Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0292)
| Name |
Apatinib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Apatinib; 811803-05-1; rivoceranib; Apatinib free base; N-(4-(1-Cyanocyclopentyl)phenyl)-2-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)nicotinamide; YN968D1; N-[4-(1-cyanocyclopentyl)phenyl]-2-(pyridin-4-ylmethylamino)pyridine-3-carboxamide; 5S371K6132; N-(4-(1-cyanocyclopentyl)phenyl)-2-(pyridin-4-ylmethylamino)nicotinamide; 3-Pyridinecarboxamide, N-(4-(1-cyanocyclopentyl)phenyl)-2-((4-pyridinylmethyl)amino)-; UNII-5S371K6132; apatinib (in China); RIVOCERANIB [INN]; Rivoceranib (USAN/INN); RIVOCERANIB [USAN]; RIVOCERANIB [WHO-DD]; GTPL7648; SCHEMBL1814966; CHEMBL3186534; Apatinib free base; YN-968D1; DTXSID601024366; AMY21302; BCP02840; EX-A1794; HY-13342A; MFCD21648511; NSC772886; NSC799333; s5248; AKOS024464453; CCG-268625; DB14765; DS-7455; NSC-772886; NSC-799333; SB16590; N-[4-(1-Cyanocyclopentyl)phenyl]-2-[(4-pyridinylmethyl)amino]-3-pyridinecarboxamide; NCGC00249393-01; NCGC00249393-08; AC-27461; BA175030; CS-0003200; C76598; D11288; AB01274807-01; AB01274807_02; Q27262801; N-[4-(1-Cyanocyclopentyl)phenyl]-2-[(4-pyridinylmethyl)amino]nicotinamide; N-[4-(1-Cyanocyclopentyl)phenyl]-2-[(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino]pyridine-3-carboxamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
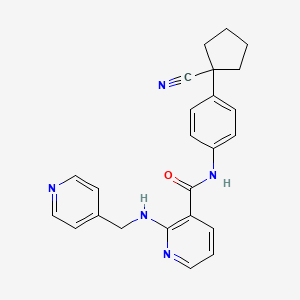 |
||||
| Formula |
C24H23N5O
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
N-[4-(1-cyanocyclopentyl)phenyl]-2-(pyridin-4-ylmethylamino)pyridine-3-carboxamide
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1CCC(C1)(C#N)C2=CC=C(C=C2)NC(=O)C3=C(N=CC=C3)NCC4=CC=NC=C4
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C24H23N5O/c25-17-24(11-1-2-12-24)19-5-7-20(8-6-19)29-23(30)21-4-3-13-27-22(21)28-16-18-9-14-26-15-10-18/h3-10,13-15H,1-2,11-12,16H2,(H,27,28)(H,29,30)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
WPEWQEMJFLWMLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 2 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Gastric cancer | ICD-11: 2B72 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBF1) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | MGC-803 cells | Gastric mucinous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5334 | |
| MKN45 cells | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0434 | ||
| BGC-823 cells | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3360 | ||
| SGC-7901 cells | Gastric carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0520 | ||
| AGS cells | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0139 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Female nude mice (BALB/c, nu/nu, 18-22 g, 4-5 weeks old) were obtained from Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal center, China, and maintained under specific pathogen-free conditions on a 12h/12h light/dark cycle. Each mouse was injected subcutaneously with eight million luciferase-expressing cells resuspended in 50 ul of PBS and 50 ul of Matrigel (BD Biosciences). When a palpable mass had developed, the mice were randomly divided into five groups: apatinib (50 mg/kg/day oral dose for 14 days); RSL3 (100 mg/kg injection of RSL3 twice per week for 2 weeks at the same site); both; apatinib (50 mg/kg/day oral dose for 14 days) plus vitamin E (100 mg/kg/day oral dose for 14 days); and vehicle (DMSO, 100 ul oral dose for 14 days).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Apatinib exerted antitumor effects against gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo through the induction of lipid peroxidation mediated by GPX4, then lead to ferroptosis. Furethermore, we found apatinib inhibited transcription of GPX4 via a SREBP1a-mediated pathway. These results indicated that GPX4 may be a potential target for anti-GC efficacy evaluation and treatment of apatinib. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [4] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer | ICD-11: 2C73 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 | |
| OVCAR-3 cells | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | ||
| Response regulation | Apatinib combined with olaparib-induced ferroptosis via a p53-dependent manner in ovarian cancer. Further studies showed that apatinib combined with olaparib-induced ferroptosis by inhibiting the expression of Nrf2 and autophagy, thereby inhibiting the expression of GPX4. The Nrf2 activator RTA408 and the autophagy activator rapamycin rescued the combination drug-induced ferroptosis. | ||||
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 4 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma | ICD-11: 2A00 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (KDR) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Pathways in cancer | hsa05200 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | U87 MG-Red-Fluc cells | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5J12 | |
