Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0174)
| Name |
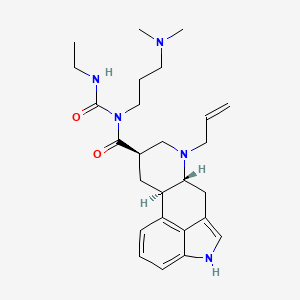
Cabergoline
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
cabergoline; 81409-90-7; Dostinex; Cabaser; Cabergolinum [Latin]; Cabergolina [Spanish]; Cabergolinum; Cabergolina; FCE-21336; FCE 21336; Velactis; C26H37N5O2; 1-((6-Allylergolin-8beta-yl)carbonyl)-1-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-3-ethylurea; Cabaseril; CHEBI:3286; LL60K9J05T; DTXSID6022719; 1-[(6-allylergoline-8beta-yl)carbonyl]-1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-ethylurea; 1-ethyl-3-(3'-dimethylamionpropyl)-2-(6'-allylergoline-8'beta-carbonyl)urea; (8R)-6-allyl-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)ergoline-8-carboxamide; (6aR,9R,10aR)-7-allyl-N-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-4,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide; (8beta)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-6-(2-propenyl)-ergoline-8-carboxamide; DTXCID502719; Sogilen; Dostinex (TN); 1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-ethyl-1-{[(2R,4R,7R)-6-(prop-2-en-1-yl)-6,11-diazatetracyclo[7.6.1.0^{2,7}.0^{12,16}]hexadeca-1(16),9,12,14-tetraen-4-yl]carbonyl}urea; Cabaser (TN); CAS-81409-90-7; SR-05000001493; BRN 6020775; UNII-LL60K9J05T; Caberlin; 1-[(6-allylergolin-8beta-yl)carbonyl]-1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-ethylurea; NCGC00167821-01; Cabergoline [USAN:USP:INN:BAN]; CG-101; MFCD00867887; CABERGOLINE [MI]; CABERGOLINE [INN]; CABERGOLINE [JAN]; CABERGOLINE [USAN]; GTPL37; CABERGOLINE [VANDF]; CABERGOLINE [MART.]; SCHEMBL42292; CABERGOLINE [USP-RS]; CABERGOLINE [WHO-DD]; BIDD:GT0775; Cabergoline (JAN/USP/INN); CHEMBL1201087; Cabergoline, >=98% (HPLC); CABERGOLINE [ORANGE BOOK]; KORNTPPJEAJQIU-KJXAQDMKSA-N; CABERGOLINE [EP MONOGRAPH]; HMS2090A09; HMS3886H05; CABERGOLINE [USP MONOGRAPH]; Tox21_112589; BDBM50426497; s5842; 1-Ethyl-3-(3'-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-(6'-allylergoline-8'beta-carbonyl)urea; AKOS015961587; Tox21_112589_1; DB00248; FCE-21336FCE-21336; CABERGOLINE [EMA EPAR VETERINARY]; NCGC00344544-01; (8beta)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-6-(prop-2-en-1-yl)ergoline-8-carboxamide; (8beta)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-6-prop-2-en-1-ylergoline-8-carboxamide; AC-26126; Ergoline-8-carboxamide, N-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-N-((ethylamino)carbonyl)-6-(2-propenyl)-, (8-beta)-; Ergoline-8beta-carboxamide, N-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-N-((ethylamino)carbonyl)-6-(2-propenyl)-; HY-15296; MS-28208; Cabergoline 1000 microg/mL in Acetonitrile; C08187; D00987; F17353; AB01275484-01; EN300-19767804; Q423308; SR-05000001493-1; SR-05000001493-2; BRD-K86882815-001-01-6; Cabergoline, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Cabergoline, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; ETHYL4-METHYL-2-PYRIDIN-3-YL-1,3-THIAZOLE-5-CARBOXYLATE; 6-allyl-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-ergoline-8beta-carboxamide; N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-6-allyl-ergoline-8beta-carboxamide; (6aR,9R,10aR)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-7-prop-2-enyl-6,6a,8,9,10,10a-hexahydro-4H-indolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide; (9R,10aR)-7-allyl-N-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-4,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide; 1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-ethyl-1-[(2R,4R,7R)-6-(prop-2-en-1-yl)-6,11-diazatetracyclo[7.6.1.0^{2,7}.0^{12,16}]hexadeca-1(15),9,12(16),13-tetraene-4-carbonyl]urea; Cabergoline; 1-Ethyl-3-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-[[(6aR,9R,10aR)-7-(prop-2-enyl)-4,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinolin-9-yl]carbonyl]urea; ERGOLINE-8.BETA.-CARBOXAMIDE, N-(3-(DIMETHYLAMINO)PROPYL)-N-((ETHYLAMINO)CARBONYL)-6-(2-PROPENYL)-
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
 |
||||
| Formula |
C26H37N5O2
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
(6aR,9R,10aR)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-7-prop-2-enyl-6,6a,8,9,10,10a-hexahydro-4H-indolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CCNC(=O)N(CCCN(C)C)C(=O)C1CC2C(CC3=CNC4=CC=CC2=C34)N(C1)CC=C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C26H37N5O2/c1-5-11-30-17-19(25(32)31(26(33)27-6-2)13-8-12-29(3)4)14-21-20-9-7-10-22-24(20)18(16-28-22)15-23(21)30/h5,7,9-10,16,19,21,23,28H,1,6,8,11-15,17H2,2-4H3,(H,27,33)/t19-,21-,23-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
