Ferroptosis Target Information
General Information of the Ferroptosis Target (ID: TAR10044)
| Target Name | Natural resistance-associated macrophage protein 2 (SLC11A2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Divalent cation transporter 1; Divalent metal transporter 1; Solute carrier family 11 member 2
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene Name | SLC11A2 | ||||
| Sequence |
MVLGPEQKMSDDSVSGDHGESASLGNINPAYSNPSLSQSPGDSEEYFATYFNEKISIPEE
EYSCFSFRKLWAFTGPGFLMSIAYLDPGNIESDLQSGAVAGFKLLWILLLATLVGLLLQR LAARLGVVTGLHLAEVCHRQYPKVPRVILWLMVELAIIGSDMQEVIGSAIAINLLSVGRI PLWGGVLITIADTFVFLFLDKYGLRKLEAFFGFLITIMALTFGYEYVTVKPSQSQVLKGM FVPSCSGCRTPQIEQAVGIVGAVIMPHNMYLHSALVKSRQVNRNNKQEVREANKYFFIES CIALFVSFIINVFVVSVFAEAFFGKTNEQVVEVCTNTSSPHAGLFPKDNSTLAVDIYKGG VVLGCYFGPAALYIWAVGILAAGQSSTMTGTYSGQFVMEGFLNLKWSRFARVVLTRSIAI IPTLLVAVFQDVEHLTGMNDFLNVLQSLQLPFALIPILTFTSLRPVMSDFANGLGWRIAG GILVLIICSINMYFVVVYVRDLGHVALYVVAAVVSVAYLGFVFYLGWQCLIALGMSFLDC GHTCHLGLTAQPELYLLNTMDADSLVSR Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Family | NRAMP family | ||||
| Function |
Proton-coupled metal ion symporter operating with a proton to metal ion stoichiometry of 1:1. Selectively transports various divalent metal cations, in decreasing affinity: Cd(2+) > Fe(2+) > Co(2+), Mn(2+) >> Zn(2+), Ni(2+), VO(2+). Essential for maintenance of iron homeostasis by modulating intestinal absorption of dietary Fe(2+) and TF-associated endosomal Fe(2+) transport in erythroid precursors and other cells. Enables Fe(2+) and Mn(2+) ion entry into mitochondria, and is thus expected to promote mitochondrial heme synthesis, iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis and antioxidant defense. Can mediate uncoupled fluxes of either protons or metal ions.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene ID | 4891 | ||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Target Type | Driver Suppressor Marker | ||||
| Mechanism Diagram | Click to View the Original Diagram | ||||
|
|||||
Tissue Relative Abundances of This Target
Full List of Regulator(s) of This Ferroptosis Target and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
SLC11A2 can be involved in and affect the ferroptosis by the following regulators, and result in corresponding disease/drug response(s). You can browse corresponding disease or drug response(s) resulting from the regulation of certain regulators.
Browse Regulator related Disease
Browse Regulator related Drug
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 (MAPK14)
Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [1] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Artesunate | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
In Vitro Model |
U-251MG cells | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0021 | |
| In Vivo Model |
The xenografts were established via the subcutaneous inoculation of U251 cells (1 x 107 cells/per mouse) into the armpit of one mouse. After two weeks of growth, the cancer tissues were cut into pieces with the dimensions of 1.5 x 1.5 x 1.5 mm3 and inoculated subcutaneously into the right armpit of the mice with a puncture needle. When tumor volume reached approximately 80 mm3, mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 5): Vehicle control, ART (20 mg/kg), ART (40 mg/kg), and TMZ (40 mg/kg). TMZ was used as the positive control. Drugs and vehicle were given by intraperitoneal injection daily for 21 days. Tumor volume and body weight were measured every three days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Artesunate triggers ferroptosis in glioblastoma in vitro and in vivo through regulation of iron metabolism and p38 ( MAPK14) and ERK signaling pathways. Meanwhile, ART reduced the protein level of GPX4 and FPN1, increased the protein level of DMT1, TfR, ferritin and NCOA4. | ||||
mmu-miR-375-3p (miRNA)
Ulcerative colitis [ICD-11: DD71]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [2] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
hCCs (Colon cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Mice were orally administered 0.1 g/kg Co-Q10 daily for 8 weeks after the DMM model was established to investigate the therapeutic effect of Co-Q10 in GPX4-CKO mice with osteoarthritis. Mice and rats were anaesthetized with pentobarbital. Destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) surgery was performed under a microscope. The incision was sutured and disinfected daily until it healed.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
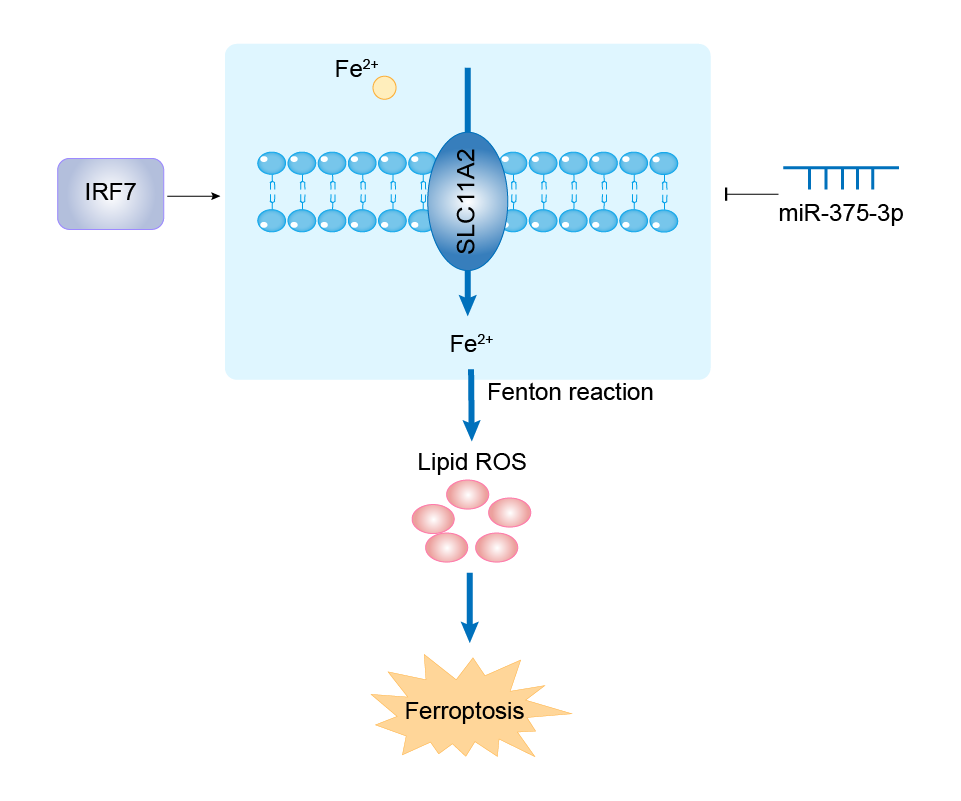
| Response Description | IRF7 upregulated SLC11A2 transcription by inhibiting miR-375-3p expression, thereby prompting ferroptosis of colonic ECs and ulcerative colitis progression in DSS-treated mice. | ||||
Metalloreductase STEAP3 (STEAP3)
Ischemia/reperfusion injury [ICD-11: DB98]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [3] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
rBMMSCs (Rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells) | |||
