this study. Under a 12 h light/dark cycle, rats had free access to water and food and were maintained in a room with controlled temperature, humidity. These rats were adapted to the environment for at least 2 week before we began to enter the experimental procedure.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Klotho overexpression inhibits ferroptosis in temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) with cognitive deficits and has a neuroprotective effect. Moreover, for the first time, we found that klotho overexpression inhibits ferroptosis and iron overload in TLE with cognitive deficits. In addition, klotho overexpression down-regulated the expression of DMT1 and up-regulated FPN expression which regulated iron metabolism balance. | ||||
Edaravone
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [22] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cerebral ischemia [ICD-11: 8B10] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Seventy-three specific-pathogen-free (SPF)grade healthy male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats, weighing 240 ± 20 g, were purchased from Hunan Slake Jingda Experimental Animal Co., Ltd., China (animal certificate number SCXK (Xiang) 2013-0004). The animals were reared in an SPF animal laboratory, and the ambient temperature was maintained at 23 ± 1 . All protocols followed the ARRIVE guidelines in terms of study design, sample size, randomization, outcome measures, data analysis, experimental procedures, and reporting of results. This study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Hunan University of Chinese Medicine.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Edaravone inhibits ferroptosis to attenuate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, probably through the activation of the Nrf2/FPN pathway. | ||||
Atorvastatin
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [23] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cardiomyopathy [ICD-11: BC43] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | CHO-S/H9C2 cells | Normal | Cricetulus griseus | CVCL_A0TS | |
| In Vivo Model |
A total of 18 Wistar rats (250~300 g) were purchased from Hunan slake Jingda experimental animal Co., Ltd. The rats were randomly divided into the Sham group, I/R group, and I/R + ATV group (n = 6/group).They received standard diet and water before myocardial I/R. Rats in the I/R + ATV group were orally treated with ATV (10 mg/kg/d) for 2 weeks before myocardial I/R (9).The Sham and I/R model rats were constructed as follows: The rats were anesthetized with sodium pentobarbital (50 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection), ligation of the left anterior descending branch with 4-0 silk thread for 30 min, and then reperfusion for 180 min. In the sham control group, the entire procedure was performed with silk thread passing below the coronary artery, but the LAD coronary artery was not ligated. At the end of reperfusion, the rats were given excessive isoflurane for 10 min and sacrificed by bloodletting. Then the rat myocardial tissues were isolated for subsequent detection.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Atorvastatin (ATV) intervention blocked erastin or H/R-induced ferroptosis in H9C2 cells by activating SMAD7 expression and thereby down-regulating the hepcidin/FPN1 pathway. The in vivo study also demonstrated that ATV inhibited ferroptosis in ischemia-reperfusion rat myocardium through the SMAD7/hepcidin pathway. | ||||
Sesamin
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [24] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cardiovascular diseases [ICD-11: BE2Z] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | rHTs (Rat hippocampal tissues) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Forty specific pathogen-free normal Sprague Dawley (SD) rats (7 weeks old and 251-275 g in weight) were supplied by Charles River Laboratories. The SD rats were randomly allocated into five groups (n = 8). In the PM2.5 exposure group, the rats were treated with 0.5% CMC (10 mL per kg b.w.) for 21 days. The SD rats were anesthetized with isoflurane and administered with PM2.5 suspension by intratracheal instillation (10 mg per kg b.w.) every other day for a total of three times. In the saline control group, the SD rats were treated with 0.5% CMC (10 mL per kg b.w.) for 21 days. The SD rats were anesthetized with isoflurane and intratracheally instilled with 0.9% saline (1 mL per kg b.w.) every other day for a total of three times. In the Ses pretreatment groups, the SD rats were gavaged with low (L-Ses, 40 mg per kg b.w), medium (M-Ses, 80 mg per kg b.w.), and high (H-Ses, 160 mg per kg b.w.) doses of Ses. The SD rats were anesthetized with isoflurane and administered with PM2.5 suspension by intratracheal instillation (10 mg per kg b.w.) every other day for a total of three times.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Sesamin pretreatment upregulated the expression levels of GPX4, SLC7A11, TFRC, and FPN1 and inhibited the expression levels of FTH1 and FTL. Ses pretreatment could ameliorate PM2.5-induced cardiovascular injuries perhaps by inhibiting ferroptosis. | ||||
Bleomycin
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [25] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Pulmonary fibrosis [ICD-11: CB03] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | MLE-12 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_3751 | |
| In Vivo Model |
