Ferroptosis Target Information
General Information of the Ferroptosis Target (ID: TAR10063)
| Target Name | Stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
FADS5; SCD1; SCDOS; hSCD1; Acyl-CoA desaturase; Delta(9)-desaturase (Delta-9 desaturase); Fatty acid desaturase
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene Name | SCD | ||||
| Sequence |
MPAHLLQDDISSSYTTTTTITAPPSRVLQNGGDKLETMPLYLEDDIRPDIKDDIYDPTYK
DKEGPSPKVEYVWRNIILMSLLHLGALYGITLIPTCKFYTWLWGVFYYFVSALGITAGAH RLWSHRSYKARLPLRLFLIIANTMAFQNDVYEWARDHRAHHKFSETHADPHNSRRGFFFS HVGWLLVRKHPAVKEKGSTLDLSDLEAEKLVMFQRRYYKPGLLMMCFILPTLVPWYFWGE TFQNSVFVATFLRYAVVLNATWLVNSAAHLFGYRPYDKNISPRENILVSLGAVGEGFHNY HHSFPYDYSASEYRWHINFTTFFIDCMAALGLAYDRKKVSKAAILARIKRTGDGNYKSG Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Family | Fatty acid desaturase type 1 family | ||||
| Function |
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase that utilizes O2 and electrons from reduced cytochrome b5 to introduce the first double bond into saturated fatty acyl-CoA substrates. Catalyzes the insertion of a cis double bond at the delta-9 position into fatty acyl-CoA substrates including palmitoyl-CoA and stearoyl-CoA. Gives rise to a mixture of 16:1 and 18:1 unsaturated fatty acids. Plays an important role in lipid biosynthesis. Plays an important role in regulating the expression of genes that are involved in lipogenesis and in regulating mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. Plays an important role in body energy homeostasis. Contributes to the biosynthesis of membrane phospholipids, cholesterol esters and triglycerides.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene ID | 6319 | ||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Target Type | Driver Suppressor Marker | ||||
| Mechanism Diagram | Click to View the Original Diagram | ||||
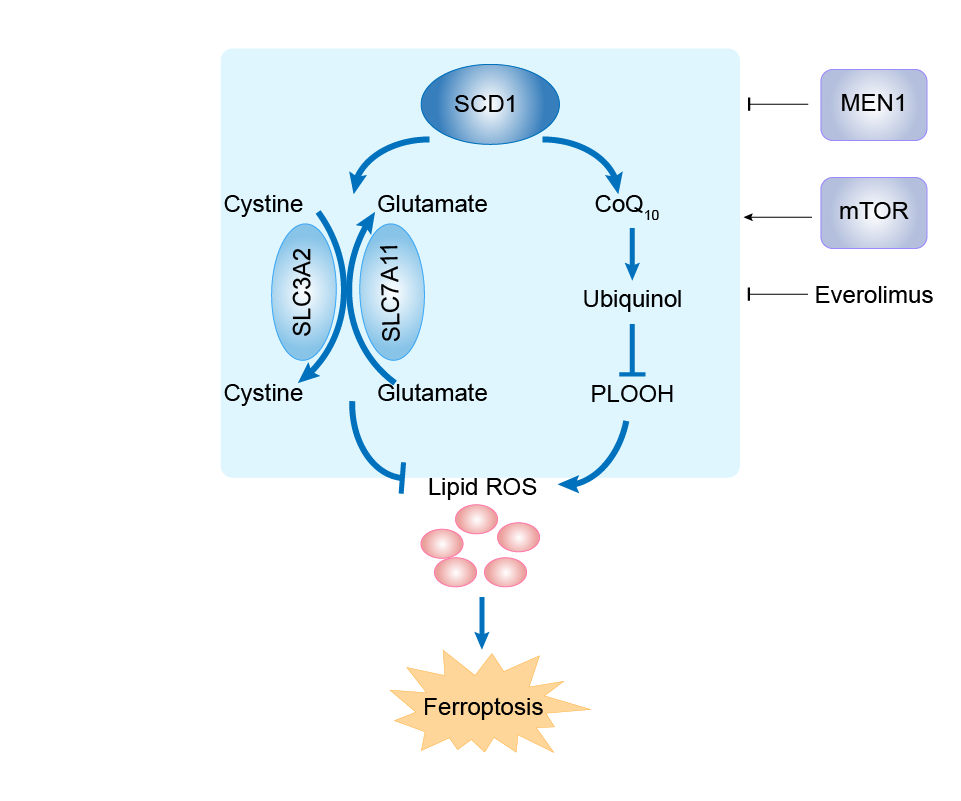
|
|||||
Tissue Relative Abundances of This Target
Full List of Regulator(s) of This Ferroptosis Target and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
SCD can be involved in and affect the ferroptosis by the following regulators, and result in corresponding disease/drug response(s). You can browse corresponding disease or drug response(s) resulting from the regulation of certain regulators.