| IAR 20 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5296 | |
| Response Description | MiR-124-3p in HM-exos downregulates Steap3 expression to inhibit ferroptosis, thereby attenuating graft ischemia reperfusion injury. And HUCB-MSCs-exos inhibited the expression of DMT1 by delivering miR-23a-3p, which suppressed cardiomyocyte ferroptosis after myocardial infarction. | |||
Interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF7)
Ulcerative colitis [ICD-11: DD71]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [2] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
hCCs (Colon cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Mice were orally administered 0.1 g/kg Co-Q10 daily for 8 weeks after the DMM model was established to investigate the therapeutic effect of Co-Q10 in GPX4-CKO mice with osteoarthritis. Mice and rats were anaesthetized with pentobarbital. Destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) surgery was performed under a microscope. The incision was sutured and disinfected daily until it healed.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | IRF7 upregulated SLC11A2 transcription by inhibiting miR-375-3p expression, thereby prompting ferroptosis of colonic ECs and ulcerative colitis progression in DSS-treated mice. | ||||
hsa-miR-23a-3p (miRNA)
Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [4] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
hUCB-MSCs (Human umbilical cord blood derived mesenchymal stem cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
A total of 72 C57BL/6J mice (six animals per group) were obtained from the Shanghai Laboratory Animals Center. The mouse model of AMI was performed by permanent ligation of the LAD coronary artery. PBS or exosomes (5 ug, in 20 ul PBS) was injected into the border zone of infarcted heart at three sites.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | The exosome of MSCs derived from human umbilical cord blood (HUCB-MSC) has been reported to have cardioprotective effects on mouse models of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and cardiomyocyte hypoxia injury. HUCB-MSCs-exosomes may suppress DMT1 expression by miR-23a-3p to inhibit ferroptosis and attenuate myocardial injury. | ||||
hsa-miR-124-3p (miRNA)
Ischemia/reperfusion injury [ICD-11: DB98]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [3] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
rBMMSCs (Rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells) | |||
| IAR 20 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5296 | |
| Response Description | MiR-124-3p in HM-exos downregulates Steap3 expression to inhibit ferroptosis, thereby attenuating graft ischemia reperfusion injury. And HUCB-MSCs-exos inhibited the expression of DMT1 by delivering miR-23a-3p, which suppressed cardiomyocyte ferroptosis after myocardial infarction. | |||
hsa-miR-10a-5p (miRNA)
Intervertebral disc degeneration [ICD-11: FA80]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [5] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
hCDs (Chondrocytes) | |||
| Response Description | Inflammatory cytokine IL-6 appeared in Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) aggravates its degeneration by inducing cartilage cell ferroptosis. This is caused partially by inhibiting miR-10a-5p and subsequently derepressing IL-6R signaling pathway. The ferroptosis-inhibitory effect exhibited by overexpressing miR-10a-5p was achieved by promoting GPX4 and ferroportin-1 (FPN1) but suppressing divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) expression in IL-6-treated cartilage cells. | |||
Unspecific Regulator
Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [6] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Temozolomide | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
TG905 (Human glioblastoma cells) | |||
| Response Description | Temozolomide may suppress cell growth partly by inducing ferroptosis by targeting DMT1 expression in glioblastoma cells. The results also showed that temozolomide-induced ferroptosis is associated with regulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. | |||
Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [7] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Bavachin | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
MG-63 cells | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0426 |
| HOS cells | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0312 | |
| Response Description | Bavachin could induce Osteosarcoma cell ferroptosis. Furthermore, bavachin elevated intracellular ferrous iron levels by increasing TFRC and DMT1 (SLC11A2) expression and decreasing FTH and FTL expressions. Bavachin also reduced SLC7A11 and GPX4 expression and promoted ROS and MDA accumulation by downregulating p-STAT3 to upregulate P53 expression. | |||
