Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0269)
| Name |
Astragaloside IV
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Astragaloside IV; 84687-43-4; Astragaloside A; Cyclosiversioside F; Astrasieversianin XIV; 1J6XA9YCFV; CHEBI:65457; 83207-58-3; (2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[[(1S,3R,6S,8R,9S,11S,12S,14S,15R,16R)-14-hydroxy-15-[(2R,5S)-5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyloxolan-2-yl]-7,7,12,16-tetramethyl-6-[(2S,3R,4S,5R)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-9-pentacyclo[9.7.0.01,3.03,8.012,16]octadecanyl]oxy]-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol; AS-IV; (2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[[(1S,3R,8R,9S,11S,12S,14S,15R,16R)-14-Hydroxy-15-[(2R,5S)-5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyloxolan-2-yl]-7,7,12,16-tetramethyl-6-[(2S,3R,4S,5R)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-9-pentacyclo[9.7.0.01,3.03,8.012,16]octadecanyl]oxy]-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol; AstragalosideIV; 3-O-beta-D-xylopyranosyl-6-O-beta-D-glucopyranosylcycloastragenol; C41H68O14; AST-IV; Astramembrannin I;Astragalin A; UNII-1J6XA9YCFV; beta-D-Glucopyranoside, (3beta,6alpha,16beta,20R,24S)-20,24-epoxy-16,25-dihydroxy-3-(beta-D-xylopyranosyloxy)-9,19-cyclolanostan-6-yl; Cyclosieversioside F; Astragaloside IV 95%; ASTRAVERSIANIN XIV; Astragaloside IV, >98.0%; CHEMBL3121562; SCHEMBL21888259; ASTRAGALOSIDE IV [USP-RS]; DTXSID801026063; HMS3885E12; HY-N0431; MFCD16036240; s3901; AKOS025311424; CCG-270470; AS-19402; C17799; Q27133900; ASTRAGALOSIDE IV (CONSTITUENT OF ASTRAGALUS) [DSC]; Astragaloside IV, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Astragaloside IV, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; (2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-(((2aR,3R,4S,5aS,5bS,7S,7aR,9S,11aR,12aS)-4-hydroxy-3-((2R,5S)-5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-2a,5a,8,8-tetramethyl-9-(((2S,3R,4S,5R)-3,4,5-trihydroxytetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)tetradecahydro-1H,12H-cyclopenta[a]cyclopropa[e]phenanthren-7-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol; .BETA.-D-GLUCOPYRANOSIDE, (3.BETA.,6.ALPHA.,16.BETA.,20R,24S)-20,24-EPOXY-16,25-DIHYDROXY-3-(.BETA.-D-XYLOPYRANOSYLOXY)-9,19-CYCLOLANOSTAN-6-YL
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Investigative
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
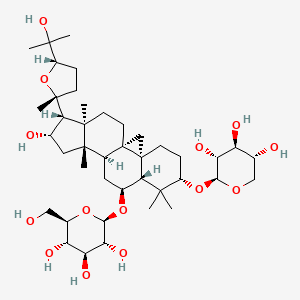 |
||||
|
3D MOL
|
|||||
| Formula |
C41H68O14
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[[(1S,3R,6S,8R,9S,11S,12S,14S,15R,16R)-14-hydroxy-15-[(2R,5S)-5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyloxolan-2-yl]-7,7,12,16-tetramethyl-6-[(2S,3R,4S,5R)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-9-pentacyclo[9.7.0.01,3.03,8.012,16]octadecanyl]oxy]-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1(C(CCC23C1C(CC4C2(C3)CCC5(C4(CC(C5C6(CCC(O6)C(C)(C)O)C)O)C)C)OC7C(C(C(C(O7)CO)O)O)O)OC8C(C(C(CO8)O)O)O)C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C41H68O14/c1-35(2)24(54-33-29(48)26(45)20(44)17-51-33)9-11-41-18-40(41)13-12-37(5)31(39(7)10-8-25(55-39)36(3,4)50)19(43)15-38(37,6)23(40)14-21(32(35)41)52-34-30(49)28(47)27(46)22(16-42)53-34/h19-34,42-50H,8-18H2,1-7H3/t19-,20+,21-,22+,23-,24-,25-,26-,27+,28-,29+,30+,31-,32-,33-,34+,37+,38-,39+,40-,41+/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
QMNWISYXSJWHRY-YLNUDOOFSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 10 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Subarachnoid Hemorrhage | ICD-11: 8B01 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
SAH model was constructed by applying endovascular perforation in the rats, according to the protocol introduced in a previous study (Wei et al., 2020), except for slight modifications. Briefly, after performing intraperitoneal anesthesia with 40 mg/kg sodium pentobarbital, the right common carotid, external and internal carotid arteries of the rats were exposed and isolated. The right external carotid artery was ligated, and a 4-0 single-strand nylon thread was used to insert the right internal carotid artery through the stump of the external carotid artery and the bifurcation of the common carotid artery. When resistance is felt when the suture enters the intracranial segment, proceed approximately 3 mm to penetrate internal carotid artery at the bifurcation of middle cerebral artery. The suture was held in this position for 10 s and was then withdrawn. The rats in the Sham group went through an identical procedure, without the suture at the point of resistance. Throughout the experiment, the body temperature of the rats was sustained at around 37 by using a thermal blanket. After the wounds were sutured, the rats were placed in a separate cage and neurological function was closely observed.