Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0043)
| Name |
Etoposide
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
etoposide; 33419-42-0; VePesid; Toposar; trans-Etoposide; Lastet; (-)-Etoposide; Zuyeyidal; Etoposidum; VP-16; Etoposido; Etoposidum [INN-Latin]; VP-16-213; Etoposide (VP16); VP 16-213; Vepesid J; Sintopozid; 4-Demethylepipodophyllotoxin beta-D-ethylideneglucoside; NSC-141540; DTXSID5023035; Etoposide (VP-16); VP 16 (pharmaceutical); 4'-Demethylepipodophyllotoxin 9-(4,6-O-(R)-ethylidene-beta-D-glucopyranoside); VP 16; 6PLQ3CP4P3; Epipodophyllotoxin VP-16213; CHEMBL44657; CHEBI:4911; NK 171; Demethylepipodophyllotoxin-beta-D-ethylideneglucoside; NSC 141540; 4'-Demethylepipodophyllotoxin 9-(4,6-O-ethylidene-beta-D-glucopyranoside); Etosid; Etoposido [INN-Spanish]; (5S,5aR,8aR,9R)-5-[[(2R,4aR,6R,7R,8R,8aS)-7,8-dihydroxy-2-methyl-4,4a,6,7,8,8a-hexahydropyrano[3,2-d][1,3]dioxin-6-yl]oxy]-9-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-5a,6,8a,9-tetrahydro-5H-[2]benzofuro[6,5-f][1,3]benzodioxol-8-one; (5S,5aR,8aR,9R)-9-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-8-oxo-5,5a,6,8,8a,9-hexahydrofuro[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4,6-O-[(1R)-ethylidene]-beta-D-glucopyranoside; Etopophos (phosphate salt); DTXCID601473876; Etopol; VP 16213; NSC141540; (10R,11R,15R,16S)-16-{[(2R,4aR,6R,7R,8R,8aS)-7,8-dihydroxy-2-methyl-hexahydro-2H-pyrano[3,2-d][1,3]dioxin-6-yl]oxy}-10-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-4,6,13-trioxatetracyclo[7.7.0.0^{3,7}.0^{11,15}]hexadeca-1(9),2,7-trien-12-one; (5R,5aR,8aR,9S)-9-(((4aR,6R,7R,8R,8aS)-7,8-Dihydroxy-2-methylhexahydropyrano[3,2-d][1,3]dioxin-6-yl)oxy)-5-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-5,5a,8a,9-tetrahydrofuro[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-6(8H)-one; 9-((4,6-O-Ethylidine-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy)-5,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-5-(4-hydroxy-3,4-dimethyloxyphenyl)furo(3',4'':6,7)naptho-(2,3-d)-1,3-dioxol-6(5aH)-one; SMR000112002; CCRIS 2392; Demethyl-epiodophyllotoxin ethylidene glucoside; HSDB 6517; VePESID (TN); EINECS 251-509-1; UNII-6PLQ3CP4P3; 4'-Demethylepipodophyllotoxin ethylidene-.beta.-D-glucoside; Etoposide,(S); NCGC00016821-01; (5S,5aR,8aR,9R)-9-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-8-oxo-5,5a,6,8,8a,9-hexahydrofuro[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol -5-yl 4,6-O-[(1R)-ethylidene]-beta-D-glucopyranoside; EVP; Furo[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d]-1,3-dioxol-6(5aH)-one, 9-[[4,6-O-(1R)-ethylidene-.beta.-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy]-5,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-5-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-, (5R,5aR,8aR,9S)-; 4'-O-Demethyl-1-O-(4,6-O-ethylidene-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)epipodophyllotoxin; Epipodophyllotoxin, 4'-demethyl-, 9-(4,6-O-ethylidene-beta-D-glucopyranoside); CAS-33419-42-0; Etoposide [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN]; Etoposide; VP-16; CPD000112002; Epipodophyllotoxin-beta-D-ethyliden-glucoside, 4'-demethyl-; ETOPOSIDE [INN]; ETOPOSIDE [JAN]; ETOPOSIDE [MI]; ETOPOSIDE [HSDB]; ETOPOSIDE [IARC]; ETOPOSIDE [USAN]; Prestwick3_000396; ETOPOSIDE [VANDF]; ETOPOSIDE [MART.]; Epipodophyllotoxin, 4'-demethyl-, 4,6-O-ethylidene-beta-D-glucopyranoside; ETOPOSIDE [USP-RS]; ETOPOSIDE [WHO-DD]; ETOPOSIDE [WHO-IP]; SCHEMBL4259; BSPBio_000611; 9-((4,6-O-Ethylidene-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy)-5,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-5-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-furo(3',4':6,7)naphtho(2,3-d)-1,3-dioxol-6(5aH)-one, (5R-(5alpha,5abeta,8aalpha,9beta(R*)))-; 9-((4,6-O-Ethylidine-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy)-5,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-5-(4- hydroxy-3,4-dimethyloxyphenyl)furo (3',4'':6,7) naptho-(2,3-d)-1,3-dioxol-6 (5aH)-one; MLS000049957; MLS001074951; MLS001424283; MLS002153463; MLS002207239; MLS002222184; Etoposide (JP17/USP/INN); BPBio1_000673; GTPL6815; ETOPOSIDE [EP IMPURITY]; ETOPOSIDE [ORANGE BOOK]; ETOPOSIDE [EP MONOGRAPH]; ETOPOSIDE [USP IMPURITY]; ETOPOSIDE [USP MONOGRAPH]; ETOPOSIDUM [WHO-IP LATIN]; VJJPUSNTGOMMGY-MRVIYFEKSA-N; etoposide4-o-b-d-galactopyranoside; HMS2052N05; HMS2089F14; HMS2096O13; HMS2232L03; HMS3713O13; EX-A1207; Tox21_110630; Tox21_302201; BDBM50127140; s1225; Etoposide - CAS 33419-42-0; AKOS007930275; BCP9000669; CCG-101165; CS-1774; DB00773; Etoposide, synthetic, >=98%, powder; NC00415; SDCCGSBI-0050405.P002; 4'-Demethyl-epipodophyllotoxin 9-[4,6-O-(R)-ethylidene-beta-D-glucopyranoside; NCGC00179504-02; NCGC00255126-01; AS-35312; BE164434; Furo(3',4':6,7)naphtho(2,3-d)-1,3-dioxol-6(5aH)-one, 9-((4,6-O-(1R)-ethylidene-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy)-5,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-5-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-, (5R,5aR,8aR,9S)-; Furo(3',4':6,7)naphtho(2,3-d)-1,3-dioxol-6(5aH)-one-, 9-((4,6-O-ethylidene-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy)5,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-5-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl), (5R-(5alpha,5abeta,8aalpha,9beta(R*)))-; HY-13629; SBI-0051910.P002; AB00438905; EN300-97099; C01576; D00125; AB00438905-17; AB00438905-18; AB00438905_19; Q418817; SR-01000763196; SR-01000763196-3; BRD-K37798499-001-02-5; BRD-K37798499-001-05-8; BRD-K37798499-001-10-8; BRD-K37798499-001-14-0; BRD-K37798499-001-27-2; -5-yl 4,6-O-[(1R)-ethylidene]-beta-D-glucopyranoside; Etoposide, British Pharmacopoeia (BP) Reference Standard; Z1304065033; Etoposide, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Etoposide, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; 4''-Demethylepipodophyllotoxin 9-(4,6-O-(R)-ethylidene-beta-D-glucopyranoside); 4'-DEMETHYLEPIPODOPHYLLOTOXIN 9-(4,6-O-(R)-ETHYLIDENE-.BETA.-D-GLUCOPYRANOSIDE); Etoposide for system suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; (5R,5AR,8aR,9S)-9-(((2R,4aR,6R,7R,8R,8aS)-7,8-dihydroxy-2-methylhexahydropyrano[3,2-d][1,3]dioxin-6-yl)oxy)-5-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-5,5a,8a,9-tetrahy; (5R,5aR,8aR,9S)-9-(((2R,4aR,6R,7R,8R,8aS)-7,8-dihydroxy-2-methylhexahydropyrano[3,2-d][1,3]dioxin-6-yl)oxy)-5-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-5,5a,8a,9-tetrahydrofuro[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-6(8H)-one; (5R,5AR,8AR,9S)-9-((4,6-O-((1R)-ETHANE-1,1-DIYL)-.ALPHA.-D-GLUCOPYRANOSYL)OXY)-5-(4-HYDROXY-3,5-DIMETHOXYPHENYL)-5,8,8A,9-TETRAHYDRO(2)BENZOFURO(5,6-F)(1,3)BENZODIOXOL-6(5AH)-ONE; (5R,5aR,8aR,9S)-9-[[4,6-O-(1R)-Ethylidene-beta-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy]-5,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-5-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)furo[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d]-1,3-dioxol-6(5aH)-one; (5S,5aR,8aR,9R)-5-[[(2R,4aR,6R,7R,8R,8aS)-7,8-dihydroxy-2-methyl-4,4a,6,7,8,8a-hexahydropyrano[3,2-d][1,3]dioxin-6-yl]oxy]-9-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)-5a,6,8a,9-tetrahydro-5H-isobenzofuro[5,6-f][1,3]benzodioxol-8-one; (5S,5aR,8aR,9R)-9-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-8-oxo-5,5a,6,8,8a,9-hexahydrofuro[3'',4'':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4,6-O-[(1R)-ethylidene]-beta-D-glucopyranoside; [5R-[5?,5a?,8a?,9?(R*)]]-9-[(4,6-?-Ethylidene-?-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-5,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-5-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)furo[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d]-1,3-dioxol-6-(5aH)-one; 121471-01-0; 9-((4,6-O-Ethylidine-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy)-5,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-5-(4-hydroxy-3,4-dimethyloxyphenyl)furo(3'',4'''':6,7)naptho-(2,3-d)-1,3-dioxol-6(5aH)-one; FURO(3',4':6,7)NAPHTHO(2,3-D)-1,3-DIOXOL-6(5AH)-ONE-, 9-((4,6-O-ETHYLIDENE-.BETA.-D-GLUCOPYRANOSYL)OXY)5,8,8A,9-TETRAHYDRO-5-(4-HYDROXY-3,5-DIMETHOXYPHENYL), (5R-(5.ALPHA.,5A.BETA.,8A.ALPHA.,9.BETA.(R*)))-