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [8] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Sulfasalazine | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| T-47D cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| BT-549 cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| Response Description | Sulfasalazine (SAS) upregulated TFRC and DMT1. Knockdown of the ER increased TFRC expression in breast cancer cells. In conclusion SAS could trigger ferroptosis in breast cancer cells, especially in cells with low ER expression. | |||
Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [9] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Epigallocatechin Gallate | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Response Description | Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) pretreatment counteracted 6-OHDA-induced increased expression of divalent metal transporter-1 (DMT1) and hepcidin and decreased expression of the iron-export protein ferroportin 1 (Fpn1), leading to a 28% reduction in Fe2+ uptake. EGCG inhibits iron overload, decreased LPO, and increased GSH levels in Parkinson disease models, which are the three major hallmarks of ferroptosis. | |||
Temporal lobe epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A61]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [10] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Klotho | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
rHTs (Rat hippocampal tissues) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Adult male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats aged between 6 and 8 weeks old and weighing between 280 and 320 g were purchased from Hunan slake jingda laboratory animal company (Changsha, China) and used in this study. Under a 12 h light/dark cycle, rats had free access to water and food and were maintained in a room with controlled temperature, humidity. These rats were adapted to the environment for at least 2 week before we began to enter the experimental procedure.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Klotho overexpression inhibits ferroptosis in temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) with cognitive deficits and has a neuroprotective effect. Moreover, for the first time, we found that klotho overexpression inhibits ferroptosis and iron overload in TLE with cognitive deficits. In addition, klotho overexpression down-regulated the expression of DMT1 and up-regulated FPN expression which regulated iron metabolism balance. | ||||
Cerebral ischemia [ICD-11: 8B10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [11] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Naotaifang Extract | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Specific pathogen-free adult male SD rats, (80 ± 5) days old and weighing 220-250 g, were provided by the Hunan Slack Jingda Experimental Animal Co., Ltd (Hunan, China). SD rats were randomly divided into 4 groups with 15 in each group: sham operation group, MCAO group, MCAO + DFP group and MCAO + NTE group. The rats were treated with drugs via oral gavage. According to the average body weight, the MCAO + NTE rats were given NTE at 27 g/kg, and the sham operation and the MCAO rats were given the same volume of saline (2.5 mL) for 7 consecutive days. The MCAO + DFP rats were given DFP at a dose of 125 mg/kg for 3 consecutive days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Acute cerebral ischemia induces neuronal ferroptosis and the effects of treating MCAO rats with naotaifang extract involved inhibition of ferroptosis through the TFR1/DMT1 and SCL7A11/GPX4 pathways. | ||||
Pulmonary fibrosis [ICD-11: CB03]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [12] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Bleomycin | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
In Vitro Model |
MLE-12 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_3751 | |
| In Vivo Model |
C57BL/6 J mice (8-week old) from SLAC Laboratory Animal Co. LTD (Shanghai, China) were housed in a specific pathogen-free (SPF) barrier system at 20 with 12-h light/dark cycles. They were randomly grouped as follows: (1) intratracheal saline (control group); (2) intraperitoneal deferoxamine (DFO, Sigma-Aldrich; DFO group); (3) intratracheal bleomycin (BLM, Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd.; BLM group); and (4) intratracheal BLM plus intraperitoneal deferoxamine (BLM + DFO group). They were intratracheally injected with 50 ul of BLM (5 mg/kg) on day 0. For the preventive anti-fibrotic treatment, DFO (50 mg/kg2 day-1) was administered from day 0 to day 20. Lung samples were collected at day 21.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Bleomycin (BLM) can induce the inhibition of cellular GPX4, leading to the generation of lipid ROS. Besides, BLM treatment significantly increased the expression levels of TfR1 and DMT1 in a concentration- and time-dependent manner but similarly decreased those of FPN. TfR1 expression was significantly increased by BLM treatment but decreased by BLM + DFO treatment. These findings indicate that iron metabolism disorder, iron deposition, and ferroptosis in ATII cells may be involved in the pathogenesis of BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis. | ||||
