Ferroptosis Target Information
General Information of the Ferroptosis Target (ID: TAR10036)
| Target Name | NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Mitogenic oxidase 1; NADH/NADPH mitogenic oxidase subunit P65-MOX; NOH-1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene Name | NOX1 | ||||
| Sequence |
MGNWVVNHWFSVLFLVVWLGLNVFLFVDAFLKYEKADKYYYTRKILGSTLACARASALCL
NFNSTLILLPVCRNLLSFLRGTCSFCSRTLRKQLDHNLTFHKLVAYMICLHTAIHIIAHL FNFDCYSRSRQATDGSLASILSSLSHDEKKGGSWLNPIQSRNTTVEYVTFTSIAGLTGVI MTIALILMVTSATEFIRRSYFEVFWYTHHLFIFYILGLGIHGIGGIVRGQTEESMNESHP RKCAESFEMWDDRDSHCRRPKFEGHPPESWKWILAPVILYICERILRFYRSQQKVVITKV VMHPSKVLELQMNKRGFSMEVGQYIFVNCPSISLLEWHPFTLTSAPEEDFFSIHIRAAGD WTENLIRAFEQQYSPIPRIEVDGPFGTASEDVFQYEVAVLVGAGIGVTPFASILKSIWYK FQCADHNLKTKKIYFYWICRETGAFSWFNNLLTSLEQEMEELGKVGFLNYRLFLTGWDSN IVGHAALNFDKATDIVTGLKQKTSFGRPMWDNEFSTIATSHPKSVVGVFLCGPRTLAKSL RKCCHRYSSLDPRKVQFYFNKENF Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
NOH-1S is a voltage-gated proton channel that mediates the H(+) currents of resting phagocytes and other tissues. It participates in the regulation of cellular pH and is blocked by zinc. NOH-1L is a pyridine nucleotide-dependent oxidoreductase that generates superoxide and might conduct H(+) ions as part of its electron transport mechanism, whereas NOH-1S does not contain an electron transport chain.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene ID | 27035 | ||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Target Type | Driver Suppressor Marker | ||||
| Mechanism Diagram | Click to View the Original Diagram | ||||
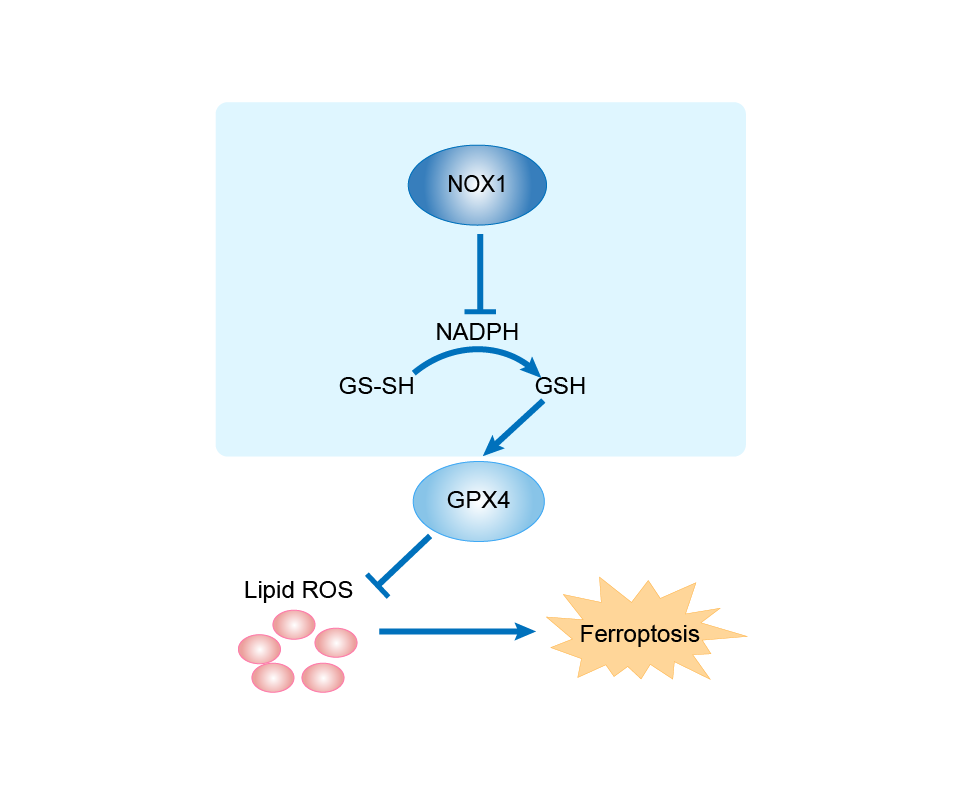
|
|||||
Tissue Relative Abundances of This Target
Full List of Regulator(s) of This Ferroptosis Target and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
NOX1 can be involved in and affect the ferroptosis by the following regulators, and result in corresponding disease/drug response(s). You can browse corresponding disease or drug response(s) resulting from the regulation of certain regulators.