Browse Regulator related Disease
Browse Regulator related Drug
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBF1)
Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [1] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Lactate | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
In Vitro Model |
CAF cells | Normal | Carassius auratus | CVCL_R883 | |
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| L-02 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | ||
| Hep-G2 cells | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | ||
| Hep 3B2.1-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | ||
| Huh-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Female mice aged around 6-7 weeks were used for this study, which were purchased through Laboratory Animal Center of Chongqing Medical University from Vital River Co. Ltd (Beijing, China).After one week, each mouse was injected subcutaneously with 100 uL of Huh-7 cell suspension (5 x 106 units) to establish the tumor model. The mice were grouped randomly, and then subjected to different treatments after subcutaneous tumors became visually detectable.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | The monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1)-mediated lactate uptake could promote ATP production in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells and deactivate the energy sensor AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), leading to the upregulation of SREBP1 (SREBF1) and the downstream stearoyl-coenzyme A (CoA) desaturase-1 (SCD1) to enhance the production of anti-ferroptosis monounsaturated fatty acids. | ||||
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [2] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Drug | NL01 | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
In Vitro Model |
Anglne cells | Ovarian carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_U287 | |
| HO8910PM cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0310 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
BALB/c Nude female mice were adjusted for 7 days in a SPF room and divided into 2 groups (6 mice per group): DMSO and NL01 (5 mg/kg). NL01 was dissolved in 1% carboxymethylcellulose (Millipore, USA). DMSO (control) used the same volume of vehicle (1% carboxymethylcellulose). HO8910PM cells were grown in tissue culture, and counted. 1 x 106 cells were inoculated to subcutaneously. Ten days after inoculation, the drugs were administered every five days subcutaneously to the mice for 15 days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | NL01 induced iron death and inhibited ovarian cancer proliferation. NL01 was able to reduce the expression of HCAR1/MCT1 and activate the AMPK signaling pathway, which in turn induced cellular ferroptosis via SREBP1 (SREBF1) pathway. SCD1 (Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1) is the downstream target of SREBP1. Further study showed that NL01 promoted the downregulation of GPX4 expression. | ||||
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [3] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Drug | D-(-)-Fructose | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
hLCs (Liver cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Four-week-old male and female C57BL/6N mice were obtained from the Central Lab Animal Inc. (Seoul, South Korea) and housed in 42 x 27 x 15 cm polycarbonate cages (six mice per cage). The animals were assigned into either the control group (n = 12; six mice per sex) or fructose intervention group (n = 12; six mice per sex). After a week of acclimation, the fructose group was subjected to 34% fructose in deionized water (wt:vol) over six weeks to induce NAFLD conditions as previously described.11 To note, compared to conventional sugary beverages (e.g., soft drinks), the supplementation level of fructose is higher (11% vs. 34%) to induce liver damage markers within a reasonable intervention time range (i.e., 6 weeks).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | The protein expressions of SREBP1 and its downstream targets ACC1, FASN and SCD1 were all increased in fructose-treated AML12 hepatocytes, which demonstrates fructose mediated upregulation of SREBP1. MiR-33-5p (miR-33) was identified as the key miRNA responsible for SREBP1 regulation upon fructose intake, which was validated by in vitro transfection assay. Collectively, fructose-induced oxidative damage induces ferroptosis, and miR-33 could be used as a serological biomarker of fructose-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). | ||||
Fibrosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B53]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [5] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
HT-1080 cells | Fibrosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0317 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | ||
| MDA-MB-453 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | ||
| BT-474 cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | ||
| MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | ||
| T-47D cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | ||
| U-87MG cells | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_GP63 | ||
| Hep-G2 cells | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | ||
| PC-3 cells | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0035 | ||
| DU145 cells | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0105 | ||
| A-549 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | ||
| NCI-H1299 cells | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | ||
| LN-229 cells | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | ||
| SK-MEL-2 cells (MEK inhibitor-resistant) cells | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0069 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
