Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0124)
| Name |
Chrysin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
chrysin; 480-40-0; 5,7-Dihydroxyflavone; 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one; Chrysine; 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenylchromen-4-one; Crysin; 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-; NSC-407436; FLAVONE, 5,7-DIHYDROXY-; NSC 407436; Chrysinic acid; 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one; EINECS 207-549-7; UNII-3CN01F5ZJ5; 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-phenyl-chromen-4-one; BRN 0233276; 3CN01F5ZJ5; DTXSID1022396; CHEBI:75095; MFCD00006834; NSC407436; 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-benzo(b)pyran-4-one; CHEMBL117; DTXCID902396; 5-18-04-00076 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); CAS-480-40-0; 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-benzo[b]pyran-4-one; SMR000112318; 5,7-dihydroxy-flavone; SR-01000765660; 3ebo; 4des; 57D; Chrysin,(S); 5,7-diOH-Flavone; Flavone,7-dihydroxy-; Chrysin, 97%; Ois 3; Spectrum_000245; 5, 7-Dihydroxyflavone; CHRYSIN [INCI]; CHRYSIN [MI]; Prestwick0_000889; Prestwick1_000889; Prestwick2_000889; Prestwick3_000889; Spectrum2_000753; Spectrum3_001399; Spectrum4_000780; Spectrum5_001503; Chrysin, analytical standard; Oprea1_045160; SCHEMBL44474; BSPBio_000678; BSPBio_002514; BSPBio_003018; KBioGR_001200; KBioSS_000725; MLS000697728; MLS001074879; MLS006011841; BIDD:ER0484; DivK1c_000614; SPECTRUM1500709; SPECTRUM1505144; SPBio_000766; SPBio_002897; BDBM7461; BPBio1_000746; GTPL8789; MEGxp0_001416; ACon1_000087; cid_5281607; HMS501O16; KBio1_000614; KBio2_000725; KBio2_003293; KBio2_005861; KBio3_002238; NINDS_000614; HMS1570B20; HMS1921E20; HMS2097B20; HMS2268I23; HMS3468N08; HMS3655L20; BCP22863; Tox21_302335; BBL010449; CCG-40148; LMPK12110189; NSC818102; s2281; STK801609; AKOS000275936; BCP9000172; CS-7531; DB15581; GS-0927; NSC-818102; SDCCGMLS-0066586.P001; IDI1_000614; SMP1_000070; NCGC00016456-01; NCGC00016456-02; NCGC00016456-03; NCGC00016456-04; NCGC00016456-05; NCGC00016456-06; NCGC00016456-07; NCGC00016456-08; NCGC00016456-09; NCGC00016456-10; NCGC00016456-12; NCGC00094842-01; NCGC00094842-02; NCGC00094842-03; NCGC00094842-04; NCGC00094842-05; NCGC00168807-01; NCGC00168807-02; NCGC00168807-03; NCGC00168807-04; NCGC00255307-01; AC-10052; HY-14589; NCI60_003886; SY050125; AB00513947; C1652; FT-0619846; FT-0686390; SW197197-2; 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one #; 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-; C-5980; EN300-303044; S00112; Chrysin 1000 microg/mL in Acetonitrile:Methanol; A827426; Q973741; SR-01000765660-3; SR-01000765660-4; 34B3B4AD-EEDD-4943-A1C6-8857D2FAA8E0; 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one, 9CI; BRD-K22861715-001-07-5; BRD-K22861715-001-12-5; Z1824566175
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Investigative
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
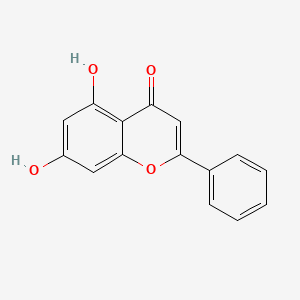 |
||||
| Formula |
C15H10O4
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenylchromen-4-one
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=CC(=O)C3=C(C=C(C=C3O2)O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C15H10O4/c16-10-6-11(17)15-12(18)8-13(19-14(15)7-10)9-4-2-1-3-5-9/h1-8,16-17H
|
||||
| InChIKey |
RTIXKCRFFJGDFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Ferritin heavy chain (FTH1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer | ICD-11: 2C10 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Carbonyl reductase [NADPH] 1 (CBR1) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| In Vitro Model | PANC-1 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | |
| Capan-2 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0026 | ||
| BxPC-3 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0186 | ||
| AsPC-1 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0152 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Male BALB/c nude mice (5 weeks old, weighing 18-20 g) were provided by Jiangsu Jicui Yaokang Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China). The mice were subcutaneously transplanted with non-targeting shRNA (shcontrol) or CBR1-targeting shRNA (shCBR1)-transfected PANC-1 cells (200 uL, 1 x 107 cells). Tumor volumes and body weights were measured every 4 days (n = 4, each), tumor volume = 0.5 x (a x a x b) (a, smallest diameter; b, largest diameter). The mice were subcutaneously inoculated with PANC-1 cells (200 uL, 1 x 107 cells) in the combination treatment. When the tumor volume reached 80-100 mm3, the mice were treated with chrysin (30 mg/kg/i.P., daily), gemcitabine (20 mg/kg/i.p., once every other day), or in combination for four weeks.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Inhibition of CBR1 by chrysin increased cellular ROS levels and led to ROS-dependent autophagy, which resulted in the degradation of ferritin heavy polypeptide 1 (FTH1) and an increase in the intracellular free iron level that participates in ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer (PC) cells. Finally, chrysin enhanced PC sensitivity to gemcitabine by inducing ferroptotic death in vitro and in vivo.? | ||||
Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cerebral ischemia | ICD-11: 8B10 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Male SD rats were randomly divided into a sham group, a model group, high-, medium-, and low-dose chrysin groups (200, 100, and 50 mg/kg), and a positive drug group (Ginaton, 21.6 mg/kg). The CIRI model was induced in rats by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO). The indexes were evaluated and the samples were taken 24 h after the operation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | The chrysin groups showed reduced content of total iron, lipid peroxide, and malondialdehyde in brain tissues and serum, increased mRNA and protein expression levels of SLC7A11 and GPX4, and decreased mRNA and protein expression levels of TFR1, PTGS2, and ACSL4. Chrysin may regulate iron metabolism via regulating the related targets of ferroptosis and inhibit neuronal ferroptosis induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. | ||||
Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 (PTGS2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cerebral ischemia | ICD-11: 8B10 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Male SD rats were randomly divided into a sham group, a model group, high-, medium-, and low-dose chrysin groups (200, 100, and 50 mg/kg), and a positive drug group (Ginaton, 21.6 mg/kg). The CIRI model was induced in rats by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO). The indexes were evaluated and the samples were taken 24 h after the operation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | The chrysin groups showed reduced content of total iron, lipid peroxide, and malondialdehyde in brain tissues and serum, increased mRNA and protein expression levels of SLC7A11 and GPX4, and decreased mRNA and protein expression levels of TFR1, PTGS2, and ACSL4. Chrysin may regulate iron metabolism via regulating the related targets of ferroptosis and inhibit neuronal ferroptosis induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. | ||||
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cerebral ischemia | ICD-11: 8B10 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Male SD rats were randomly divided into a sham group, a model group, high-, medium-, and low-dose chrysin groups (200, 100, and 50 mg/kg), and a positive drug group (Ginaton, 21.6 mg/kg). The CIRI model was induced in rats by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO). The indexes were evaluated and the samples were taken 24 h after the operation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | The chrysin groups showed reduced content of total iron, lipid peroxide, and malondialdehyde in brain tissues and serum, increased mRNA and protein expression levels of SLC7A11 and GPX4, and decreased mRNA and protein expression levels of TFR1, PTGS2, and ACSL4. Chrysin may regulate iron metabolism via regulating the related targets of ferroptosis and inhibit neuronal ferroptosis induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. | ||||
Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 4 (ACSL4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cerebral ischemia | ICD-11: 8B10 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Male SD rats were randomly divided into a sham group, a model group, high-, medium-, and low-dose chrysin groups (200, 100, and 50 mg/kg), and a positive drug group (Ginaton, 21.6 mg/kg). The CIRI model was induced in rats by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO). The indexes were evaluated and the samples were taken 24 h after the operation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | The chrysin groups showed reduced content of total iron, lipid peroxide, and malondialdehyde in brain tissues and serum, increased mRNA and protein expression levels of SLC7A11 and GPX4, and decreased mRNA and protein expression levels of TFR1, PTGS2, and ACSL4. Chrysin may regulate iron metabolism via regulating the related targets of ferroptosis and inhibit neuronal ferroptosis induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. | ||||
Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cerebral ischemia | ICD-11: 8B10 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Male SD rats were randomly divided into a sham group, a model group, high-, medium-, and low-dose chrysin groups (200, 100, and 50 mg/kg), and a positive drug group (Ginaton, 21.6 mg/kg). The CIRI model was induced in rats by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO). The indexes were evaluated and the samples were taken 24 h after the operation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | The chrysin groups showed reduced content of total iron, lipid peroxide, and malondialdehyde in brain tissues and serum, increased mRNA and protein expression levels of SLC7A11 and GPX4, and decreased mRNA and protein expression levels of TFR1, PTGS2, and ACSL4. Chrysin may regulate iron metabolism via regulating the related targets of ferroptosis and inhibit neuronal ferroptosis induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. | ||||
References