Traumatic brain injury [ICD-11: NA07]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [13] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Ebselen | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were introduced into research, for the present SAH model a total of 383 rats, weighing 250-300 g, were purchased from the Animal Center of Chongqing Medical University. The adult male SD rats assigned to SAH model procedures were randomly divided into several groups. The rats assigned to SAH model procedures were randomly divided into the groups, first to determine the expression of hepcidin, DMT1, FPN1, and GPX4, the main regulator of ferroptosis, and to subsequently select the most suitable timing for drug injections. Second, adult male SD rats were randomly divided into the groups to determine the significant preoperative doses of ebselen, heparin and OSM in terms of their effects on hepcidin, DMT1, FPN1, and GPX4 for further study. Lastly, male SD rats were randomly divided into the groups to determine the effects of hepcidin and DMT1 on iron metabolism, ferroptosis, and EBI, by using heparin, ebselen and OSM as the experimental interventions.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Inhibition of DMT1 by ebselen could suppress iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation, and thereby alleviate ferroptosis and early brain injury (EBI) in SAH rats. Heparin downregulated the expression of hepcidin and DMT1, increased FPN1, and exerted protective effects that were equivalent to those of ebselen on ferroptosis and EBI. In addition, OSM increased the expression of hepcidin and DMT1, decreased FPN1, and aggravated ferroptosis and EBI, while the effect on ferroptosis was reversed by ebselen. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [13] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Hepcidin | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were introduced into research, for the present SAH model a total of 383 rats, weighing 250-300 g, were purchased from the Animal Center of Chongqing Medical University. The adult male SD rats assigned to SAH model procedures were randomly divided into several groups. The rats assigned to SAH model procedures were randomly divided into the groups, first to determine the expression of hepcidin, DMT1, FPN1, and GPX4, the main regulator of ferroptosis, and to subsequently select the most suitable timing for drug injections. Second, adult male SD rats were randomly divided into the groups to determine the significant preoperative doses of ebselen, heparin and OSM in terms of their effects on hepcidin, DMT1, FPN1, and GPX4 for further study. Lastly, male SD rats were randomly divided into the groups to determine the effects of hepcidin and DMT1 on iron metabolism, ferroptosis, and EBI, by using heparin, ebselen and OSM as the experimental interventions.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Inhibition of DMT1 by ebselen could suppress iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation, and thereby alleviate ferroptosis and early brain injury (EBI) in SAH rats. Heparin downregulated the expression of hepcidin and DMT1, increased FPN1, and exerted protective effects that were equivalent to those of ebselen on ferroptosis and EBI. In addition, OSM increased the expression of hepcidin and DMT1, decreased FPN1, and aggravated ferroptosis and EBI, while the effect on ferroptosis was reversed by ebselen. | ||||
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 (MAPK14)
Artesunate
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [1] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00] | ||||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | U-251MG cells | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0021 | |
| In Vivo Model |
The xenografts were established via the subcutaneous inoculation of U251 cells (1 x 107 cells/per mouse) into the armpit of one mouse. After two weeks of growth, the cancer tissues were cut into pieces with the dimensions of 1.5 x 1.5 x 1.5 mm3 and inoculated subcutaneously into the right armpit of the mice with a puncture needle. When tumor volume reached approximately 80 mm3, mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 5): Vehicle control, ART (20 mg/kg), ART (40 mg/kg), and TMZ (40 mg/kg). TMZ was used as the positive control. Drugs and vehicle were given by intraperitoneal injection daily for 21 days. Tumor volume and body weight were measured every three days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Artesunate triggers ferroptosis in glioblastoma in vitro and in vivo through regulation of iron metabolism and p38 ( MAPK14) and ERK signaling pathways. Meanwhile, ART reduced the protein level of GPX4 and FPN1, increased the protein level of DMT1, TfR, ferritin and NCOA4. | ||||