For the in vivo xenograft mouse model, 17-b-estradiol 60-d release pellets (Innovative Research of America) were implanted subcutaneously into the left flank 7 d before tumor inoculation. GPX4 iKO BT474 cells were inoculated by injecting 5 x 106 cells in 50% Matrigel subcutaneously in the right flank of 6- to 8-wk-old female athymicnu/numice (Envigo). For PC-3 tumor models, male athymic nu/nu mice aged 5 to 6 wk were injected in the right flank with 5 x 106 PC-3 cells.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Hyperactive mutation of PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling protects cancer cells from oxidative stress and ferroptotic death through SREBP1/SCD1-mediated lipogenesis, and combination of mTORC1 inhibition with ferroptosis induction shows therapeutic promise of preclinical models in Fibrosarcoma. | ||||
Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [4] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Drug | Everolimus | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
BON-1 cells | Pancreatic serotonin-producing neuroendocrine tumor | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3985 |
| QGP-1 cells | Pancreatic somatostatinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3143 | |
| Response Description | The negative correlation between MEN1 and SCD1 is further verified in clinical specimens. Furthermore, BON-1 and QGP-1 cells with MEN1 overexpression are more sensitive to everolimus, a widely used drug in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNETs) that targets mTOR signaling. | |||
mmu-miR-33-5p (miRNA)
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [3] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Drug | D-(-)-Fructose | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
hLCs (Liver cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Four-week-old male and female C57BL/6N mice were obtained from the Central Lab Animal Inc. (Seoul, South Korea) and housed in 42 x 27 x 15 cm polycarbonate cages (six mice per cage). The animals were assigned into either the control group (n = 12; six mice per sex) or fructose intervention group (n = 12; six mice per sex). After a week of acclimation, the fructose group was subjected to 34% fructose in deionized water (wt:vol) over six weeks to induce NAFLD conditions as previously described.11 To note, compared to conventional sugary beverages (e.g., soft drinks), the supplementation level of fructose is higher (11% vs. 34%) to induce liver damage markers within a reasonable intervention time range (i.e., 6 weeks).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | The protein expressions of SREBP1 and its downstream targets ACC1, FASN and SCD1 were all increased in fructose-treated AML12 hepatocytes, which demonstrates fructose mediated upregulation of SREBP1. MiR-33-5p (miR-33) was identified as the key miRNA responsible for SREBP1 regulation upon fructose intake, which was validated by in vitro transfection assay. Collectively, fructose-induced oxidative damage induces ferroptosis, and miR-33 could be used as a serological biomarker of fructose-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). | ||||
Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 1 (HCAR1)
Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [1] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Lactate | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
In Vitro Model |
CAF cells | Normal | Carassius auratus | CVCL_R883 | |
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| L-02 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | ||
| Hep-G2 cells | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | ||
| Hep 3B2.1-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | ||
| Huh-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Female mice aged around 6-7 weeks were used for this study, which were purchased through Laboratory Animal Center of Chongqing Medical University from Vital River Co. Ltd (Beijing, China).After one week, each mouse was injected subcutaneously with 100 uL of Huh-7 cell suspension (5 x 106 units) to establish the tumor model. The mice were grouped randomly, and then subjected to different treatments after subcutaneous tumors became visually detectable.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Lactate regulates the ferroptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. And blocking the lactate uptake via hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 1 (HCAR1)/MCT1 inhibition promotes ferroptosis by activating the AMPK to downregulate SCD1, which may synergize with its acyl-coenzyme A synthetase 4 (ACSL4)-promoting effect to amplify the ferroptotic susceptibility. | ||||
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [2] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Drug | NL01 | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
In Vitro Model |
Anglne cells | Ovarian carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_U287 | |
| HO8910PM cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0310 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
BALB/c Nude female mice were adjusted for 7 days in a SPF room and divided into 2 groups (6 mice per group): DMSO and NL01 (5 mg/kg). NL01 was dissolved in 1% carboxymethylcellulose (Millipore, USA). DMSO (control) used the same volume of vehicle (1% carboxymethylcellulose). HO8910PM cells were grown in tissue culture, and counted. 1 x 106 cells were inoculated to subcutaneously. Ten days after inoculation, the drugs were administered every five days subcutaneously to the mice for 15 days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | NL01 induced iron death and inhibited ovarian cancer proliferation. NL01 was able to reduce the expression of HCAR1/MCT1 and activate the AMPK signaling pathway, which in turn induced cellular ferroptosis via SREBP1 (SREBF1) pathway. SCD1 (Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1) is the downstream target of SREBP1. Further study showed that NL01 promoted the downregulation of GPX4 expression. | ||||
Regulatory-associated protein of mTOR (RPTOR)
Fibrosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B53]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [5] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
HT-1080 cells | Fibrosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0317 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | ||
| MDA-MB-453 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0418 | ||
| BT-474 cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0179 | ||
| MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | ||
