Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0274)
| Name |
GKT137831
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
1218942-37-0; GKT137831; Setanaxib; GKT-137831; 2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-4-(3-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridine-3,6(2H,5H)-dione; GKT-831; GKT831; 2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-4-(3-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazolo(4,3-c)pyridine-3,6(2H,5H)-dione; 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-4-[3-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-5-methyl-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridine-3,6-dione; 45II35329V; 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-4-(3-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridine-3,6(5H)-dione; 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-4-[3-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-5-methyl-1H,2H,3H,5H,6H-pyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridine-3,6-dione; UNII-45II35329V; 1H-PYRAZOLO(4,3-C)PYRIDINE-3,6(2H,5H)-DIONE, 2-(2-CHLOROPHENYL)-4-(3-(DIMETHYLAMINO)PHENYL)-5-METHYL-; 1H-Pyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridine-3,6(2H,5H)-dione, 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-4-[3-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-5-methyl-; GKT 137831; SETANAXIB [INN]; GTPL9932; SCHEMBL1302603; CHEMBL4303187; DTXSID30153432; EX-A577; BCP14159; MFCD27923122; s7171; AKOS022176138; CCG-268595; CS-3290; SB19230; NCGC00378460-05; NCGC00378460-08; NCGC00378460-09; AC-33132; AS-74753; HY-12298; FT-0700121; A14433; EN300-20043919; J-690070; Q27258840; 2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-4-[3-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-5-methylpyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridine-3,6(2H,5H)-dione
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Phase 2
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
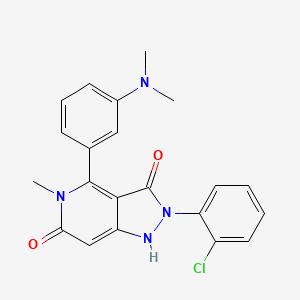 |
||||
| Formula |
C21H19ClN4O2
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
2-(2-chlorophenyl)-4-[3-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-5-methyl-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridine-3,6-dione
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CN1C(=O)C=C2C(=C1C3=CC(=CC=C3)N(C)C)C(=O)N(N2)C4=CC=CC=C4Cl
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H19ClN4O2/c1-24(2)14-8-6-7-13(11-14)20-19-16(12-18(27)25(20)3)23-26(21(19)28)17-10-5-4-9-15(17)22/h4-12,23H,1-3H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
RGYQPQARIQKJKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rhabdomyosarcoma | ICD-11: 2B55 | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | RD cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1649 |
| Rh18 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1659 | |
| Rh30 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0041 | |
| Rh36 cells | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_M599 | |
| Rh41 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2176 | |
| T 174 cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_U955 | |
| TE 381.T cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1751 | |
| KYM-1 cells | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3007 | |
| Response regulation | Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) cells might be vulnerable to oxidative stress-induced cell death. The broad-spectrum protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor Bisindolylmaleimide I as well as the PKC- and -selective inhibitor G6976 significantly reduced Erastin-induced cell death. Furthermore, the broad-spectrum nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-oxidase (NOX) inhibitor Diphenyleneiodonium and the selective NOX1/4 isoform inhibitor GKT137831 significantly decreased Erastin-stimulated ROS, lipid ROS and cell death. | |||
NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rhabdomyosarcoma | ICD-11: 2B55 | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | RD cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1649 |
| Rh18 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1659 | |
| Rh30 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0041 | |
| Rh36 cells | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_M599 | |
| Rh41 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2176 | |
| T 174 cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_U955 | |
| TE 381.T cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1751 | |
| KYM-1 cells | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3007 | |
| Response regulation | Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) cells might be vulnerable to oxidative stress-induced cell death. The broad-spectrum protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor Bisindolylmaleimide I as well as the PKC- and -selective inhibitor G6976 significantly reduced Erastin-induced cell death. Furthermore, the broad-spectrum nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-oxidase (NOX) inhibitor Diphenyleneiodonium and the selective NOX1/4 isoform inhibitor GKT137831 significantly decreased Erastin-stimulated ROS, lipid ROS and cell death. | |||