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) triggered Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and alleviated ferroptosis due to the induction of subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). The Nrf2 inhibitor ML385 blocked the beneficial effects of neuroprotection. Ferroptosis is profoundly implicated in facilitating EBI in SAH, and that AS-IV thwarts the process of ferroptosis in SAH by activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. The liberation of Nrf2 from Keap1, its cytoplasmic repressor will provoke Nrf2 accumulation in the nucleus. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cerebral ischemia | ICD-11: 8B10 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Sequestosome-1 (SQSTM1) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | SH-SY5Y cells | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0019 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Rats were randomly divided into the Sham, middle cerebral artery occlusion-reperfusion (MCAO/R), and MCAO/R + AST IV (28 mg/kg) groups. The MCAO/R + AST IV group was intragastrically injected with 10 mL/kg AST IV at 50, 26, and 2 h before modelling (Xiao et al., 2021). The Sham and MCAO/R groups received equal amounts of normal saline. As described previously, the modified Longa method (Longa et al., 1989) was used to establish the MCAO/R model. After anaesthesia with 2%sodium pentobarbital, the left common carotid artery(CCA), the external carotid artery(ECA), and the internal carotid artery(ICA) were isolated. The distal end of the ECA was ligated, a small incision was made at the stump of the ECA, and a suture (Batch number: 2636A2, Beijing Seinong Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China; head-end diameter: 0.36 ± 0.02 mm) was inserted into the ICA from the ECA through the bifurcation of the CCA. To achieve cerebral ischaemia, the head-end was used to block blood flow in the middle cerebral artery until the intracranial segment of the ICA was inserted. The suture was removed after 2 h, and follow-up experiments were performed 24 h after reperfusion. In the Sham group, the CCA, ECA, and ICA were exposed and separated, but no sutures were inserted. Penicillin powder was used to fight infection after operation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV (AST IV) increased the P62 (SQSTM1) and Nrf2 levels and decreased the Keap1 levels. P62 silencing reduced the effects of AST IV on the P62/Keap1/Nrf2 pathway and ferroptosis. Our findings suggest that AST IV mitigates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via activation of the P62/Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. | ||||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cerebral ischemia | ICD-11: 8B10 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | SH-SY5Y cells | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0019 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Rats were randomly divided into the Sham, middle cerebral artery occlusion-reperfusion (MCAO/R), and MCAO/R + AST IV (28 mg/kg) groups. The MCAO/R + AST IV group was intragastrically injected with 10 mL/kg AST IV at 50, 26, and 2 h before modelling (Xiao et al., 2021). The Sham and MCAO/R groups received equal amounts of normal saline. As described previously, the modified Longa method (Longa et al., 1989) was used to establish the MCAO/R model. After anaesthesia with 2%sodium pentobarbital, the left common carotid artery(CCA), the external carotid artery(ECA), and the internal carotid artery(ICA) were isolated. The distal end of the ECA was ligated, a small incision was made at the stump of the ECA, and a suture (Batch number: 2636A2, Beijing Seinong Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China; head-end diameter: 0.36 ± 0.02 mm) was inserted into the ICA from the ECA through the bifurcation of the CCA. To achieve cerebral ischaemia, the head-end was used to block blood flow in the middle cerebral artery until the intracranial segment of the ICA was inserted. The suture was removed after 2 h, and follow-up experiments were performed 24 h after reperfusion. In the Sham group, the CCA, ECA, and ICA were exposed and separated, but no sutures were inserted. Penicillin powder was used to fight infection after operation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV (AST IV) increased the P62 (SQSTM1) and Nrf2 levels and decreased the Keap1 levels. P62 silencing reduced the effects of AST IV on the P62/ Keap1/Nrf2 pathway and ferroptosis. Our findings suggest that AST IV mitigates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via activation of the P62/ Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. | ||||
| Experiment 4 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [3] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Retinopathy | ICD-11: 9B71 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | hsa-miR-138-5p (miRNA) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | ARPE-19 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0145 | |
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) inhibited miR-138-5p expression, subsequently increasing Sirt1/Nrf2 activity and cellular antioxidant capacity to alleviate ferroptosis, resulting decreased cell death, which potentially inhibits the diabetic retinopathy pathological process. | ||||
