Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0082)
| Name |
Busulfan
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
busulfan; 55-98-1; Myleran; Busulphan; Sulphabutin; Leucosulfan; Busulfex; Myelosan; Myeloleukon; Citosulfan; Mielucin; Misulban; Mitostan; Mylecytan; Sulfabutin; Mablin; Mielevcin; Mielosan; Milecitan; Mileran; 1,4-Dimesyloxybutane; butane-1,4-diyl dimethanesulfonate; 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIMETHANESULFONATE; Buzulfan; Myeleukon; Busulfanum; Myelosanum; 1,4-Dimethanesulfonoxybutane; Tetramethylene dimethane sulfonate; Busilvex; Busulfano; 1,4-Butanediol, dimethanesulfonate; 1,4-Dimethylsulfonyloxybutane; 1,4-Dimethanesulfonyloxybutane; NCI-C01592; 1,4-Dimethylsulfonoxybutane; 1,4-Bis(methanesulfonoxy)butane; 1,4-Butanediol dimethylsulfonate; Busulphane; Mitosan; 1,4-Bis(methanesulfonyloxy)butane; GT 41; NSC-750; 1,4-Butanediol dimethanesulphonate; CB 2041; Tetramethylene bis(methanesulfonate); AN 33501; Methanesulfonic acid, tetramethylene ester; 1,4-Dimethanesulphonyloxybutane; NSC 750; 4-methylsulfonyloxybutyl methanesulfonate; 1,4-Dimethanesulfonoxylbutane; Tetramethylenester kyseliny methansulfonove; C.B. 2041; X 149; GT 2041; 1,4-Butanediyl dimethanesulfonate; 1,4-Dimethane sulfonyl oxybutane; 1,4-Butanediol, dimethanesulphonate; CCRIS 418; Bisulfex; NSC750; CHEBI:28901; Busulfex IV; Butanedioldimethanesulfonate; Tetramethylene bis[methanesulfonate]; 2041 C. B.; EINECS 200-250-2; UNII-G1LN9045DK; BRN 1791786; G1LN9045DK; DTXSID3020910; 1,4-Bis[methanesulfonoxy]butane; AI3-25012; HSDB 7605; G.T. 41; DTXCID10910; BUSULFAN FRESENIUS KABI; 2041 C.B.; 4-(methanesulfonyloxy)butyl methanesulfonate; NCGC00090905-06; BUSULFAN (IARC); BUSULFAN [IARC]; TETRAMETHYLENE DI(METHANESULFONATE); BUSULFAN (MART.); BUSULFAN [MART.]; Busulfanum [INN-Latin]; Busulfano [INN-Spanish]; BUSULFAN (EP IMPURITY); BUSULFAN [EP IMPURITY]; BUSULFAN (EP MONOGRAPH); BUSULFAN [EP MONOGRAPH]; BUSULFAN (USP MONOGRAPH); BUSULFAN [USP MONOGRAPH]; Methanesulfonic; Myleran tablets; CAS-55-98-1; SR-01000765405; Bussulfam; Joacamine; Misulfan; Busulfan;; Busulfan/Myleran; Busulfan [USP:INN:BAN:JAN]; Tetramethylenester kyseliny methansulfonove [Czech]; Prestwick_989; (1,4-Bis(methanesulfonyloxy)butane); MFCD00007562; Tetramethylene {bis[methanesulfonate]}; Spectrum_000092; BUSULFAN [HSDB]; BUSULFAN [INN]; BUSULFAN [JAN]; BUSULFAN [MI]; BUSULFAN [VANDF]; Spectrum2_000067; Spectrum3_000320; Spectrum4_000259; Spectrum5_000928; BUSULFAN [WHO-DD]; BUSULFAN [WHO-IP]; CHEMBL820; NCIMech_000192; SCHEMBL4373; BUSULFAN [EMA EPAR]; MYELOSANUM [WHO-IP]; WLN: WS1&O4OSW1; BSPBio_001920; KBioGR_000698; KBioSS_000512; 1,4-Dimethanesulphonoxybutane; MLS001076666; 1,4-Dimethylsulphonoxy-butane; Busulfan (Myleran, Busulfex); DivK1c_000847; SPECTRUM1500152; Busulfan (JP17/USP/INN); SPBio_000253; Tetramethylenedimethanesulfonate; BUSULFAN [ORANGE BOOK]; GTPL7136; 1,4-di(methylsulfonyloxy)butane; COVZYZSDYWQREU-UHFFFAOYSA-; HMS502K09; KBio1_000847; KBio2_000512; KBio2_003080; KBio2_005648; KBio3_001420; 1,4-Bis(methanesulphonoxy)butane; 1,4-di(methanesulfonyloxy)butane; butane-1,4-diyldimethanesulfonate; L01AB01; 1, 4-Bis(methanesulfonoxy)butane; 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIMESYLATE; BUSULFANUM [WHO-IP LATIN]; NINDS_000847; GT-41; HMS1920I07; HMS2091O09; HMS2233H04; HMS3259G15; HMS3370E11; HMS3655A21; HMS3712A20; Pharmakon1600-01500152; AMY33355; HY-B0245; Tetramethylene bis(methanesulphonate); Tox21_111038; Tox21_201848; Tox21_300318; 1, {4-Bis[methanesulfonoxy]butane}; 2041CB; AC-198; BDBM50237623; CCG-35458; NSC755916; s1692; AKOS003614975; Tox21_111038_1; CB-2041; DB01008; KS-5212; NC00498; NSC-755916; IDI1_000847; methanesulfonic acid tetramethylene ester; 1,4-Bitanediol Dimethanesulfonate Esters; NCGC00090905-01; NCGC00090905-02; NCGC00090905-03; NCGC00090905-04; NCGC00090905-05; NCGC00090905-07; NCGC00090905-08; NCGC00090905-09; NCGC00090905-10; NCGC00090905-11; NCGC00090905-12; NCGC00254038-01; NCGC00259397-01; NCI60_041640; SMR000058613; WR-19508; Methanesulphonic acid, tetramethylene ester; SBI-0051300.P003; B1022; FT-0623291; FT-0663910; SW198555-3; C06862; D00248; D88731; EN300-118686; 4-[(Methylsulfonyl)oxy]butyl methanesulfonate #; AB00051929-10; AB00051929-11; AB00051929_12; AB00051929_14; Busulfan, analytical standard, for drug analysis; Busulfan; Butane-1,4-diyl di(methanesulfonate); Q348922; SR-01000765405-2; SR-01000765405-3; SR-01000765405-7; Busulfan, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Z276508890; InChI=1/C6H14O6S2/c1-13(7,8)11-5-3-4-6-12-14(2,9)10/h3-6H2,1-2H3; 129316-96-7; BUS
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Approved
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
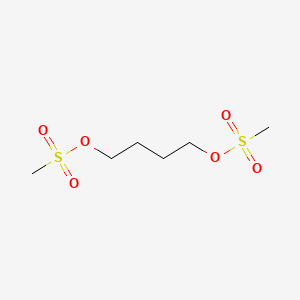 |
||||