| T-47D cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | ||
| U-87MG cells | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_GP63 | ||
| Hep-G2 cells | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | ||
| PC-3 cells | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0035 | ||
| DU145 cells | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0105 | ||
| A-549 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | ||
| NCI-H1299 cells | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | ||
| LN-229 cells | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | ||
| SK-MEL-2 cells (MEK inhibitor-resistant) cells | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0069 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (SD rats, weighing 250-300 g) aged 11-12 weeks were purchased from SLAC Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All 96 rats were randomly divided into four groups of 24 rats each: Sham group, Sham + IRN (30 mg/Kg) group, ICH group, and ICH + IRN (30 mg/Kg) group. The rats in sham group were injected with PBS solution, and the Sham + IRN (30 mg/Kg) group was received an equal amount of 30 mg/Kg IRN solution (intra-peritoneal injection) after the sham operation. After ICH, the rats in ICH group were injected with PBS solution, and the ICH + IRN (30 mg/Kg) group was received an equal amount of 30 mg/Kg IRN solution (intra-peritoneal injection).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Hyperactive mutation of PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling protects cancer cells from oxidative stress and ferroptotic death through SREBP1/SCD1-mediated lipogenesis, and combination of mTORC1 (RPTOR is a core component of mTORC1) inhibition with ferroptosis induction shows therapeutic promise of preclinical models in Fibrosarcoma. | ||||
Nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1 (NR4A1)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [6] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
PANC-1 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 |
| SW1990 cells | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
| Response Description | FBW7 (FBXW7) inhibited the expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD1) via inhibiting nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1 (NR4A1). SCD1 was reported to inhibit both ferroptosis and apoptosis. And activating ferroptosis and apoptosis immensely increased gemcitabine sensitivity, which might provide strategies for the combination therapy for pancreatic cancer. | |||
Menin (MEN1)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [4] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
BON-1 cells | Pancreatic serotonin-producing neuroendocrine tumor | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3985 |
| QGP-1 cells | Pancreatic somatostatinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3143 | |
| Response Description | We show that stearoyl-coA desaturase (SCD1) is the downstream of MEN1-mTOR signaling and oleic acid (OA), a metabolite of SCD1, recues the lipid peroxidation caused by MEN1 overexpression. The negative correlation between MEN1 and SCD1 is further verified in clinical specimens. Furthermore, we find that BON-1 and QGP-1 cells with MEN1 overexpression are more sensitive to everolimus, a widely used drug in pNETs that targets mTOR signaling. | |||
Membrane-spanning 4-domains subfamily A member 15 (MS4A15)
Fibrosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B53]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [7] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell migration | ||||
In Vitro Model |
HT-1080 cells | Fibrosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0317 |
| Calu-1 cells | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0608 | |
| MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | |
| NCI-H1975 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| HeLa cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| A-549 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| Response Description | MS4A15 regulation of anti-ferroptotic lipid reservoirs provides a key resistance mechanism that is distinct from antioxidant and lipid detoxification pathways. And Scd1 and Fads2 are counterregulated with Ms4a15 OE in Fibrosarcoma. | |||
Lymphoid-specific helicase (HELLS)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [8] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| Cell migration | |||||
| Cell invasion | |||||
In Vitro Model |
MRC-5 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0440 | |
| HBE1 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0287 | ||
| A-549 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | ||
| NCI-H358 cells | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1559 | ||
| NCI-H522 cells | Non-small cell lung carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1567 | ||
| PC-9 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B260 | ||
| 95C cells | Lung giant cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7109 | ||
| 95D cells | Lung giant cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_7110 | ||
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
SCID Mice (Hunan SJA Laboratory Animal Co.Ltd.) were injected with A549 (1 x 106 cells/mouse) or H358 (2 x 106 cells/mouse) cells via mammary fat pad (10 mice/group). Mice with A549 or H358 cells were imaged from dorsal and ventral views every three days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | LSH (HELLS) is involved in ferroptosis and is a potential therapeutic target in cancer because of its crucial role in ferroptosis. LSH functioned as an oncogene in lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. And LSH promotes the lipid metabolic genes, including SCD1 and FADS2. | ||||
LINC01606 (IncRNA)
Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [9] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| Cell stemness | |||||
In Vitro Model |
SW480 cells | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| HT29 cells | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | ||