| Experiment 5 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [3] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Retinopathy | ICD-11: 9B71 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | ARPE-19 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0145 | |
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) inhibited miR-138-5p expression, subsequently increasing Sirt1/Nrf2 activity and cellular antioxidant capacity to alleviate ferroptosis, resulting decreased cell death, which potentially inhibits the diabetic retinopathy pathological process. | ||||
| Experiment 6 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [8] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cerebral ischemia | ICD-11: 8B10 | |||
| Pathway Response | Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Rats were randomly assigned to six groups: (1) the sham group, (2) the middle cerebral artery ischaemia-occlusion-reperfusion (MCAO/R) group, (3) the AST IV group, (4) the PNS group, (5) the combination group and (6) the combination + brusatol group. One hundred rats were used in the experiment, of which 9 died during surgery, 10 died of intracranial haemorrhage and brain injury and 63 rats were successfully modelled, for a final success rate of 76.8%. Each group included 9 rats. Behavioural testing was performed on 5 animals in each group. After behavioural testing, 3 rats were used for TTC staining and 6 were used for kit detection and western blot analysis. Existing studies have revealed the toxicological effects of the compatibility of astragalus and P. notoginseng. The dosage and method of AST IV (28 mg/kg) and PNS (80 mg/kg) alone or in combination have been previously determined and were administered intragastrically for three consecutive days (10 ml/kg each time), and the optimal administration times were 50, 26 and 2 h before model establishment.Brusatol (1 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally for 1 h prior to modelling. The sham group and the MCAO/R group were given the same amount of saline.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Combining Astragaloside IV and Panax notoginseng saponins attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating Nrf2 to inhibit ferroptosis and inflammatory responses. | ||||
| Experiment 7 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [9] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cerebral ischaemic stroke | ICD-11: 8B11 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
1% sodium pentobarbital (40 mg/kg) was administered to the rats intraperitoneally to anesthetize them before placing them in a brain stereotaxic device. An incision was created in the midline of the neck to expose the common internal and external carotid arteries. After ligating and cutting the external carotid artery on the left side, a 3-mm stump was exposed. We then perforated the carotid artery at the bifurcation of the middle and anterior cerebral arteries utilizing an 18-20-mm-long surgical filament (0.26 mm diameter; Beijing Cinontech Co. Ltd., China) was threaded through the external carotid artery stump into the internal carotid artery and left in situ for 120 min. After that, the filament was withdrawn to facilitate reperfusion. Rats in the sham surgery group received the identical procedure as the other rats but without filament insertion.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) administration decreased the infarct volume, brain edema, neurological deficits, and inflammatory cytokines TNF-, interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, and NF-B, increased the levels of SLC7A11 and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), decreased lipid reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, and prevented neuronal ferroptosis. Meanwhile, AS-IV triggered the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and alleviated ferroptosis due to the induction of stroke. | ||||
| Experiment 8 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [10] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cardiomyopathy | ICD-11: BC43 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | rHTs (Rat hippocampal tissues) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
A total of 24 SD male rats weighing 200-210 g from the Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology Co., Ltd. were divided randomly into control, ADR, ADR+AsIV, and AsIV group (n = 6). AsIV was administered by gavage at a dose of 10 mg/kg/day over a period of five weeks. ADR was administered intraperitoneally once a week (30 mg/kg/week) for five weeks. Controls were administered saline intraperitoneally (i.p.) at the same dose as ADR and intragastrically at the same dose as AsIV.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Adriamycin (ADR) was found to promote cardiac ferroptosis, whereas administration of Astragaloside IV (AsIV) attenuated the process via activating Nrf2 signaling pathway and the subsequent GPX4 expression increasing. These results suggest that AsIV might play a protective role against ADR-induced myocardial fibrosis. | ||||