| Formula |
C6H14O6S2
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
4-methylsulfonyloxybutyl methanesulfonate
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CS(=O)(=O)OCCCCOS(=O)(=O)C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C6H14O6S2/c1-13(7,8)11-5-3-4-6-12-14(2,9)10/h3-6H2,1-2H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
COVZYZSDYWQREU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Solute carrier family 40 member 1 (SLC40A1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Male infertility | ICD-11: GB04 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | mTTs (Mouse testicular tissues) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Eight-week-old healthy ICR male mice, weighted 20-24 g, were provided by Experimental Animal Center of Nantong University (Nantong, China). For the first animal study, eight-week-old ICR male mice were randomly assigned to four groups: control, busulfan, busulfan plus Fer-1 and busulfan plus DFO groups (n = 6 per group). Mice were anesthetized and then given testicular injection of busulfan on both sides at the dose of 4 mg/kg body weight. The solution containing busulfan was directly injected from the scrotum into testicular transverse diameter. Fer-1 and DFO were administered by intraperitoneal injectionat concentrations of 1 mg/kg and 30 mg/kg respectively three times a week after busulfan injection. Four weeks later, the epididymal spermatozoa and testes from all mice were collected for assessment.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Busulfan treatment induced spermatogenic cells ferroptosis by down-regulating nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) expressions, and decreasing iron efflux through reduction of ferroportin 1 (FPN1) expression. Targeting ferroptosis serves as a potential strategy for prevention of busulfan-induced damage and male infertility. | ||||
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Male infertility | ICD-11: GB04 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | mTTs (Mouse testicular tissues) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Eight-week-old healthy ICR male mice, weighted 20-24 g, were provided by Experimental Animal Center of Nantong University (Nantong, China). For the first animal study, eight-week-old ICR male mice were randomly assigned to four groups: control, busulfan, busulfan plus Fer-1 and busulfan plus DFO groups (n = 6 per group). Mice were anesthetized and then given testicular injection of busulfan on both sides at the dose of 4 mg/kg body weight. The solution containing busulfan was directly injected from the scrotum into testicular transverse diameter. Fer-1 and DFO were administered by intraperitoneal injectionat concentrations of 1 mg/kg and 30 mg/kg respectively three times a week after busulfan injection. Four weeks later, the epididymal spermatozoa and testes from all mice were collected for assessment.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Busulfan treatment induced spermatogenic cells ferroptosis by down-regulating nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) expressions, and decreasing iron efflux through reduction of ferroportin 1 (FPN1) expression. Targeting ferroptosis serves as a potential strategy for prevention of busulfan-induced damage and male infertility. | ||||
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Male infertility | ICD-11: GB04 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | mTTs (Mouse testicular tissues) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Eight-week-old healthy ICR male mice, weighted 20-24 g, were provided by Experimental Animal Center of Nantong University (Nantong, China). For the first animal study, eight-week-old ICR male mice were randomly assigned to four groups: control, busulfan, busulfan plus Fer-1 and busulfan plus DFO groups (n = 6 per group). Mice were anesthetized and then given testicular injection of busulfan on both sides at the dose of 4 mg/kg body weight. The solution containing busulfan was directly injected from the scrotum into testicular transverse diameter. Fer-1 and DFO were administered by intraperitoneal injectionat concentrations of 1 mg/kg and 30 mg/kg respectively three times a week after busulfan injection. Four weeks later, the epididymal spermatozoa and testes from all mice were collected for assessment.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Busulfan treatment induced spermatogenic cells ferroptosis by down-regulating nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) expressions, and decreasing iron efflux through reduction of ferroportin 1 (FPN1) expression. Targeting ferroptosis serves as a potential strategy for prevention of busulfan-induced damage and male infertility. | ||||
