Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0072)
| Name |
Sodium arsenite
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
SODIUM ARSENITE; 7784-46-5; Sodium metaarsenite; Sodium dioxoarsenate; sodium;oxoarsinite; sodium meta-arsenite; Sodium (meta)arsenite; Arsenite, sodium; NaAsO2; Arsenious acid, sodium salt; Arsenious acid, monosodium salt; 48OVY2OC72; CHEBI:29678; Arsenenous acid, sodium salt (1:1); Prodalumnol; Sodanit; Penite; Kill-All; Prodalumnol double; Rat Death Liquid; Chem Pels C; Chem-Sen 56; Caswell No. 744; MFCD00003472; Sodium arsenenite; Atlas A; Arsenite de sodium; Arsenenous acid, sodium salt; Arsenite de sodium [French]; CCRIS 5554; HSDB 693; EINECS 232-070-5; EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 013603; UNII-48OVY2OC72; (NaAsO2)n; SODIUM META ARSENITE; SODIUM ARSENITE [MI]; SODIUM ARSENITE [HSDB]; 7784-46-5 (anhydrous); CHEMBL1909078; DTXSID5020104; Sodium (meta)arsenite, >=90%; SODIUM ARSENITE [WHO-DD]; AKOS025295751; Na(+)n-(-As(O(-))O-)-n; Sodium (meta)arsenite, p.a., 98.0%; Q419586
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
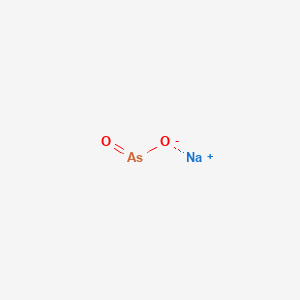
| Structure |
 |
||||
|
3D MOL
|
|||||
| Formula |
AsNaO2
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
sodium;oxoarsinite
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
[O-][As]=O.[Na+]
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/AsHO2.Na/c2-1-3;/h(H,2,3);/q;+1/p-1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
PTLRDCMBXHILCL-UHFFFAOYSA-M
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 4 (ACSL4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease | ICD-11: DB92 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Mitofusin-2 (MFN2) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | L-02 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (300 g-350 g, specific pathogen free) were obtained from Institute of Genome Engineered Animal Models for Human Disease of Dalian Medical University (Dalian, China). To explore the influence of NaAsO2 (CAS No.7784-46-5, Sigma-Aldrich, USA) on the liver, the rats were subjected to NaAsO2 at the dosage of 0, 2.5, and 5 mg/kg by gavage for 9 months. The control group was gavaged with distilled water as vehicle.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Arsenic induces rat liver nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and Ferroptosis via interacting between Mitofusin-2 with IRE1. NaAsO2 increases IRE1 and Mfn2 expression, subsequently led to upregulated ACSL4 expression and 5-HETE via the directly combination Mfn2 with IRE1, ultimately induced ferroptotic cell death. | ||||
Unspecific Target
| In total 3 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Hereditary Leiomyomatosis | ICD-11: 2C90 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3B {ECO:0000305} (MAP1LC3B) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| In Vitro Model | PC12 cells | Adrenal gland pheochromocytoma | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0481 | |
| In Vivo Model |
A total of thirty-two healthy specificpathogenfree C57BL/6J male mice at seven weeks of age and weighted 20-24 g were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of Chongqing Medical University. After administration of arsenite via drinking water, the animals were euthanized by pentobarbital sodium, three of the animals were subjected to the perfusion fixation, and subsequently, the hippocampus tissues were rapidly dissected on ice and immersed into 4% paraformaldehyde for pre-fixation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Arsenite was able to trigger ferroptosis in the adrenal gland pheochromocytoma cells. Arsenite significantly decreased the expressions of ferritin and NCOA4, but sharply enhanced the level of autophagy marker LC3B, suggesting the activation of ferritinophagy by arsenite. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [3] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic dysfunction | ICD-11: DC35 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Autophagy | |||||
| In Vitro Model | MIN6 cells | Insulinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0431 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Groups of 18 specific pathogen free (SPF) Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (300 g -350 g) obtained from Institute of Genome Engineered Animal Models for Human Disease of Dalian Medical University (China). The rats were divided randomly into 3 groups, control, low-dose of NaAsO2 (2.5 mg/kg) and high-dose of NaAsO2 (5 mg/kg), 6 animals in each group. NaAsO2 (CAS No. 7784-46-5) was gained from Sigma Aldrich. The rats were subjected to NaAsO2 at a dose of 0, 2.5 and 5 mg/kg by gavage for 5 months. Control group was given distilled water using the above method.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Sodium arsenite-induced ferroptotic cell death is relied on the MtROS-dependent autophagy by regulating the iron homeostasis. Ferroptosis is involved in pancreatic dysfunction triggered by arsenic, and arsenic-induced ferroptosis involves MtROS, autophagy, ferritin. | ||||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [4] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Male reproductive disorders | ICD-11: VV5Z | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | GC-2spd(ts) cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_6633 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Specific pathogen free C57BL/6J male mice, aged 7 weeks old, weighted 20-24 g, were provided by Experimental Animal Center of Chongqing Medical University. The animals were adaptive feeding for a week, then randomly divided into four groups: control group, 0.5 mg/L arsenite group, 5 mg/L arsenite group and 50 mg/L arsenite group (n = 8). After exposure of arsenite via drinking water for 6 months, the animals were anesthetized, and the bilateral testicles were immediately separated on ice, weighted and calculated to get viscera coefficient.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Sodium arsenite induced oxidative stress and consequently leading to testicular cell death by ferroptosis. These findings demonstrate a potential beneficial role of supplementation of ferroptosis inhibitors for prevention or treatment of arsenite-related male reproductive toxicity. | ||||
References