| Experiment 9 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [11] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Urinary system disease | ICD-11: GC2Z | |||
| Pathway Response | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HK-2 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0302 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Male SD rats (200 ± 10 g) were obtained from Beijing Vital River Company (Beijing, China). They were kept under 12-h light/dark cycles and allowed free access to food and water. Rats were randomly divided into CON, ADR, ADR + ASIV, and ASIV groups (n = 6). Rats in ADR and ADR + ASIV groups received four equal injections of ADR intraperitoneally (4 mg/kg) in 5 weeks. Rats in ASIV and ADR + ASIV groups intragastrically received ASIV (10 mg/kg, daily) for 5weeks, while rats in CON and ADR groups were administered the same dose of solvent as ADR. Finally, the rats were euthanized, and the bilateral kidneys were excised.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV increased the phosphorylation of Pi3K, Akt, and the expression of Nrf2 and glutathione peroxidase 4 compared to HK-2 cells stimulated by ADR. In conclusion, ferroptosis may involve in Adriamycin (ADR)-induced nephrotoxicity, and ASIV might protect nephrocytes against ADR-induced ferroptosis, perhaps via activations of the Pi3K/Akt and Nrf2 signaling pathways. | ||||
| Experiment 10 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [7] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Lung injury | ICD-11: NB32 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hT2AECs (Type II alveolar epithelial cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
The animals were randomly assigned to six groups (7 mice in each) as follows: (I) Normal saline (NS) group, (II) Ast-IV 100 mg/kg (Ast) group, (III) PM2.5 group, (IV) Ast-IV 50 mg/kg + PM2.5 (Ast-L) group, (V) Ast 100 mg/kg + PM2.5 (Ast-H) group, and (VI) Ast-IV 100 mg/kg + erastin 20 mg/kg + PM2.5 (Era) group. Based on our previous results, this study adopted anintraperitoneal injection(i.p.) of Ast-IV (dissolved in normal saline containing 0.1% DMSO for preventive treatment. After all the mice were adaptively fed for 5 days, in the NS and PM2.5 groups, mice received the normal saline containing 0.1% DMSO viai.p.once a day for the next three consecutive days. Similar to the NS group, in the Ast, Ast-H, and Era groups, mice received Ast-IV (100 mg/kg) viai.p. Ast-L group received Ast-IV (50 mg/kg) viai.p. To evaluate the effect of Ast-IV on ferroptosis in PM2.5-induced lung injury, we used the ferroptosis agonist erastin to activate ferroptosisin vivo. In the Era group, mice received erastin (20 mg/kg, 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5%Tween80 + 45% normal saline) 30 min before each preventive treatment of Ast-IV.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV (Ast-IV) reduced the lung wet-dry ratio and the levels of interleukin 6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor- (TNF-) and interleukin 1 (IL-1) in serum. Ast-IV could also improve the oxidative stress level in BALF, restore the GSH level in the lung tissue, and reduce the iron content in the lung tissue. Western blot outcomes revealed that Ast-IV regulated the ferroptosis signaling pathway via the Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis to protect PM2.5-mediated lung injury. | ||||
Unspecific Target
| In total 2 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [4] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cardiomyopathy | ICD-11: BC43 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Platelet glycoprotein 4 (CD36) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | CHO-S/H9C2 cells | Normal | Cricetulus griseus | CVCL_A0TS | |
| In Vivo Model |
Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (160-180 g) were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine. After 1 week of acclimatization, the rats were randomly divided into two groups: the control group (standard diet,n = 6) and the high-fat diet (HFD) group. The control group was given a standard diet for 8 weeks, and the HFD group was given a high-fat diet (feed item No. D12451, Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center) for 8 weeks. Subsequently, intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (STZ, 40 mg/kg) was performed in the HFD group for inducing diabetic symptoms, and an equal volume of saline was given to the control group. A diabetes model was successfully established under the condition that the fasting blood glucose levels were > 16.7 mmol/L over three consecutive days. Diabetic rats in the HFD group were divided into five groups: a DCM group, three AS-IV treatment groups (20, 40, and 80 mg/kg/day by gavage,n = 6), and an atorvastatin treatment group (ALE group, used as a positive control drug, 10 mg/kg, by gavage,n = 6). Rats were given the standard diet during drug gavage. After 12 weeks of treatment, all animals were anesthetized and then euthanized by intraperitoneal injection with an overdose of pentobarbital sodium. The animal experiments in this study were randomized and single-blind.