C57BL/6 J mice (8-week old) from SLAC Laboratory Animal Co. LTD (Shanghai, China) were housed in a specific pathogen-free (SPF) barrier system at 20 with 12-h light/dark cycles. They were randomly grouped as follows: (1) intratracheal saline (control group); (2) intraperitoneal deferoxamine (DFO, Sigma-Aldrich; DFO group); (3) intratracheal bleomycin (BLM, Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd.; BLM group); and (4) intratracheal BLM plus intraperitoneal deferoxamine (BLM + DFO group). They were intratracheally injected with 50 ul of BLM (5 mg/kg) on day 0. For the preventive anti-fibrotic treatment, DFO (50 mg/kg2 day-1) was administered from day 0 to day 20. Lung samples were collected at day 21.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Bleomycin (BLM) can induce the inhibition of cellular GPX4, leading to the generation of lipid ROS. Besides, BLM treatment significantly increased the expression levels of TfR1 and DMT1 in a concentration- and time-dependent manner but similarly decreased those of FPN. TfR1 expression was significantly increased by BLM treatment but decreased by BLM + DFO treatment. These findings indicate that iron metabolism disorder, iron deposition, and ferroptosis in ATII cells may be involved in the pathogenesis of BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis. | ||||
Biochanin A
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [26] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Knee osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA01] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hCDs (Chondrocytes) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Male mice were purchased from Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine's Experimental Animal Center C57BL/6 mice (7-week-old, 20 g) (Guangzhou, China). After one week of adaptively feeding with chow meals and sterilized water, the animals were separated into five groups of ten mice randomly assigned to the negative control (NC); model, positive control (PC); model group; high dosage of BCA treatment (BCA-H) group; and low dosage of BCA treatment (BCA-L) group. The iron overload mice model was designed based on earlier research. Except for the NC group, mice were administered ID intraperitoneally (500 mg/kg) once a week for eight weeks. In the right knee joints, OA was induced with the initial injection of iron dextran two weeks after the injection by destabilizing the medial meniscus (DMM) using a microscope. After the operation, the positive control group was administered with NAC intragastrically (100 mg/kg) for eight weeks. BCA-H and BCA-L groups were administered 20 mg/kg and 40 mg/kg of BCA separately for eight weeks according to previous studies.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Biochanin A (BCA) could directly reduce intracellular iron concentration by inhibiting TfR1 and promoting FPN but also target the Nrf2/system xc-/GPX4 signaling pathway to scavenge free radicals and prevent lipid peroxidation. The results of this research indicate that BCA regulates iron homeostasis during the progression of osteoarthritis, which can open a new field of treatment for knee osteoarthritis. | ||||
Busulfan
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [27] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Male infertility [ICD-11: GB04] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | mTTs (Mouse testicular tissues) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Eight-week-old healthy ICR male mice, weighted 20-24 g, were provided by Experimental Animal Center of Nantong University (Nantong, China). For the first animal study, eight-week-old ICR male mice were randomly assigned to four groups: control, busulfan, busulfan plus Fer-1 and busulfan plus DFO groups (n = 6 per group). Mice were anesthetized and then given testicular injection of busulfan on both sides at the dose of 4 mg/kg body weight. The solution containing busulfan was directly injected from the scrotum into testicular transverse diameter. Fer-1 and DFO were administered by intraperitoneal injectionat concentrations of 1 mg/kg and 30 mg/kg respectively three times a week after busulfan injection. Four weeks later, the epididymal spermatozoa and testes from all mice were collected for assessment.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Busulfan treatment induced spermatogenic cells ferroptosis by down-regulating nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) expressions, and decreasing iron efflux through reduction of ferroportin 1 (FPN1) expression. Targeting ferroptosis serves as a potential strategy for prevention of busulfan-induced damage and male infertility. | ||||
Hepcidin
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [28] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Traumatic brain injury [ICD-11: NA07] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were introduced into research, for the present SAH model a total of 383 rats, weighing 250-300 g, were purchased from the Animal Center of Chongqing Medical University. The adult male SD rats assigned to SAH model procedures were randomly divided into several groups. The rats assigned to SAH model procedures were randomly divided into the groups, first to determine the expression of hepcidin, DMT1, FPN1, and GPX4, the main regulator of ferroptosis, and to subsequently select the most suitable timing for drug injections. Second, adult male SD rats were randomly divided into the groups to determine the significant preoperative doses of ebselen, heparin and OSM in terms of their effects on hepcidin, DMT1, FPN1, and GPX4 for further study. Lastly, male SD rats were randomly divided into the groups to determine the effects of hepcidin and DMT1 on iron metabolism, ferroptosis, and EBI, by using heparin, ebselen and OSM as the experimental interventions.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Inhibition of DMT1 by ebselen could suppress iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation, and thereby alleviate ferroptosis and early brain injury (EBI) in SAH rats. Heparin downregulated the expression of hepcidin and DMT1, increased FPN1, and exerted protective effects that were equivalent to those of ebselen on ferroptosis and EBI. In addition, OSM increased the expression of hepcidin and DMT1, decreased FPN1, and aggravated ferroptosis and EBI, while the effect on ferroptosis was reversed by ebselen. | ||||
References
