Ferroptosis Target Information
General Information of the Ferroptosis Target (ID: TAR10031)
| Target Name | Iron-responsive element-binding protein 2 (IREB2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Iron regulatory protein 2
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene Name | IREB2 | ||||
| Sequence |
MDAPKAGYAFEYLIETLNDSSHKKFFDVSKLGTKYDVLPYSIRVLLEAAVRNCDGFLMKK
EDVMNILDWKTKQSNVEVPFFPARVLLQDFTGIPAMVDFAAMREAVKTLGGDPEKVHPAC PTDLTVDHSLQIDFSKCAIQNAPNPGGGDLQKAGKLSPLKVQPKKLPCRGQTTCRGSCDS GELGRNSGTFSSQIENTPILCPFHLQPVPEPETVLKNQEVEFGRNRERLQFFKWSSRVFK NVAVIPPGTGMAHQINLEYLSRVVFEEKDLLFPDSVVGTDSHITMVNGLGILGWGVGGIE TEAVMLGLPVSLTLPEVVGCELTGSSNPFVTSIDVVLGITKHLRQVGVAGKFVEFFGSGV SQLSIVDRTTIANMCPEYGAILSFFPVDNVTLKHLEHTGFSKAKLESMETYLKAVKLFRN DQNSSGEPEYSQVIQINLNSIVPSVSGPKRPQDRVAVTDMKSDFQACLNEKVGFKGFQIA AEKQKDIVSIHYEGSEYKLSHGSVVIAAVISCTNNCNPSVMLAAGLLAKKAVEAGLRVKP YIRTSLSPGSGMVTHYLSSSGVLPYLSKLGFEIVGYGCSICVGNTAPLSDAVLNAVKQGD LVTCGILSGNKNFEGRLCDCVRANYLASPPLVVAYAIAGTVNIDFQTEPLGTDPTGKNIY LHDIWPSREEVHRVEEEHVILSMFKALKDKIEMGNKRWNSLEAPDSVLFPWDLKSTYIRC PSFFDKLTKEPIALQAIENAHVLLYLGDSVTTDHISPAGSIARNSAAAKYLTNRGLTPRE FNSYGARRGNDAVMTRGTFANIKLFNKFIGKPAPKTIHFPSGQTLDVFEAAELYQKEGIP LIILAGKKYGSGNSRDWAAKGPYLLGVKAVLAESYEKIHKDHLIGIGIAPLQFLPGENAD SLGLSGRETFSLTFPEELSPGITLNIQTSTGKVFSVIASFEDDVEITLYKHGGLLNFVAR KFS Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Family | Aconitase/IPM isomerase family | ||||
| Function |
RNA-binding protein that binds to iron-responsive elements (IRES), which are stem-loop structures found in the 5'-UTR of ferritin, and delta aminolevulinic acid synthase mRNAs, and in the 3'-UTR of transferrin receptor mRNA. Binding to the IRE element in ferritin results in the repression of its mRNA translation. Binding of the protein to the transferrin receptor mRNA inhibits the degradation of this otherwise rapidly degraded mRNA.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene ID | 3658 | ||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Target Type | Driver Suppressor Marker | ||||
| Mechanism Diagram | Click to View the Original Diagram | ||||
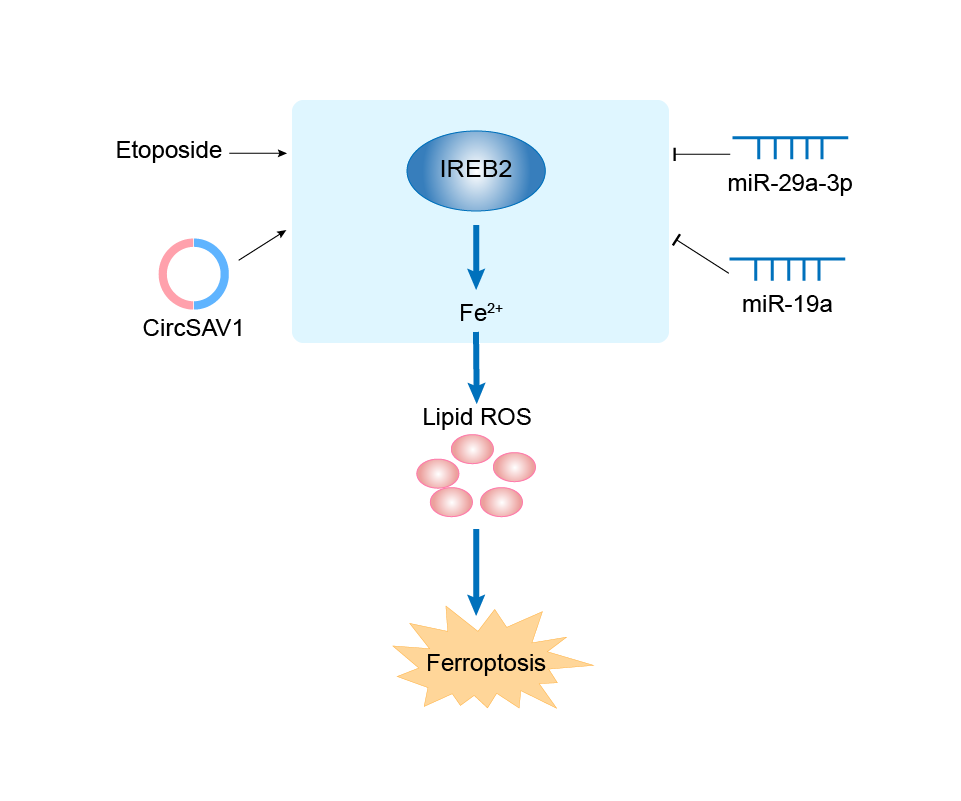
|
|||||
Tissue Relative Abundances of This Target
Full List of Regulator(s) of This Ferroptosis Target and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
IREB2 can be involved in and affect the ferroptosis by the following regulators, and result in corresponding disease/drug response(s). You can browse corresponding disease or drug response(s) resulting from the regulation of certain regulators.
Browse Regulator related Disease
Browse Regulator related Drug
rno-miR-29a-3p (miRNA)
Ischemia/reperfusion injury [ICD-11: DB98]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [1] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
rBMMSCs (Rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells) | ||||
| IAR 20 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5296 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Clean-grade male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were purchased from China Food and Drug Administration (Beijing, China). SD rats were fed a high-fat diet (Composition: 15% triglyceride, 15% sucrose, 10% egg yolk powder, 1% cholesterol, 0.2% bile salt, 58.8% basic feed) for 20 weeks. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) and oil red O staining showed that the area of mixed macrovesicular steatosis was more than 60% under the microscope, indicating that a model of severe steatotic liver was established successfully. A 70% liver thermal ischemia model was established, continuously blocked for 80 min, and then, the ischemic liver was obtained 24 h after reperfusion.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | miR-29a-3p, which targets IREB2, is abundant in HO-1/BMMSC-exosomes and could decrease the IREB2 protein level. The reduced IREB2 level led to an increase in the level of FTH1 and decreased the level of TFR1 through posttranscriptional regulation, which ultimately reduced the level of intracellular Fe2+ and the production of lipid ROS and inhibited the occurrence of ferroptosis in SHP-HR. In conclusion, ferroptosis plays an important role in HO-1/BMMSC-mediated alleviation of steatotic hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. | ||||