KORNTPPJEAJQIU-KJXAQDMKSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Prolactinoma | ICD-11: 2F37 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | CircOMA1 (circRNA) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | MMQ cells | Pituitary gland neoplasm | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_2117 | |
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
All animal studies were performed in the Laboratory Animal Center of Sun Yat-sen University and conducted in accordance with the institutional policies for animal care. Approximately 5 x 106 MMQ_vector cells or MMQ_circOMA1 cells in 150 uL were injected into the right flank of BALB/c nude mice (total of 12 female mice, 4-6 weeks, SCXK2021-0029). After tumor formation (10 days), mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 3 mice/group) as follows: vector (saline solution, intraperitoneally injected), circOMA1 (saline solution, intraperitoneally injected), vector + CAB (0.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally injected), and circOMA1 + CAB (0.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally injected) in accordance with previous studies. CAB was injected intraperitoneally every 2 days for 14 days. The size of the tumor was measured every 3 days. On Day 15, mice were anesthetized with 0.3% pentobarbital sodium solution and then sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and the xenograft tumors were removed and weighed.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | GCLM was directly targeted by miR-145-5p and indirectly regulated by circOMA1. Importantly, circOMA1 induced ferroptosis resistance through the increased expression of Nrf2, GPX4, and FTH1, and circOMA1 attenuated cabergoline (CAB)-induced ferroptosis in MMQ cells in vivo and in vitro. circOMA1 may be a new therapeutic target for the individualized treatment of DA-resistant prolactinoma patients. | ||||
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Prolactinoma | ICD-11: 2F37 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | CircOMA1 (circRNA) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | MMQ cells | Pituitary gland neoplasm | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_2117 | |
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
All animal studies were performed in the Laboratory Animal Center of Sun Yat-sen University and conducted in accordance with the institutional policies for animal care. Approximately 5 x 106 MMQ_vector cells or MMQ_circOMA1 cells in 150 uL were injected into the right flank of BALB/c nude mice (total of 12 female mice, 4-6 weeks, SCXK2021-0029). After tumor formation (10 days), mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 3 mice/group) as follows: vector (saline solution, intraperitoneally injected), circOMA1 (saline solution, intraperitoneally injected), vector + CAB (0.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally injected), and circOMA1 + CAB (0.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally injected) in accordance with previous studies. CAB was injected intraperitoneally every 2 days for 14 days. The size of the tumor was measured every 3 days. On Day 15, mice were anesthetized with 0.3% pentobarbital sodium solution and then sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and the xenograft tumors were removed and weighed.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | GCLM was directly targeted by miR-145-5p and indirectly regulated by circOMA1. Importantly, circOMA1 induced ferroptosis resistance through the increased expression of Nrf2, GPX4, and FTH1, and circOMA1 attenuated cabergoline (CAB)-induced ferroptosis in MMQ cells in vivo and in vitro. circOMA1 may be a new therapeutic target for the individualized treatment of DA-resistant prolactinoma patients. | ||||
Glutamate--cysteine ligase regulatory subunit (GCLM)
| In total 2 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Prolactinoma | ICD-11: 2F37 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | hsa-miR-145-5p (miRNA) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | MMQ cells | Pituitary gland neoplasm | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_2117 | |
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