| U-251MG cells | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0021 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Female BALB/c nude mice (age, 4 weeks old) were purchased from Changzhou Cavens Experimental Animal Co., Ltd. (Changzhou, China).The gliomas from the nude mice were fixed in 10% paraformaldehyde at 4 for 12 h and then dehydrated in different concentrations of ethanol. The tumor tissues were permeabilized using xylene and embedded in paraffin. They were then sliced (0.5 um), rehydrated, and stained with HE at 4 for 10 min and sealed. For IHC assessment of Ki-67 in gliomas, the DAKO Envision system (Dako; Agilent Technologies, Inc.) was used.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Apatinib could restrain proliferation of glioma cells through induction of ferroptosis via inhibiting the activation of VEGFR2/Nrf2/Keap1 pathway. Overexpression of Nrf2 could counteract the induction of ferroptosis by apatinib. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma | ICD-11: 2A00 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Pathways in cancer | hsa05200 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | U87 MG-Red-Fluc cells | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5J12 | |
| U-251MG cells | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0021 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Female BALB/c nude mice (age, 4 weeks old) were purchased from Changzhou Cavens Experimental Animal Co., Ltd. (Changzhou, China).The gliomas from the nude mice were fixed in 10% paraformaldehyde at 4 for 12 h and then dehydrated in different concentrations of ethanol. The tumor tissues were permeabilized using xylene and embedded in paraffin. They were then sliced (0.5 um), rehydrated, and stained with HE at 4 for 10 min and sealed. For IHC assessment of Ki-67 in gliomas, the DAKO Envision system (Dako; Agilent Technologies, Inc.) was used.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Apatinib could restrain proliferation of glioma cells through induction of ferroptosis via inhibiting the activation of VEGFR2/Nrf2/ Keap1 pathway. Overexpression of Nrf2 could counteract the induction of ferroptosis by apatinib. | ||||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Glioblastoma | ICD-11: 2A00 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Pathways in cancer | hsa05200 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | U87 MG-Red-Fluc cells | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5J12 | |
| U-251MG cells | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0021 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Female BALB/c nude mice (age, 4 weeks old) were purchased from Changzhou Cavens Experimental Animal Co., Ltd. (Changzhou, China).The gliomas from the nude mice were fixed in 10% paraformaldehyde at 4 for 12 h and then dehydrated in different concentrations of ethanol. The tumor tissues were permeabilized using xylene and embedded in paraffin. They were then sliced (0.5 um), rehydrated, and stained with HE at 4 for 10 min and sealed. For IHC assessment of Ki-67 in gliomas, the DAKO Envision system (Dako; Agilent Technologies, Inc.) was used.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Apatinib could restrain proliferation of glioma cells through induction of ferroptosis via inhibiting the activation of VEGFR2/Nrf2/Keap1 pathway. Overexpression of Nrf2 could counteract the induction of ferroptosis by apatinib. | ||||
| Experiment 4 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [4] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer | ICD-11: 2C73 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 | |
| OVCAR-3 cells | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | ||
| Response regulation | Apatinib combined with olaparib-induced ferroptosis via a p53-dependent manner in ovarian cancer. Further studies showed that apatinib combined with olaparib-induced ferroptosis by inhibiting the expression of Nrf2 and autophagy, thereby inhibiting the expression of GPX4. The Nrf2 activator RTA408 and the autophagy activator rapamycin rescued the combination drug-induced ferroptosis. | ||||
Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 4 (ACSL4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [3] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Elongation of very long chain fatty acids protein 6 (ELOVL6) | Suppressor | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HCT 116 cells | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| HIEC-6 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6C21 | |
| Response regulation | ACSL4, a vital regulator of ferroptosis, could interact with ELOVL6 directly. Apatinib promoted ferroptosis in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells by targeting ELOVL6/ACSL4, providing a new mechanism support for apatinib application in the clinical treatment of CRC. | |||
Unspecific Target
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [4] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer | ICD-11: 2C73 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53) | Driver | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 |
| OVCAR-3 cells | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| Response regulation | Apatinib combined with olaparib-induced ferroptosis via a p53-dependent manner in ovarian cancer. Further studies showed that apatinib combined with olaparib-induced ferroptosis by inhibiting the expression of Nrf2 and autophagy, thereby inhibiting the expression of GPX4. The Nrf2 activator RTA408 and the autophagy activator rapamycin rescued the combination drug-induced ferroptosis. | |||
References