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Four-week-old female nude mice were purchased from Cavens (Changzhou, China). Nude mice were randomly divided into four groups. SW480 and HT29 cells infected with sh-LINC01606, Lv-LINC01606 and control vectors were subcutaneously implanted in mice (n = 6 per group), respectively. Tumour volumes (V = length x width2/2) were measured every 3 days, and tumour weights were determined after 4 weeks.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | LINC01606 functions as an oncogene to facilitate tumor cell stemness, proliferation and inhibit ferroptosis and is a promising therapeutic target for colon cancer. Mechanistically, LINC01606 enhanced the expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 (SCD1), serving as a competing endogenous RNA to modulate miR-423-5p expression, subsequently activating the canonical Wnt/-catenin signaling, and transcription factor binding to IGHM enhancer 3 (TFE3) increased LINC01606 transcription after recruitment to the promoter regions of LINC01606. | ||||
hsa-miR-423-5p (miRNA)
Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [9] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Pathway Response | Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| Cell stemness | |||||
In Vitro Model |
SW480 cells | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| HT29 cells | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | ||
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Four-week-old female nude mice were purchased from Cavens (Changzhou, China). Nude mice were randomly divided into four groups. SW480 and HT29 cells infected with sh-LINC01606, Lv-LINC01606 and control vectors were subcutaneously implanted in mice (n = 6 per group), respectively. Tumour volumes (V = length x width2/2) were measured every 3 days, and tumour weights were determined after 4 weeks.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | LINC01606 functions as an oncogene to facilitate tumor cell stemness, proliferation and inhibit ferroptosis and is a promising therapeutic target for colon cancer. Mechanistically, LINC01606 enhanced the expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 (SCD1), serving as a competing endogenous RNA to modulate miR-423-5p expression, subsequently activating the canonical Wnt/-catenin signaling, and transcription factor binding to IGHM enhancer 3 (TFE3) increased LINC01606 transcription after recruitment to the promoter regions of LINC01606. | ||||
F-box/WD repeat-containing protein 7 (FBXW7)
Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [6] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
PANC-1 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 |
| SW1990 cells | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1723 | |
| Response Description | FBW7 (FBXW7) inhibited the expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD1) via inhibiting nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1 (NR4A1). SCD1 was reported to inhibit both ferroptosis and apoptosis. And activating ferroptosis and apoptosis immensely increased gemcitabine sensitivity, which might provide strategies for the combination therapy for pancreatic cancer. | |||
Unspecific Regulator
Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [10] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Sorafenib | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
L-02 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | |
| Hep-G2 cells | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | ||
| Hep 3B2.1-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | ||
| SMMC-7721 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 | ||
| Huh-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | ||
| BEL-7402 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5492 | ||
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Six-week-old male BALB/c athymic nude mice were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of Peking (Beijing, China). Stable cells (5 x 106) were seeded into the right flanks of the mice. After the xenografts had grown to 200 mm3, saline as a vehicle or sorafenib (30 mg/kg) was administered by gavage every day, and the mice were euthanized by the cervical dislocation method five weeks later. Before sacrifice, the tumor sizes and body weights were measured twice per week. The tumor volume (V) was calculated as follows: (L x W2)/2 (length, L, and width, W). The xenografts were excised and further assessed.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Sorafenib decreased HBXIP expression, and overexpression of HBXIP blocked sorafenib-induced Hepatocellular carcinoma cell death. Regarding the molecular mechanism, HBXIP transcriptionally induced the expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD) via coactivating the transcriptional factor ZNF263, resulting in the accumulation of free fatty acids and suppression of ferroptosis. | ||||
Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [11] | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Lorlatinib | Investigative | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
SK-MEL-28 cells | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0526 | |
| A-375 cells | Amelanotic melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0132 | ||
| WM35 cells | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | ||
| SK-MEL-5 cells | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0527 | ||
| 786-O cells | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1051 | ||
| Caki-1 cells | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0234 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | ||
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
All animal experiments were approved by the Ethical Review of Experimental Animals at Central South University. To generate subcutaneous tumors, 2 x 106 control A375 cells or GPX4 KO cells were suspended in 100 ul PBS and injected subcutaneously into nude mice (Shanghai SLAC). Tumor-bearing mice were randomly allocated into groups and treated with vehicle (2% DMSO + 30% PEG300, per day by orally) or lorlatinib (10 mg/kg, per day by orally). Liproxstatin-1 (10 mg/kg) was administrated through intraperitoneal injection per day. Tumors were weighted and photographed on day 18 after treatment. Tumor size were recorded every three days and calculated as [(length x width x width)/2].