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
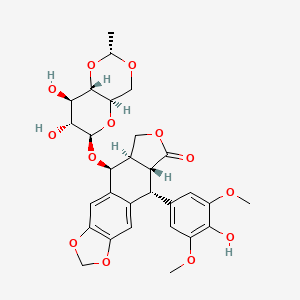 |
||||
| Formula |
C29H32O13
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
(5S,5aR,8aR,9R)-5-[[(2R,4aR,6R,7R,8R,8aS)-7,8-dihydroxy-2-methyl-4,4a,6,7,8,8a-hexahydropyrano[3,2-d][1,3]dioxin-6-yl]oxy]-9-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-5a,6,8a,9-tetrahydro-5H-[2]benzofuro[6,5-f][1,3]benzodioxol-8-one
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1OCC2C(O1)C(C(C(O2)OC3C4COC(=O)C4C(C5=CC6=C(C=C35)OCO6)C7=CC(=C(C(=C7)OC)O)OC)O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C29H32O13/c1-11-36-9-20-27(40-11)24(31)25(32)29(41-20)42-26-14-7-17-16(38-10-39-17)6-13(14)21(22-15(26)8-37-28(22)33)12-4-18(34-2)23(30)19(5-12)35-3/h4-7,11,15,20-22,24-27,29-32H,8-10H2,1-3H3/t11-,15+,20-,21-,22+,24-,25-,26-,27-,29+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
VJJPUSNTGOMMGY-MRVIYFEKSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Unspecific Target
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Medium-chain acyl-CoA ligase ACSF2, mitochondrial (ACSF2) | Driver | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 |
| MCF-10A cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| Response regulation | The combined treatment of etoposide and erastin synergistically induced oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, while suppressing glutathione peroxidase activity in breast cancer cells. More importantly, the combination treatment synergistically increased iron accumulation, which was associated with altered expression of IREB2/FPN1. Additionally, ferroptosis-regulating proteins ACSF2 and GPX4 were altered more potently by the combination treatment, compared to untreated cells and erastin treatment alone (p<0.05). | |||
Solute carrier family 40 member 1 (SLC40A1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 |
| MCF-10A cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| Response regulation | The combined treatment of etoposide and erastin synergistically induced oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, while suppressing glutathione peroxidase activity in breast cancer cells. More importantly, the combination treatment synergistically increased iron accumulation, which was associated with altered expression of IREB2/FPN1. Additionally, ferroptosis-regulating proteins ACSF2 and GPX4 were altered more potently by the combination treatment, compared to untreated cells and erastin treatment alone (p<0.05). | |||
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 |
| MCF-10A cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| Response regulation | The combined treatment of etoposide and erastin synergistically induced oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, while suppressing glutathione peroxidase activity in breast cancer cells. More importantly, the combination treatment synergistically increased iron accumulation, which was associated with altered expression of IREB2/FPN1. Additionally, ferroptosis-regulating proteins ACSF2 and GPX4 were altered more potently by the combination treatment, compared to untreated cells and erastin treatment alone (p<0.05). | |||
Iron-responsive element-binding protein 2 (IREB2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 |
| MCF-10A cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| Response regulation | The combined treatment of etoposide and erastin synergistically induced oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, while suppressing glutathione peroxidase activity in breast cancer cells. More importantly, the combination treatment synergistically increased iron accumulation, which was associated with altered expression of IREB2/FPN1. Additionally, ferroptosis-regulating proteins ACSF2 and GPX4 were altered more potently by the combination treatment, compared to untreated cells and erastin treatment alone (p<0.05). | |||
References