hsa-mir-19a (Precursor RNA)
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [2] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
In Vitro Model |
HT29 cells | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ |
| Response Description | IREB2 was negatively regulated by miR-19a in Colorectal cancer (CRC) cells. In addition, ferroptosis was suppressed by miR-19a through inhibiting IREB2. | |||
Unspecific Regulator
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [3] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Etoposide | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 |
| MCF-10A cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| Response Description | The combined treatment of etoposide and erastin synergistically induced oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, while suppressing glutathione peroxidase activity in breast cancer cells. More importantly, the combination treatment synergistically increased iron accumulation, which was associated with altered expression of IREB2/FPN1. Additionally, ferroptosis-regulating proteins ACSF2 and GPX4 were altered more potently by the combination treatment, compared to untreated cells and erastin treatment alone (p<0.05). | |||
Presbycusis [ICD-11: AB54]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [4] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | D-Galactose | Phase 2 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
In Vitro Model |
PC12 cells | Adrenal gland pheochromocytoma | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0481 | |
| In Vivo Model |
A total of 150 male Sprague-Dawley rats were obtained from the Experimental Animal Centre of Hubei Province. After deep anaesthesia, we placed each rat on an electric blanket to maintain its body temperature. We placed the positive electrode under the skin of the vertex, the negative electrode into the measured ear and the ground electrode into the other ear. We used a Tucker-Davis Technologies System (RZ6; Tucker-Davis Tech. Inc., Alachua, FL, USA) to record the responses of the rats to sounds of different frequencies as previously described.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | The study measured iron levels in a simulated ageing model established by the addition of d-galactose (d-gal). These changes were accompanied by upregulation of iron regulatory protein 2 (IRP-2), which led to an increase in transferrin receptor 1 (TfR-1), thus increasing iron entry into cells and potentially leading to ferroptosis. Relieving ferroptosis might be a new intervention strategy for age-related hearing loss. | ||||
Liver fibrosis [ICD-11: DB93]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [5] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Artemether | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
hHSCs (Human hepatic stellate cells) | ||||
| HSC-T6 cells | Normal | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0315 | ||
| LO #2 cells | Amelanotic melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C7SD | ||
| Hep-G2 cells | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
The animal experiment scheme was approved by the institution of Nanjing University ofChinese Medicine (Nanjing, China) and the local animal protection and utilization committee. After the last administration, diet was prohibited, but drinking water was not restricted. 24 h later, the mice were weighed and taken blood.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | ART (artemether) could lead to the accumulation of IRP2 a in hepatic stellate cell by inhibiting the ubiquitination of it, thus inducing the increase of iron in HSC (hepatic stellate cell), which could product a large number of ROS (reactive oxide species), resulting the occurrence of ferroptosis in cells. The findings provided an experimental basis for ART to become a drug for the treatment of liver fibrosis. | ||||