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Lorlatinib sensitized melanoma to ferroptosis through targeting IGF1R-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling axis and its downstream SCD expression. | ||||
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [12] | |||
| Responsed Drug | MI463 | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
In Vitro Model |
OVCAR-8 cells | High grade ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1629 |
| OVCAR-3 cells | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| OVCAR-4 cells | Ovarian adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1627 | |
| A-549 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| Lu-99 cells | Lung giant cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3015 | |
| Lu-65 cells | Lung giant cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1392 | |
| PC-7 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_A786 | |
| BT-549 cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| MDA-MB-468 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| T-47D cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| PANC-1 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| BxPC-3 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| CFPAC-1 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| Response Description | The MI463 induced decrease in cell viability may be at least partly associated with the inhibition of SCD1 activity. In addition, the potent induction of HO1 contributed to the synergistic effects of MI463 plus auranofin. Therefore, meninMLL inhibitors, such as MI463, in combination with auranofin represent an effective therapeutic approach for several types of cancer via the induction of ferroptosis in High grade ovarian serous adenocarcinoma. | |||
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [13] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
In Vitro Model |
MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| LL/2 (LLC1) cells | Lung cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_4358 | ||
| HUVECs (Human umbilical vein endothelial cells) | |||||
| In Vivo Model |
For treatment with RSL3 (20 mg/kg), drug was administered in mice bearing LLC tumors by i.p. injection every other day for 2 weeks. For cisplatin, BALB/c mice bearing 4T1 tumors (50-100 mm3) were administered by i.p. injection of vehicle (0.7% DMSO in PBS) or cisplatin (7 mg/kg/week) for 3 weeks.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | SCD1 and FABP4 were also found upregulated in recurrent human breast cancer samples and correlated with worse prognosis of cancer patients with different types of tumors. Mechanistically, SCD1 leads to fatty acid (FA) desaturation and FABP4 derived from TEM enhances lipid droplet (LD) in cancer cells, which cooperatively protect from oxidative stress-induced ferroptosis. | ||||
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBF1)
Lactate
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [1] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | CAF cells | Normal | Carassius auratus | CVCL_R883 | |
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| L-02 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | ||
| Hep-G2 cells | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | ||
| Hep 3B2.1-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | ||
| Huh-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Female mice aged around 6-7 weeks were used for this study, which were purchased through Laboratory Animal Center of Chongqing Medical University from Vital River Co. Ltd (Beijing, China).After one week, each mouse was injected subcutaneously with 100 uL of Huh-7 cell suspension (5 x 106 units) to establish the tumor model. The mice were grouped randomly, and then subjected to different treatments after subcutaneous tumors became visually detectable.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | The monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1)-mediated lactate uptake could promote ATP production in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells and deactivate the energy sensor AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), leading to the upregulation of SREBP1 (SREBF1) and the downstream stearoyl-coenzyme A (CoA) desaturase-1 (SCD1) to enhance the production of anti-ferroptosis monounsaturated fatty acids. | ||||
NL01
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [2] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | Anglne cells | Ovarian carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_U287 | |
| HO8910PM cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0310 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
BALB/c Nude female mice were adjusted for 7 days in a SPF room and divided into 2 groups (6 mice per group): DMSO and NL01 (5 mg/kg). NL01 was dissolved in 1% carboxymethylcellulose (Millipore, USA). DMSO (control) used the same volume of vehicle (1% carboxymethylcellulose). HO8910PM cells were grown in tissue culture, and counted. 1 x 106 cells were inoculated to subcutaneously. Ten days after inoculation, the drugs were administered every five days subcutaneously to the mice for 15 days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | NL01 induced iron death and inhibited ovarian cancer proliferation. NL01 was able to reduce the expression of HCAR1/MCT1 and activate the AMPK signaling pathway, which in turn induced cellular ferroptosis via SREBP1 (SREBF1) pathway. SCD1 (Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1) is the downstream target of SREBP1. Further study showed that NL01 promoted the downregulation of GPX4 expression. | ||||
D-(-)-Fructose