Unspecific Regulator
Temozolomide
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [6] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | TG905 (Human glioblastoma cells) | |||
| Response Description | Temozolomide may suppress cell growth partly by inducing ferroptosis by targeting DMT1 expression in glioblastoma cells. The results also showed that temozolomide-induced ferroptosis is associated with regulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. | |||
Bavachin
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [7] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51] | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | MG-63 cells | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0426 |
| HOS cells | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0312 | |
| Response Description | Bavachin could induce Osteosarcoma cell ferroptosis. Furthermore, bavachin elevated intracellular ferrous iron levels by increasing TFRC and DMT1 (SLC11A2) expression and decreasing FTH and FTL expressions. Bavachin also reduced SLC7A11 and GPX4 expression and promoted ROS and MDA accumulation by downregulating p-STAT3 to upregulate P53 expression. | |||
Sulfasalazine
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [8] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| T-47D cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| BT-549 cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| Response Description | Sulfasalazine (SAS) upregulated TFRC and DMT1. Knockdown of the ER increased TFRC expression in breast cancer cells. In conclusion SAS could trigger ferroptosis in breast cancer cells, especially in cells with low ER expression. | |||
Epigallocatechin Gallate
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [9] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00] | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Response Description | Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) pretreatment counteracted 6-OHDA-induced increased expression of divalent metal transporter-1 (DMT1) and hepcidin and decreased expression of the iron-export protein ferroportin 1 (Fpn1), leading to a 28% reduction in Fe2+ uptake. EGCG inhibits iron overload, decreased LPO, and increased GSH levels in Parkinson disease models, which are the three major hallmarks of ferroptosis. | |||
Klotho
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [10] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Temporal lobe epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A61] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | rHTs (Rat hippocampal tissues) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Adult male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats aged between 6 and 8 weeks old and weighing between 280 and 320 g were purchased from Hunan slake jingda laboratory animal company (Changsha, China) and used in this study. Under a 12 h light/dark cycle, rats had free access to water and food and were maintained in a room with controlled temperature, humidity. These rats were adapted to the environment for at least 2 week before we began to enter the experimental procedure.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Klotho overexpression inhibits ferroptosis in temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) with cognitive deficits and has a neuroprotective effect. Moreover, for the first time, we found that klotho overexpression inhibits ferroptosis and iron overload in TLE with cognitive deficits. In addition, klotho overexpression down-regulated the expression of DMT1 and up-regulated FPN expression which regulated iron metabolism balance. | ||||
Naotaifang Extract
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [11] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cerebral ischemia [ICD-11: 8B10] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Specific pathogen-free adult male SD rats, (80 ± 5) days old and weighing 220-250 g, were provided by the Hunan Slack Jingda Experimental Animal Co., Ltd (Hunan, China). SD rats were randomly divided into 4 groups with 15 in each group: sham operation group, MCAO group, MCAO + DFP group and MCAO + NTE group. The rats were treated with drugs via oral gavage. According to the average body weight, the MCAO + NTE rats were given NTE at 27 g/kg, and the sham operation and the MCAO rats were given the same volume of saline (2.5 mL) for 7 consecutive days. The MCAO + DFP rats were given DFP at a dose of 125 mg/kg for 3 consecutive days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Acute cerebral ischemia induces neuronal ferroptosis and the effects of treating MCAO rats with naotaifang extract involved inhibition of ferroptosis through the TFR1/DMT1 and SCL7A11/GPX4 pathways. | ||||
Bleomycin
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [12] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Pulmonary fibrosis [ICD-11: CB03] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | MLE-12 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_3751 | |
