Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0037)
| Name |
Simvastatin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
simvastatin; 79902-63-9; Zocor; Synvinolin; Sinvacor; Denan; Lipex; MK-733; Sivastin; Lodales; Cholestat; Simvastatine; Colemin; Medipo; Pantok; Simovil; Labistatin; Simvastatina; Simvastatinum; Velostatin; Coledis; Corolin; Nivelipol; Rendapid; Vasotenal; Zorced; Rechol; Zocord; Simvastatin (Zocor); Simvastatin lactone; MK-0733; (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-(2-((2R,4R)-4-Hydroxy-6-oxotetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl 2,2-dimethylbutanoate; Lipovas; Simcard; Simvacor; Simvoget; Simlup; Zosta; Simvastatinum [Latin]; DRG-0320; CCRIS 7558; MK 0733; HSDB 7208; UNII-AGG2FN16EV; AGG2FN16EV; 2,2-Dimethylbutyric acid, 8-ester with (4R,6R)-6-(2-((1S,2S,6R,8S,8aR)-1,2,6,7,8,8a-hexahydro-8-hydroxy-2,6-dimethyl-1-naphthyl)ethyl)tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-2H-pyran-2-one; MK 733; NSC-758706; L 644128-000U; Simvastatine [French]; BRN 4768037; CHEBI:9150; Simvastatina [Spanish]; DTXSID0023581; C10AA01; Statin; DTXCID103581; (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-{2-[(2R,4R)-4-hydroxy-6-oxotetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl}-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl 2,2-dimethylbutanoate; Butanoic acid, 2,2-dimethyl-, (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-[(2R,4R)-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]-1-naphthalenyl ester; SIMCOR COMPONENT SIMVASTATIN; VYTORIN COMPONENT SIMVASTATIN; Simcor; NSC633782; SIMVASTATIN COMPONENT OF SIMCOR; NSC 758706; [(1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-[2-[(2R,4R)-4-hydroxy-6-oxooxan-2-yl]ethyl]-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl] 2,2-dimethylbutanoate; Butanoic acid, 2,2-dimethyl-, (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-(2-((2R,4R)-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-1-naphthalenyl ester; SIMVASTATIN COMPONENT OF VYTORIN; Simvastatinum (Latin); SIMVASTATIN (MART.); SIMVASTATIN [MART.]; SIMVASTATIN (USP-RS); SIMVASTATIN [USP-RS]; Butanoic acid, 2,2-dimethyl-, 1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-(2-(tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-1-naphthalenyl ester, (1S-(1alpha,3alpha,7beta,8beta(2S*,4S*),8abeta))-; SIMVASTATIN (EP MONOGRAPH); SIMVASTATIN [EP MONOGRAPH]; SIMVASTATIN (USP MONOGRAPH); SIMVASTATIN [USP MONOGRAPH]; Simvast CR; (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-{2-[(2R,4R)-4-hydroxy-6-oxooxan-2-yl]ethyl}-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl 2,2-dimethylbutanoate; [(1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-[2-[(2R,4R)-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-tetrahydropyran-2-yl]ethyl]-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl] 2,2-dimethylbutanoate; SMR000718785; Zocor (TN); Simvastatin & Primycin; MK733; SR-05000001894; Kolestevan; Lipinorm; Modutrol; Simvotin; Sinvascor; Valemia; Eucor; Nor-Vastina; Simvastatin,(S); simvastatin predrug; (+)-Simvastatin; NCGC00016940-01; inactive simvastatin; 2,2-Dimethylbutyric acid, 8-ester with (4R,6R)-6-[2-[(1S,2S,6R,8S,8aR)-1,2,6,7,8,8a-hexahydro-8-hydroxy-2,6-dimethyl-1-naphthyl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-2H-pyran-2-one; Simvastatin [USAN:USP:INN:BAN]; TNP00259; Prestwick_171; Simvastatin- Bio-X; CAS-79902-63-9; FLOLIPID; KS-1113; Spectrum_001717; SpecPlus_000895; SIMVASTATIN [MI]; Prestwick0_000865; Prestwick1_000865; Prestwick2_000865; Prestwick3_000865; Spectrum2_001671; Spectrum3_000669; Spectrum4_000632; Spectrum5_001428; SIMVASTATIN [INN]; SIMVASTATIN [JAN]; SIMVASTATIN [HSDB]; SIMVASTATIN [USAN]; SIMVASTATIN [VANDF]; SCHEMBL2471; CHEMBL1064; BSPBio_000909; BSPBio_002337; KBioGR_001244; KBioSS_002197; SIMVASTATIN [WHO-DD]; MLS001304029; MLS001333077; MLS001333078; MLS002154038; MLS006011866; BIDD:GT0769; DivK1c_006991; SPECTRUM1504236; SPBio_001881; SPBio_002830; BPBio1_001001; GTPL2955; Simvastatin (JP17/USP/INN); Simvastatin, analytical standard; BCBcMAP01_000007; KBio1_001935; KBio2_002197; KBio2_004765; KBio2_007333; KBio3_001557; RYMZZMVNJRMUDD-HGQWONQESA-; SIMVASTATIN [ORANGE BOOK]; HMS1570N11; HMS1922H13; HMS2089D12; HMS2093E06; HMS2097N11; HMS2231N22; HMS3259B12; HMS3412P08; HMS3676P08; HMS3714N11; HMS3884G10; Pharmakon1600-01504236; BUTANOIC ACID, 2,2-DIMETHYL-, 1,2,3,7,8,8A-HEXAHYDRO-3,7-DIMETHYL-8-(2-(TETRAHYDRO-4-HYDROXY-6-OXO-2H-PYRAN-2-YL)ETHYL)-1-NAPHTHALENYL ESTER, (1S-(1.ALPHA.,3.ALPHA.,7.BETA.,8.BETA.(2S*,4S*),8A.BETA.))-; Tox21_110696; Tox21_300400; BBL024390; BDBM50139181; CCG-39069; NSC758706; s1792; STK801938; AKOS005111006; AKOS015842733; Simvastatin, >=97% (HPLC), solid; Tox21_110696_1; AC-1530; DB00641; NC00719; NSC-633782; MRF-0000729; NCGC00017324-01; NCGC00017324-02; NCGC00017324-03; NCGC00017324-04; NCGC00017324-05; NCGC00017324-07; NCGC00017324-08; NCGC00017324-09; NCGC00254418-01; 2,2-Dimethylbutanoic acid (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-[(2R,4R)-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]-1-naphthalenyl ester; BS164407; HY-17502; SBI-0206773.P001; Simvastatin 100 microg/mL in Acetonitrile; S0509; EN300-52503; D00434; AB00053395-07; AB00053395-08; AB00053395-10; AB00053395_11; AB00053395_13; A839783; Q670131; SR-05000001894-1; SR-05000001894-2; BRD-K22134346-001-05-8; BRD-K22134346-001-11-6; BRD-K22134346-001-15-7; Z754918914; Simvastatin, British Pharmacopoeia (BP) Reference Standard; Simvastatin, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Simvastatin, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; Simvastatin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material; Simvastatin for peak identification, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-1,2,3,7,8,8a-Hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-[(2R,4R)-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]-1-naphthalenyly-2,2-dimethyl butanoate; (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-(2-((2R,4R)-4-Hydroxy-6-oxotetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl 2,2-dimethylbu; (1S,7S,8S,8aR)-8-{2-[(2R,4R)-4-hydroxy-6-oxooxan-2-yl]ethyl}-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl 2,2-dimethylbutanoate; (1S-(1alpha,3alpha,7beta,8beta(2S*,4S*),8abeta))-1,2,3,7,8,8a-Hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-(2-(tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-1-naphthalenyl 2,2-dimethylbutanoate; InChI=1/C25H38O5/c1-6-25(4,5)24(28)30-21-12-15(2)11-17-8-7-16(3)20(23(17)21)10-9-19-13-18(26)14-22(27)29-19/h7-8,11,15-16,18-21,23,26H,6,9-10,12-14H2,1-5H3/t15-,16-,18+,19+,20-,21-,23-/m0/s1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
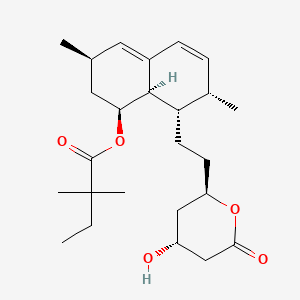
| Structure |
 |
||||
| Formula |
C25H38O5
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
[(1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-[2-[(2R,4R)-4-hydroxy-6-oxooxan-2-yl]ethyl]-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl] 2,2-dimethylbutanoate