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [3] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hLCs (Liver cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Four-week-old male and female C57BL/6N mice were obtained from the Central Lab Animal Inc. (Seoul, South Korea) and housed in 42 x 27 x 15 cm polycarbonate cages (six mice per cage). The animals were assigned into either the control group (n = 12; six mice per sex) or fructose intervention group (n = 12; six mice per sex). After a week of acclimation, the fructose group was subjected to 34% fructose in deionized water (wt:vol) over six weeks to induce NAFLD conditions as previously described.11 To note, compared to conventional sugary beverages (e.g., soft drinks), the supplementation level of fructose is higher (11% vs. 34%) to induce liver damage markers within a reasonable intervention time range (i.e., 6 weeks).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | The protein expressions of SREBP1 and its downstream targets ACC1, FASN and SCD1 were all increased in fructose-treated AML12 hepatocytes, which demonstrates fructose mediated upregulation of SREBP1. MiR-33-5p (miR-33) was identified as the key miRNA responsible for SREBP1 regulation upon fructose intake, which was validated by in vitro transfection assay. Collectively, fructose-induced oxidative damage induces ferroptosis, and miR-33 could be used as a serological biomarker of fructose-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). | ||||
Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (MTOR)
Everolimus
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [4] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | BON-1 cells | Pancreatic serotonin-producing neuroendocrine tumor | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3985 |
| QGP-1 cells | Pancreatic somatostatinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3143 | |
| Response Description | The negative correlation between MEN1 and SCD1 is further verified in clinical specimens. Furthermore, BON-1 and QGP-1 cells with MEN1 overexpression are more sensitive to everolimus, a widely used drug in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNETs) that targets mTOR signaling. | |||
mmu-miR-33-5p (miRNA)
D-(-)-Fructose
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [3] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hLCs (Liver cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Four-week-old male and female C57BL/6N mice were obtained from the Central Lab Animal Inc. (Seoul, South Korea) and housed in 42 x 27 x 15 cm polycarbonate cages (six mice per cage). The animals were assigned into either the control group (n = 12; six mice per sex) or fructose intervention group (n = 12; six mice per sex). After a week of acclimation, the fructose group was subjected to 34% fructose in deionized water (wt:vol) over six weeks to induce NAFLD conditions as previously described.11 To note, compared to conventional sugary beverages (e.g., soft drinks), the supplementation level of fructose is higher (11% vs. 34%) to induce liver damage markers within a reasonable intervention time range (i.e., 6 weeks).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | The protein expressions of SREBP1 and its downstream targets ACC1, FASN and SCD1 were all increased in fructose-treated AML12 hepatocytes, which demonstrates fructose mediated upregulation of SREBP1. MiR-33-5p (miR-33) was identified as the key miRNA responsible for SREBP1 regulation upon fructose intake, which was validated by in vitro transfection assay. Collectively, fructose-induced oxidative damage induces ferroptosis, and miR-33 could be used as a serological biomarker of fructose-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). | ||||
Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 1 (HCAR1)
Lactate
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [1] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | CAF cells | Normal | Carassius auratus | CVCL_R883 | |
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| L-02 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | ||
| Hep-G2 cells | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | ||
| Hep 3B2.1-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | ||
| Huh-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Female mice aged around 6-7 weeks were used for this study, which were purchased through Laboratory Animal Center of Chongqing Medical University from Vital River Co. Ltd (Beijing, China).After one week, each mouse was injected subcutaneously with 100 uL of Huh-7 cell suspension (5 x 106 units) to establish the tumor model. The mice were grouped randomly, and then subjected to different treatments after subcutaneous tumors became visually detectable.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Lactate regulates the ferroptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. And blocking the lactate uptake via hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 1 (HCAR1)/MCT1 inhibition promotes ferroptosis by activating the AMPK to downregulate SCD1, which may synergize with its acyl-coenzyme A synthetase 4 (ACSL4)-promoting effect to amplify the ferroptotic susceptibility. | ||||
NL01
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [2] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | Anglne cells | Ovarian carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_U287 | |
| HO8910PM cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0310 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