Hereditary Leiomyomatosis [ICD-11: 2C90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [6] | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| Cell metastasis | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
In Vitro Model |
ACHN cells | Papillary renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1067 |
| Response Description | ACO1 and IREB2 downregulation in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma were correlated with cancer aggressiveness, cellular iron homeostasis, cytotoxic immune cell infiltration, and patient survival outcomes. | |||
Unspecific Regulator
Etoposide
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [3] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 |
| MCF-10A cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0598 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| Response Description | The combined treatment of etoposide and erastin synergistically induced oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, while suppressing glutathione peroxidase activity in breast cancer cells. More importantly, the combination treatment synergistically increased iron accumulation, which was associated with altered expression of IREB2/FPN1. Additionally, ferroptosis-regulating proteins ACSF2 and GPX4 were altered more potently by the combination treatment, compared to untreated cells and erastin treatment alone (p<0.05). | |||
D-Galactose
[Phase 2]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [4] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Presbycusis [ICD-11: AB54] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| In Vitro Model | PC12 cells | Adrenal gland pheochromocytoma | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0481 | |
| In Vivo Model |
A total of 150 male Sprague-Dawley rats were obtained from the Experimental Animal Centre of Hubei Province. After deep anaesthesia, we placed each rat on an electric blanket to maintain its body temperature. We placed the positive electrode under the skin of the vertex, the negative electrode into the measured ear and the ground electrode into the other ear. We used a Tucker-Davis Technologies System (RZ6; Tucker-Davis Tech. Inc., Alachua, FL, USA) to record the responses of the rats to sounds of different frequencies as previously described.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | The study measured iron levels in a simulated ageing model established by the addition of d-galactose (d-gal). These changes were accompanied by upregulation of iron regulatory protein 2 (IRP-2), which led to an increase in transferrin receptor 1 (TfR-1), thus increasing iron entry into cells and potentially leading to ferroptosis. Relieving ferroptosis might be a new intervention strategy for age-related hearing loss. | ||||
Artemether
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [5] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Liver fibrosis [ICD-11: DB93] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hHSCs (Human hepatic stellate cells) | ||||
| HSC-T6 cells | Normal | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0315 | ||
| LO #2 cells | Amelanotic melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C7SD | ||
| Hep-G2 cells | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
The animal experiment scheme was approved by the institution of Nanjing University ofChinese Medicine (Nanjing, China) and the local animal protection and utilization committee. After the last administration, diet was prohibited, but drinking water was not restricted. 24 h later, the mice were weighed and taken blood.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | ART (artemether) could lead to the accumulation of IRP2 a in hepatic stellate cell by inhibiting the ubiquitination of it, thus inducing the increase of iron in HSC (hepatic stellate cell), which could product a large number of ROS (reactive oxide species), resulting the occurrence of ferroptosis in cells. The findings provided an experimental basis for ART to become a drug for the treatment of liver fibrosis. | ||||
References