All animal studies were performed in the Laboratory Animal Center of Sun Yat-sen University and conducted in accordance with the institutional policies for animal care. Approximately 5 x 106 MMQ_vector cells or MMQ_circOMA1 cells in 150 uL were injected into the right flank of BALB/c nude mice (total of 12 female mice, 4-6 weeks, SCXK2021-0029). After tumor formation (10 days), mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 3 mice/group) as follows: vector (saline solution, intraperitoneally injected), circOMA1 (saline solution, intraperitoneally injected), vector + CAB (0.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally injected), and circOMA1 + CAB (0.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally injected) in accordance with previous studies. CAB was injected intraperitoneally every 2 days for 14 days. The size of the tumor was measured every 3 days. On Day 15, mice were anesthetized with 0.3% pentobarbital sodium solution and then sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and the xenograft tumors were removed and weighed.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | GCLM was directly targeted by miR-145-5p and indirectly regulated by circOMA1. Importantly, circOMA1 induced ferroptosis resistance through the increased expression of Nrf2, GPX4, and FTH1, and circOMA1 attenuated cabergoline (CAB)-induced ferroptosis in MMQ cells in vivo and in vitro. circOMA1 may be a new therapeutic target for the individualized treatment of DA-resistant prolactinoma patients. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Prolactinoma | ICD-11: 2F37 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | CircOMA1 (circRNA) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | MMQ cells | Pituitary gland neoplasm | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_2117 | |
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
All animal studies were performed in the Laboratory Animal Center of Sun Yat-sen University and conducted in accordance with the institutional policies for animal care. Approximately 5 x 106 MMQ_vector cells or MMQ_circOMA1 cells in 150 uL were injected into the right flank of BALB/c nude mice (total of 12 female mice, 4-6 weeks, SCXK2021-0029). After tumor formation (10 days), mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 3 mice/group) as follows: vector (saline solution, intraperitoneally injected), circOMA1 (saline solution, intraperitoneally injected), vector + CAB (0.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally injected), and circOMA1 + CAB (0.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally injected) in accordance with previous studies. CAB was injected intraperitoneally every 2 days for 14 days. The size of the tumor was measured every 3 days. On Day 15, mice were anesthetized with 0.3% pentobarbital sodium solution and then sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and the xenograft tumors were removed and weighed.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | GCLM was directly targeted by miR-145-5p and indirectly regulated by circOMA1. Importantly, circOMA1 induced ferroptosis resistance through the increased expression of Nrf2, GPX4, and FTH1, and circOMA1 attenuated cabergoline (CAB)-induced ferroptosis in MMQ cells in vivo and in vitro. circOMA1 may be a new therapeutic target for the individualized treatment of DA-resistant prolactinoma patients. | ||||
Ferritin heavy chain (FTH1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Prolactinoma | ICD-11: 2F37 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | CircOMA1 (circRNA) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | MMQ cells | Pituitary gland neoplasm | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_2117 | |
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
All animal studies were performed in the Laboratory Animal Center of Sun Yat-sen University and conducted in accordance with the institutional policies for animal care. Approximately 5 x 106 MMQ_vector cells or MMQ_circOMA1 cells in 150 uL were injected into the right flank of BALB/c nude mice (total of 12 female mice, 4-6 weeks, SCXK2021-0029). After tumor formation (10 days), mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 3 mice/group) as follows: vector (saline solution, intraperitoneally injected), circOMA1 (saline solution, intraperitoneally injected), vector + CAB (0.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally injected), and circOMA1 + CAB (0.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally injected) in accordance with previous studies. CAB was injected intraperitoneally every 2 days for 14 days. The size of the tumor was measured every 3 days. On Day 15, mice were anesthetized with 0.3% pentobarbital sodium solution and then sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and the xenograft tumors were removed and weighed.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | GCLM was directly targeted by miR-145-5p and indirectly regulated by circOMA1. Importantly, circOMA1 induced ferroptosis resistance through the increased expression of Nrf2, GPX4, and FTH1, and circOMA1 attenuated cabergoline (CAB)-induced ferroptosis in MMQ cells in vivo and in vitro. circOMA1 may be a new therapeutic target for the individualized treatment of DA-resistant prolactinoma patients. | ||||