Browse Regulator related Disease
Browse Regulator related Drug
NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1)
Kidney injury [ICD-11: NB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [1] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cadmium | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
PC12 cells | Adrenal gland pheochromocytoma | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0481 |
| Response Description | CdCl2-initiated injury was found to result from the induction of not only apoptosis but also ferroptosis, as evidenced by the increased iron content, ROS production, and mitochondrial membrane potential along with changes in the expressions of iron death-related genes (FTH1, GPX4, ASCL4, PTGS2, and NOX1) and levels of caspase9, Bax, and Bcl-2 proteins. It is possible that the damage caused by cadmium results from the induced ferroptosis and apoptosis via the miR-34a-5p/ Sirt1 axis. | |||
hsa-miR-34a-5p (miRNA)
Kidney injury [ICD-11: NB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [1] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | |||
| Responsed Drug | Cadmium | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
PC12 cells | Adrenal gland pheochromocytoma | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0481 |
| Response Description | CdCl2-initiated injury was found to result from the induction of not only apoptosis but also ferroptosis, as evidenced by the increased iron content, ROS production, and mitochondrial membrane potential along with changes in the expressions of iron death-related genes (FTH1, GPX4, ASCL4, PTGS2, and NOX1) and levels of caspase9, Bax, and Bcl-2 proteins. It is possible that the damage caused by cadmium results from the induced ferroptosis and apoptosis via the miR-34a-5p/Sirt1 axis. | |||
Unspecific Regulator
Rhabdomyosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B55]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [2] | |||
| Responsed Drug | Diphenyleneiodonium | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
RD cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1649 |
| Rh18 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1659 | |
| Rh30 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0041 | |
| Rh36 cells | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_M599 | |
| Rh41 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2176 | |
| T 174 cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_U955 | |
| TE 381.T cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1751 | |
| KYM-1 cells | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3007 | |
| Response Description | Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) cells might be vulnerable to oxidative stress-induced cell death. The broad-spectrum protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor Bisindolylmaleimide I as well as the PKC- and -selective inhibitor G6976 significantly reduced Erastin-induced cell death. Furthermore, the broad-spectrum nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-oxidase (NOX) inhibitor Diphenyleneiodonium and the selective NOX1/4 isoform inhibitor GKT137831 significantly decreased Erastin-stimulated ROS, lipid ROS and cell death. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [2] | |||
| Responsed Drug | GKT137831 | Phase 2 | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
In Vitro Model |
RD cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1649 |
| Rh18 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1659 | |
| Rh30 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0041 | |
| Rh36 cells | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_M599 | |
| Rh41 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2176 | |
| T 174 cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_U955 | |
| TE 381.T cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1751 | |
| KYM-1 cells | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3007 | |
| Response Description | Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) cells might be vulnerable to oxidative stress-induced cell death. The broad-spectrum protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor Bisindolylmaleimide I as well as the PKC- and -selective inhibitor G6976 significantly reduced Erastin-induced cell death. Furthermore, the broad-spectrum nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-oxidase (NOX) inhibitor Diphenyleneiodonium and the selective NOX1/4 isoform inhibitor GKT137831 significantly decreased Erastin-stimulated ROS, lipid ROS and cell death. | |||
NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1)
Cadmium
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [1] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Kidney injury [ICD-11: NB92] | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | PC12 cells | Adrenal gland pheochromocytoma | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0481 |
| Response Description | CdCl2-initiated injury was found to result from the induction of not only apoptosis but also ferroptosis, as evidenced by the increased iron content, ROS production, and mitochondrial membrane potential along with changes in the expressions of iron death-related genes (FTH1, GPX4, ASCL4, PTGS2, and NOX1) and levels of caspase9, Bax, and Bcl-2 proteins. It is possible that the damage caused by cadmium results from the induced ferroptosis and apoptosis via the miR-34a-5p/ Sirt1 axis. | |||
hsa-miR-34a-5p (miRNA)
Cadmium
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [1] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | |||
| Responsed Disease | Kidney injury [ICD-11: NB92] | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | PC12 cells | Adrenal gland pheochromocytoma | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0481 |
| Response Description | CdCl2-initiated injury was found to result from the induction of not only apoptosis but also ferroptosis, as evidenced by the increased iron content, ROS production, and mitochondrial membrane potential along with changes in the expressions of iron death-related genes (FTH1, GPX4, ASCL4, PTGS2, and NOX1) and levels of caspase9, Bax, and Bcl-2 proteins. It is possible that the damage caused by cadmium results from the induced ferroptosis and apoptosis via the miR-34a-5p/Sirt1 axis. | |||
Unspecific Regulator
Diphenyleneiodonium
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rhabdomyosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B55] | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | RD cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1649 |
| Rh18 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1659 | |
| Rh30 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0041 | |
| Rh36 cells | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_M599 | |
| Rh41 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2176 | |
| T 174 cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_U955 | |
| TE 381.T cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1751 | |
| KYM-1 cells | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3007 | |
| Response Description | Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) cells might be vulnerable to oxidative stress-induced cell death. The broad-spectrum protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor Bisindolylmaleimide I as well as the PKC- and -selective inhibitor G6976 significantly reduced Erastin-induced cell death. Furthermore, the broad-spectrum nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-oxidase (NOX) inhibitor Diphenyleneiodonium and the selective NOX1/4 isoform inhibitor GKT137831 significantly decreased Erastin-stimulated ROS, lipid ROS and cell death. | |||
GKT137831
[Phase 2]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rhabdomyosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B55] | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | RD cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1649 |
| Rh18 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1659 | |
| Rh30 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0041 | |
| Rh36 cells | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_M599 | |
| Rh41 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2176 | |
| T 174 cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_U955 | |
| TE 381.T cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1751 | |
| KYM-1 cells | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3007 | |
| Response Description | Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) cells might be vulnerable to oxidative stress-induced cell death. The broad-spectrum protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor Bisindolylmaleimide I as well as the PKC- and -selective inhibitor G6976 significantly reduced Erastin-induced cell death. Furthermore, the broad-spectrum nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-oxidase (NOX) inhibitor Diphenyleneiodonium and the selective NOX1/4 isoform inhibitor GKT137831 significantly decreased Erastin-stimulated ROS, lipid ROS and cell death. | |||
References
