Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0351)
| Name |
MI463
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
MI-463; 1628317-18-9; 4-methyl-5-((4-((6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)piperidin-1-yl)methyl)-1H-indole-2-carbonitrile; CHEMBL3780895; MI463; 4-methyl-5-[[4-[[6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]piperidin-1-yl]methyl]-1H-indole-2-carbonitrile; SCHEMBL16092792; DZACSLYTXLZAAF-UHFFFAOYSA-N; BCP23982; EX-A1849; BDBM50455859; s7816; CCG-269582; CS-6219; AC-36210; BS-15946; HY-19809; A857526; 4-Methyl-5-[(4-{[6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]amino}-1-piperidinyl)methyl]-1H-indole-2-carbonitrile; 4-methyl-5-[[4-[[6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]piperidin-1-yl]methyl]-1H
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
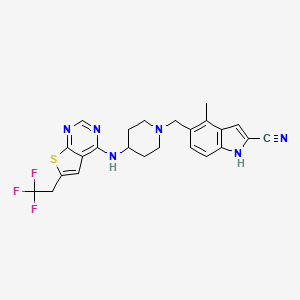 |
||||
| Formula |
C24H23F3N6S
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
4-methyl-5-[[4-[[6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]piperidin-1-yl]methyl]-1H-indole-2-carbonitrile
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(C=CC2=C1C=C(N2)C#N)CN3CCC(CC3)NC4=C5C=C(SC5=NC=N4)CC(F)(F)F
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C24H23F3N6S/c1-14-15(2-3-21-19(14)8-17(11-28)31-21)12-33-6-4-16(5-7-33)32-22-20-9-18(10-24(25,26)27)34-23(20)30-13-29-22/h2-3,8-9,13,16,31H,4-7,10,12H2,1H3,(H,29,30,32)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
DZACSLYTXLZAAF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer | ICD-11: 2C73 | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| In Vitro Model | OVCAR-8 cells | High grade ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1629 |
| OVCAR-3 cells | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| OVCAR-4 cells | Ovarian adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1627 | |
| A-549 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| Lu-99 cells | Lung giant cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3015 | |
| Lu-65 cells | Lung giant cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1392 | |
| PC-7 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_A786 | |
| BT-549 cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| MDA-MB-468 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0419 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF-7 cells | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0031 | |
| T-47D cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | |
| MIA PaCa-2 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| PANC-1 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| BxPC-3 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | |
| CFPAC-1 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | |
| Response regulation | The MI463 induced decrease in cell viability may be at least partly associated with the inhibition of SCD1 activity. In addition, the potent induction of HO1 contributed to the synergistic effects of MI463 plus auranofin. Therefore, meninMLL inhibitors, such as MI463, in combination with auranofin represent an effective therapeutic approach for several types of cancer via the induction of ferroptosis in High grade ovarian serous adenocarcinoma. | |||