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV decreased cardiomyocyte injury and myocardial dysfunction by inhibiting ferroptosis mediated by CD36 in diabetic cardiomyopathy rats. Therefore, AS-IV regulated the lipid metabolism of cardiomyocytes and inhibited cellular ferroptosis, which may have potential clinical value in DCM treatment. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [5] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Spinal cord injury | ICD-11: ND51 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Transcription factor EB (TFEB) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | PC12 cells | Adrenal gland pheochromocytoma | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0481 | |
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV markedly accelerated proliferation, suppressed apoptosis, and reduced ROS and LDH accumulation. Furthermore, AS-IV enhanced TFEB expression in H2O2-damaged PC12 cells. The effects of AS-IV on spinal cord injury were inhibited by si-TFEB, and this inhibition was further reinforced by the addition of FIN56.The results of this investigation using the SCI cell model suggested that AS-IV alleviated SCI by promoting TFEB expression and subsequently mediating ferroptosis. | ||||
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 2 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [6] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cardiovascular diseases | ICD-11: BE2Z | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | HUVECs (Human umbilical vein endothelial cells) | ||||
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV partially upregulated the levels of SLC7A11 and GPX4 expression which were reduced by LPC. The LPC-suppressed proliferation and LPC-induced apoptosis and senescence of endothelial cells were greatly attenuated by AS-IV treatment. In conclusion, AS-IV could serve as a novel drug for treating ferroptosis-related cardiovascular diseases. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [7] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Lung injury | ICD-11: NB32 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hT2AECs (Type II alveolar epithelial cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
The animals were randomly assigned to six groups (7 mice in each) as follows: (I) Normal saline (NS) group, (II) Ast-IV 100 mg/kg (Ast) group, (III) PM2.5 group, (IV) Ast-IV 50 mg/kg + PM2.5 (Ast-L) group, (V) Ast 100 mg/kg + PM2.5 (Ast-H) group, and (VI) Ast-IV 100 mg/kg + erastin 20 mg/kg + PM2.5 (Era) group. Based on our previous results, this study adopted anintraperitoneal injection(i.p.) of Ast-IV (dissolved in normal saline containing 0.1% DMSO for preventive treatment. After all the mice were adaptively fed for 5 days, in the NS and PM2.5 groups, mice received the normal saline containing 0.1% DMSO viai.p.once a day for the next three consecutive days. Similar to the NS group, in the Ast, Ast-H, and Era groups, mice received Ast-IV (100 mg/kg) viai.p. Ast-L group received Ast-IV (50 mg/kg) viai.p. To evaluate the effect of Ast-IV on ferroptosis in PM2.5-induced lung injury, we used the ferroptosis agonist erastin to activate ferroptosisin vivo. In the Era group, mice received erastin (20 mg/kg, 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5%Tween80 + 45% normal saline) 30 min before each preventive treatment of Ast-IV.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV (Ast-IV) reduced the lung wet-dry ratio and the levels of interleukin 6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor- (TNF-) and interleukin 1 (IL-1) in serum. Ast-IV could also improve the oxidative stress level in BALF, restore the GSH level in the lung tissue, and reduce the iron content in the lung tissue. Western blot outcomes revealed that Ast-IV regulated the ferroptosis signaling pathway via the Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis to protect PM2.5-mediated lung injury. | ||||
Heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Subarachnoid Hemorrhage | ICD-11: 8B01 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
SAH model was constructed by applying endovascular perforation in the rats, according to the protocol introduced in a previous study (Wei et al., 2020), except for slight modifications. Briefly, after performing intraperitoneal anesthesia with 40 mg/kg sodium pentobarbital, the right common carotid, external and internal carotid arteries of the rats were exposed and isolated. The right external carotid artery was ligated, and a 4-0 single-strand nylon thread was used to insert the right internal carotid artery through the stump of the external carotid artery and the bifurcation of the common carotid artery. When resistance is felt when the suture enters the intracranial segment, proceed approximately 3 mm to penetrate internal carotid artery at the bifurcation of middle cerebral artery. The suture was held in this position for 10 s and was then withdrawn. The rats in the Sham group went through an identical procedure, without the suture at the point of resistance. Throughout the experiment, the body temperature of the rats was sustained at around 37 by using a thermal blanket. After the wounds were sutured, the rats were placed in a separate cage and neurological function was closely observed.