BALB/c Nude female mice were adjusted for 7 days in a SPF room and divided into 2 groups (6 mice per group): DMSO and NL01 (5 mg/kg). NL01 was dissolved in 1% carboxymethylcellulose (Millipore, USA). DMSO (control) used the same volume of vehicle (1% carboxymethylcellulose). HO8910PM cells were grown in tissue culture, and counted. 1 x 106 cells were inoculated to subcutaneously. Ten days after inoculation, the drugs were administered every five days subcutaneously to the mice for 15 days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | NL01 induced iron death and inhibited ovarian cancer proliferation. NL01 was able to reduce the expression of HCAR1/MCT1 and activate the AMPK signaling pathway, which in turn induced cellular ferroptosis via SREBP1 (SREBF1) pathway. SCD1 (Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1) is the downstream target of SREBP1. Further study showed that NL01 promoted the downregulation of GPX4 expression. | ||||
Unspecific Regulator
Sorafenib
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [10] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | L-02 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | |
| Hep-G2 cells | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | ||
| Hep 3B2.1-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | ||
| SMMC-7721 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 | ||
| Huh-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | ||
| BEL-7402 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5492 | ||
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Six-week-old male BALB/c athymic nude mice were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of Peking (Beijing, China). Stable cells (5 x 106) were seeded into the right flanks of the mice. After the xenografts had grown to 200 mm3, saline as a vehicle or sorafenib (30 mg/kg) was administered by gavage every day, and the mice were euthanized by the cervical dislocation method five weeks later. Before sacrifice, the tumor sizes and body weights were measured twice per week. The tumor volume (V) was calculated as follows: (L x W2)/2 (length, L, and width, W). The xenografts were excised and further assessed.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Sorafenib decreased HBXIP expression, and overexpression of HBXIP blocked sorafenib-induced Hepatocellular carcinoma cell death. Regarding the molecular mechanism, HBXIP transcriptionally induced the expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD) via coactivating the transcriptional factor ZNF263, resulting in the accumulation of free fatty acids and suppression of ferroptosis. | ||||
Lorlatinib
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [11] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | SK-MEL-28 cells | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0526 | |
| A-375 cells | Amelanotic melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0132 | ||
| WM35 cells | Melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0580 | ||
| SK-MEL-5 cells | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0527 | ||
| 786-O cells | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1051 | ||
| Caki-1 cells | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0234 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | ||
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
All animal experiments were approved by the Ethical Review of Experimental Animals at Central South University. To generate subcutaneous tumors, 2 x 106 control A375 cells or GPX4 KO cells were suspended in 100 ul PBS and injected subcutaneously into nude mice (Shanghai SLAC). Tumor-bearing mice were randomly allocated into groups and treated with vehicle (2% DMSO + 30% PEG300, per day by orally) or lorlatinib (10 mg/kg, per day by orally). Liproxstatin-1 (10 mg/kg) was administrated through intraperitoneal injection per day. Tumors were weighted and photographed on day 18 after treatment. Tumor size were recorded every three days and calculated as [(length x width x width)/2].
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Lorlatinib sensitized melanoma to ferroptosis through targeting IGF1R-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling axis and its downstream SCD expression. | ||||
MI463
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [12] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| In Vitro Model | OVCAR-8 cells | High grade ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1629 |
| OVCAR-3 cells | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| OVCAR-4 cells | Ovarian adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1627 | |
| A-549 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| Lu-99 cells | Lung giant cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3015 | |
| Lu-65 cells | Lung giant cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1392 | |
| PC-7 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_A786 | |
| BT-549 cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| MDA-MB-468 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| T-47D cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| PANC-1 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| BxPC-3 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| CFPAC-1 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| Response Description | The MI463 induced decrease in cell viability may be at least partly associated with the inhibition of SCD1 activity. In addition, the potent induction of HO1 contributed to the synergistic effects of MI463 plus auranofin. Therefore, meninMLL inhibitors, such as MI463, in combination with auranofin represent an effective therapeutic approach for several types of cancer via the induction of ferroptosis in High grade ovarian serous adenocarcinoma. | |||
References