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CCC(C)(C)C(=O)OC1CC(C=C2C1C(C(C=C2)C)CCC3CC(CC(=O)O3)O)C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C25H38O5/c1-6-25(4,5)24(28)30-21-12-15(2)11-17-8-7-16(3)20(23(17)21)10-9-19-13-18(26)14-22(27)29-19/h7-8,11,15-16,18-21,23,26H,6,9-10,12-14H2,1-5H3/t15-,16-,18+,19+,20-,21-,23-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
RYMZZMVNJRMUDD-HGQWONQESA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Solute carrier family 40 member 1 (SLC40A1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Corpus uteri cancer | ICD-11: 2C76 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK1) | Suppressor | ||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| In Vitro Model | Ishikawa cells | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2529 |
| Response regulation | Simvastatin has the potential to be a targeted drug for endometrial cancer (EC) treatment. Besides, the inhibition to the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway allows simvastatin to induce ferroptosis through up-regulating the level of ROS, MDA, Fe2+, and TRF1 (TF) and reducing the level of GSH, SLC7A11, and FPN in cells. | |||
Serotransferrin (TF)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor/Driver | |||
| Responsed Disease | Corpus uteri cancer | ICD-11: 2C76 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK1) | Suppressor | ||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| In Vitro Model | Ishikawa cells | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2529 |
| Response regulation | Simvastatin has the potential to be a targeted drug for endometrial cancer (EC) treatment. Besides, the inhibition to the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway allows simvastatin to induce ferroptosis through up-regulating the level of ROS, MDA, Fe2+, and TRF1 (TF) and reducing the level of GSH, SLC7A11, and FPN in cells. | |||
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
MDA-MB-231 cells were injected to subcutaneous of mice to build a tumor model. When the tumor volume reaches about 60 mm3, all mice were randomly divided into five groups (n = 5) for various treatments. Then, mice were treated with PBS, Fe3O4@PCBMA, SIM, Fe3O4-SIM and Fe3O4@PCBMA-SIM through injected intravenously. The injected doses of SIM were 4 mg/kg body weight in each mouse on days 0, 3, 6, and 9.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | The study presented the ferroptosis nanomedicine by loading simvastatin (SIM), a ferroptosis drugs, into zwitterionic polymer coated of magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4@PCBMA), thereby improving the therapeutic effect of triple negative breast cancer. SIM could inhibit the expression of HMGCR to downregulate the mevalonate (MVA) pathway and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), thereby inducing cancer cell ferroptosis. | ||||
Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Corpus uteri cancer | ICD-11: 2C76 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK1) | Suppressor | ||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| In Vitro Model | Ishikawa cells | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2529 |
| Response regulation | Simvastatin has the potential to be a targeted drug for endometrial cancer (EC) treatment. Besides, the inhibition to the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway allows simvastatin to induce ferroptosis through up-regulating the level of ROS, MDA, Fe2+, and TRF1 (TF) and reducing the level of GSH, SLC7A11, and FPN in cells. | |||
References