| In Vivo Model |
C57BL/6 J mice (8-week old) from SLAC Laboratory Animal Co. LTD (Shanghai, China) were housed in a specific pathogen-free (SPF) barrier system at 20 with 12-h light/dark cycles. They were randomly grouped as follows: (1) intratracheal saline (control group); (2) intraperitoneal deferoxamine (DFO, Sigma-Aldrich; DFO group); (3) intratracheal bleomycin (BLM, Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd.; BLM group); and (4) intratracheal BLM plus intraperitoneal deferoxamine (BLM + DFO group). They were intratracheally injected with 50 ul of BLM (5 mg/kg) on day 0. For the preventive anti-fibrotic treatment, DFO (50 mg/kg2 day-1) was administered from day 0 to day 20. Lung samples were collected at day 21.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Bleomycin (BLM) can induce the inhibition of cellular GPX4, leading to the generation of lipid ROS. Besides, BLM treatment significantly increased the expression levels of TfR1 and DMT1 in a concentration- and time-dependent manner but similarly decreased those of FPN. TfR1 expression was significantly increased by BLM treatment but decreased by BLM + DFO treatment. These findings indicate that iron metabolism disorder, iron deposition, and ferroptosis in ATII cells may be involved in the pathogenesis of BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis. | ||||
Ebselen
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [13] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Traumatic brain injury [ICD-11: NA07] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were introduced into research, for the present SAH model a total of 383 rats, weighing 250-300 g, were purchased from the Animal Center of Chongqing Medical University. The adult male SD rats assigned to SAH model procedures were randomly divided into several groups. The rats assigned to SAH model procedures were randomly divided into the groups, first to determine the expression of hepcidin, DMT1, FPN1, and GPX4, the main regulator of ferroptosis, and to subsequently select the most suitable timing for drug injections. Second, adult male SD rats were randomly divided into the groups to determine the significant preoperative doses of ebselen, heparin and OSM in terms of their effects on hepcidin, DMT1, FPN1, and GPX4 for further study. Lastly, male SD rats were randomly divided into the groups to determine the effects of hepcidin and DMT1 on iron metabolism, ferroptosis, and EBI, by using heparin, ebselen and OSM as the experimental interventions.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Inhibition of DMT1 by ebselen could suppress iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation, and thereby alleviate ferroptosis and early brain injury (EBI) in SAH rats. Heparin downregulated the expression of hepcidin and DMT1, increased FPN1, and exerted protective effects that were equivalent to those of ebselen on ferroptosis and EBI. In addition, OSM increased the expression of hepcidin and DMT1, decreased FPN1, and aggravated ferroptosis and EBI, while the effect on ferroptosis was reversed by ebselen. | ||||
Hepcidin
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [13] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Traumatic brain injury [ICD-11: NA07] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were introduced into research, for the present SAH model a total of 383 rats, weighing 250-300 g, were purchased from the Animal Center of Chongqing Medical University. The adult male SD rats assigned to SAH model procedures were randomly divided into several groups. The rats assigned to SAH model procedures were randomly divided into the groups, first to determine the expression of hepcidin, DMT1, FPN1, and GPX4, the main regulator of ferroptosis, and to subsequently select the most suitable timing for drug injections. Second, adult male SD rats were randomly divided into the groups to determine the significant preoperative doses of ebselen, heparin and OSM in terms of their effects on hepcidin, DMT1, FPN1, and GPX4 for further study. Lastly, male SD rats were randomly divided into the groups to determine the effects of hepcidin and DMT1 on iron metabolism, ferroptosis, and EBI, by using heparin, ebselen and OSM as the experimental interventions.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Inhibition of DMT1 by ebselen could suppress iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation, and thereby alleviate ferroptosis and early brain injury (EBI) in SAH rats. Heparin downregulated the expression of hepcidin and DMT1, increased FPN1, and exerted protective effects that were equivalent to those of ebselen on ferroptosis and EBI. In addition, OSM increased the expression of hepcidin and DMT1, decreased FPN1, and aggravated ferroptosis and EBI, while the effect on ferroptosis was reversed by ebselen. | ||||
References