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) triggered Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and alleviated ferroptosis due to the induction of subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). The Nrf2 inhibitor ML385 blocked the beneficial effects of neuroprotection. These results consistently suggest that ferroptosis is profoundly implicated in facilitating EBI in SAH, and that AS-IV thwarts the process of ferroptosis in SAH by activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [9] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cerebral ischaemic stroke | ICD-11: 8B11 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
1% sodium pentobarbital (40 mg/kg) was administered to the rats intraperitoneally to anesthetize them before placing them in a brain stereotaxic device. An incision was created in the midline of the neck to expose the common internal and external carotid arteries. After ligating and cutting the external carotid artery on the left side, a 3-mm stump was exposed. We then perforated the carotid artery at the bifurcation of the middle and anterior cerebral arteries utilizing an 18-20-mm-long surgical filament (0.26 mm diameter; Beijing Cinontech Co. Ltd., China) was threaded through the external carotid artery stump into the internal carotid artery and left in situ for 120 min. After that, the filament was withdrawn to facilitate reperfusion. Rats in the sham surgery group received the identical procedure as the other rats but without filament insertion.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) administration decreased the infarct volume, brain edema, neurological deficits, and inflammatory cytokines TNF-, interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, and NF-B, increased the levels of SLC7A11 and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), decreased lipid reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, and prevented neuronal ferroptosis. Meanwhile, AS-IV triggered the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and alleviated ferroptosis due to the induction of stroke. | ||||
Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)
| In total 2 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [6] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cardiovascular diseases | ICD-11: BE2Z | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | HUVECs (Human umbilical vein endothelial cells) | ||||
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV partially upregulated the levels of SLC7A11 and GPX4 expression which were reduced by LPC. The LPC-suppressed proliferation and LPC-induced apoptosis and senescence of endothelial cells were greatly attenuated by AS-IV treatment. In conclusion, AS-IV could serve as a novel drug for treating ferroptosis-related cardiovascular diseases. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [7] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Lung injury | ICD-11: NB32 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hT2AECs (Type II alveolar epithelial cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
The animals were randomly assigned to six groups (7 mice in each) as follows: (I) Normal saline (NS) group, (II) Ast-IV 100 mg/kg (Ast) group, (III) PM2.5 group, (IV) Ast-IV 50 mg/kg + PM2.5 (Ast-L) group, (V) Ast 100 mg/kg + PM2.5 (Ast-H) group, and (VI) Ast-IV 100 mg/kg + erastin 20 mg/kg + PM2.5 (Era) group. Based on our previous results, this study adopted anintraperitoneal injection(i.p.) of Ast-IV (dissolved in normal saline containing 0.1% DMSO for preventive treatment. After all the mice were adaptively fed for 5 days, in the NS and PM2.5 groups, mice received the normal saline containing 0.1% DMSO viai.p.once a day for the next three consecutive days. Similar to the NS group, in the Ast, Ast-H, and Era groups, mice received Ast-IV (100 mg/kg) viai.p. Ast-L group received Ast-IV (50 mg/kg) viai.p. To evaluate the effect of Ast-IV on ferroptosis in PM2.5-induced lung injury, we used the ferroptosis agonist erastin to activate ferroptosisin vivo. In the Era group, mice received erastin (20 mg/kg, 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5%Tween80 + 45% normal saline) 30 min before each preventive treatment of Ast-IV.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Astragaloside IV (Ast-IV) reduced the lung wet-dry ratio and the levels of interleukin 6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor- (TNF-) and interleukin 1 (IL-1) in serum. Ast-IV could also improve the oxidative stress level in BALF, restore the GSH level in the lung tissue, and reduce the iron content in the lung tissue. Western blot outcomes revealed that Ast-IV regulated the ferroptosis signaling pathway via the Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis to protect PM2.5-mediated lung injury. | ||||
References
