Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0165)
| Name |
Ebselen
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ebselen; 60940-34-3; 2-Phenyl-1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one; 2-phenylbenzo[d][1,2]selenazol-3(2H)-one; Ebselenum; 2-phenyl-1,2-benzoselenazol-3-one; SPI-1005; Ebselene; Ebseleno; Ebselen [INN]; Ebselene [French]; Ebselenum [Latin]; Harmokisane; Ebseleno [Spanish]; C13H9NOSe; PZ 51; DR-3305; PZ-51; PZ51; MLS000028488; DR3305; CCRIS 3714; 1,2-Benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one, 2-phenyl-; 2-Phenyl-1,2-benzisoselenazolin-3-one; SMR000058445; UNII-40X2P7DPGH; 2-phenyl-1,2-benzoisoselenazol-3(2H)-one; CHEMBL51085; NSC 639762; Prestwick_1057; SPI-3005; Prestwick0_000740; Prestwick1_000740; Prestwick2_000740; Prestwick3_000740; Spectrum2_001441; Spectrum3_000799; Spectrum4_000445; Spectrum5_001713; Lopac-E-3520; MFCD00210937; NSC639762; NSC-639762; NSC-757883; 40X2P7DPGH; Lopac0_000541; NCGC00015412-06; BSPBio_000700; BSPBio_001342; BSPBio_002538; CPD000058445; KBioGR_000062; KBioGR_000830; KBioSS_000062; DivK1c_000951; SPBio_001301; SPBio_002639; CAS-60940-34-3; MLS001148646; BPBio1_000770; DTXSID7045150; BCBcMAP01_000149; CHEBI:77543; HMS502P13; KBio1_000951; KBio2_000062; KBio2_002630; KBio2_005198; KBio3_000123; KBio3_000124; KBio3_001758; NINDS_000951; E 3520; Bio2_000062; Bio2_000542; HMS1361D04; HMS1570C22; HMS1791D04; HMS1989D04; HMS2052N09; CCG-39161; AC-1124; IDI1_000951; IDI1_033812; QTL1_000035; NCGC00015412-01; NCGC00015412-02; NCGC00015412-03; NCGC00015412-13; NCGC00024072-03; NCGC00024072-04; NCGC00024072-05; NCGC00178610-01; NCGC00178610-02; NCGC00178610-03; AB00053217; EU-0100541; MLS-0003066.0001; BRD-K29359156-001-06-1; DR 3305; RP 60931; SR-01000003081; AC1L1FDW; CID3194; SPI1005; Ebselen (C5); nchembio.109-comp1; 2-phenyl-1,2-benzoselenazol-3(2h)-one; LS-33527; SAM001247071; EBSELEN [JAN]; EBSELEN [MI]; EBSELEN [MART.]; Opera_ID_1643; EBSELEN [WHO-DD]; Ebselen, cysteine modifier; cid_3194; C042986; SCHEMBL33829; MLS001424261; MLS006010108; E3520_SIGMA; I09-1611; DTXCID5025150; BDBM34233; GTPL10583; HMS2097C22; HMS2235A11; HMS3394N09; HMS3402D04; HMS3649O05; HMS3714C22; HMS3873N13; KUC112559N; Pharmakon1600-01501188; BCP17134; EX-A1447; SPI-1005;PZ-51; Tox21_110140; 2-Phenyl-benzo[d]isoselenazol-3-one; DAP001372; HB0270; NSC757883; s6676; AKOS015898841; CS-5534; DB12610; LP00541; NC00431; SDCCGSBI-0050524.P004; KSC-325-014; NCGC00015412-04; NCGC00015412-05; NCGC00015412-07; NCGC00015412-08; NCGC00015412-09; NCGC00015412-10; NCGC00015412-11; NCGC00015412-12; NCGC00015412-21; phenyl-1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one; 2-phenyl-1,2-benzisoselazol-3(2H)-one; HY-13750; SY052687; SBI-0050524.P003; 2-phenyl-1,2-benzisoselenazole-3(2H)-one; 2-phenyl-1,2-benzoisoselenazole-3(2H)-one; E0946; FT-0759332; 2-phenyl-1,2-benzoisoselenazole-3-(2H)-one; 2-Phenyl-benzo[d]isoselenazol-3-one(Ebselen); C75847; AB00053217_25; A868855; Q5332073; SR-01000003081-2; SR-01000003081-7; SR-01000003081-8; BRD-K29359156-001-23-6; SR-01000003081-10; SR-01000003081-14
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
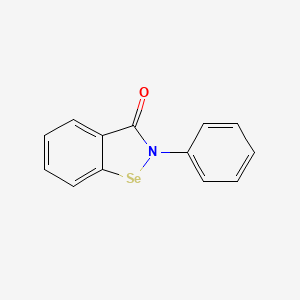 |
||||
|
3D MOL
|
|||||
| Formula |
C13H9NOSe
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
2-phenyl-1,2-benzoselenazol-3-one
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC=C(C=C1)N2C(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3[Se]2
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C13H9NOSe/c15-13-11-8-4-5-9-12(11)16-14(13)10-6-2-1-3-7-10/h1-9H
|
||||
| InChIKey |
DYEFUKCXAQOFHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Natural resistance-associated macrophage protein 2 (SLC11A2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Traumatic brain injury | ICD-11: NA07 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were introduced into research, for the present SAH model a total of 383 rats, weighing 250-300 g, were purchased from the Animal Center of Chongqing Medical University. The adult male SD rats assigned to SAH model procedures were randomly divided into several groups. The rats assigned to SAH model procedures were randomly divided into the groups, first to determine the expression of hepcidin, DMT1, FPN1, and GPX4, the main regulator of ferroptosis, and to subsequently select the most suitable timing for drug injections. Second, adult male SD rats were randomly divided into the groups to determine the significant preoperative doses of ebselen, heparin and OSM in terms of their effects on hepcidin, DMT1, FPN1, and GPX4 for further study. Lastly, male SD rats were randomly divided into the groups to determine the effects of hepcidin and DMT1 on iron metabolism, ferroptosis, and EBI, by using heparin, ebselen and OSM as the experimental interventions.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Inhibition of DMT1 by ebselen could suppress iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation, and thereby alleviate ferroptosis and early brain injury (EBI) in SAH rats. Heparin downregulated the expression of hepcidin and DMT1, increased FPN1, and exerted protective effects that were equivalent to those of ebselen on ferroptosis and EBI. In addition, OSM increased the expression of hepcidin and DMT1, decreased FPN1, and aggravated ferroptosis and EBI, while the effect on ferroptosis was reversed by ebselen. | ||||
