Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0265)
| Name |
Iridin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Iridin; 491-74-7; UNII-6NTS007OHQ; 6NTS007OHQ; CHEBI:5963; Spectrum_000619; SpecPlus_000143; Spectrum2_000198; Spectrum3_000192; DTXSID80197689; irigenin 7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside; 5-hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-6-methoxy-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one; Irigenin 7-O-glucoside; Lridin; 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 7-(beta-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-5-hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-6-methoxy-; 5-hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-6-methoxy-4-oxo-4H-1-benzopyran-7-yl beta-D-glucopyranoside; 5-HYDROXY-3-(3-HYDROXY-4,5-DIMETHOXYPHENYL)-6-METHOXY-7-((2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-TRIHYDROXY-6-(HYDROXYMETHYL)OXAN-2-YL)OXYCHROMEN-4-ONE; Irisin; C24H26O13; Spectrum4_001510; Spectrum5_000279; BSPBio_001743; KBioGR_002179; KBioSS_001099; SPECTRUM200793; DivK1c_006239; SCHEMBL243567; SPBio_000155; CHEMBL487014; KBio1_001183; KBio2_001099; KBio2_003667; KBio2_006235; KBio3_001243; DTXCID90120180; HY-N3011; CCG-38404; MFCD28166495; SDCCGMLS-0066463.P001; NCGC00179041-01; AC-34954; MS-29677; CS-0022925; Q419014; SR-05000002736; SR-05000002736-1; BRD-K22550622-001-02-7; BRD-K22550622-001-03-5; 5-hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)-6-methoxy-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydropyran-2-yl]oxy-chromen-4-one; 5-hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-6-methoxy-7-(((2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-4H-chromen-4-one; 5-hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-6-methoxy-7-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-4H-chromen-4-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
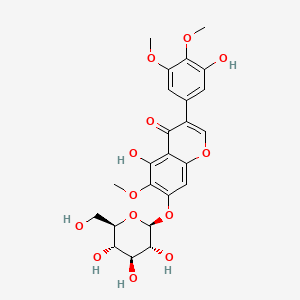 |
||||
| Formula |
C24H26O13
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
5-hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-6-methoxy-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
COC1=CC(=CC(=C1OC)O)C2=COC3=CC(=C(C(=C3C2=O)O)OC)OC4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C24H26O13/c1-32-13-5-9(4-11(26)22(13)33-2)10-8-35-12-6-14(23(34-3)19(29)16(12)17(10)27)36-24-21(31)20(30)18(28)15(7-25)37-24/h4-6,8,15,18,20-21,24-26,28-31H,7H2,1-3H3/t15-,18-,20+,21-,24-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
LNQCUTNLHUQZLR-OZJWLQQPSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 4 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Sepsis | ICD-11: 1G40 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HK-2 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0302 | |
| In Vivo Model |
All animals were purchased from the Animal Experimental Center of Wuhan University (ABLS-III Laboratory). C57BL/6 male mice weighing 20-25 g were used for this study. HK-2 cells were seeded into 96-well plates (5 x 105 cells/well) and cultured for 24 h until 80% confluence. Subsequently, we have added LPS (10 ug/ml) into the cultured cells for 22 h to establish the cell model of LPS-induced AKI.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury induced ferroptosis by increasing iron and lipid peroxidation. Irisin effectively suppressed ferroptosis and alleviated SA-AKI and improved the mitochondria functionviainduction of the SIRT1/Nrf2 signal axis. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myocardial infarction | ICD-11: BA41 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 (FNDC5) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hCMs (Human cardiomyocytes) | ||||
| Response regulation | Myocardial infarction is characterized by cardiomyocyte death and mitochondrial dysfunction induced by ischemia. FNDC5 overexpression and/or irisin administration elevated cell viability, decreased ferroptosis, and reversed mitochondrial impairments induced by hypoxia. Mechanistically, FNDC5/irisin reduced ferroptosis and reversed mitochondrial impairments by Nrf2/HO-1 axis in hypoxic cardiomyocytes. | ||||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [3] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Sepsis | ICD-11: 1G40 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HT22 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0321 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Eight-week-old wild-type (WT) and Nrf2-knockout (Nrf2-/-) littermate male mice on a C57BL/6J background were purchased from Cyagen (Suzhou, China.) and maintained at the Centre for Animals of Wuhan University (Wuhan, China). Before the experiment, the mice were separated and given light and dark cycles for 12 h, 22 ± 0.5 temperature, 60 ± 10% humidity, and free accessed to food and water for at least 1 week. Mice were randomly distributed into sham, CLP, CLP + Irisin (Ir group) and CLP + Irisin + Era (Ir + Era group) groups.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | In conclusion, irisin could ameliorate inflammatory microenvironment in sepsis-associated encephalopathy by suppressing hippocampus ferroptosis via the Nrf2/GPX4 signaling pathway. | ||||
| Experiment 4 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [4] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Ischemia/reperfusion injury | ICD-11: DB98 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | MLE-12 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_3751 | |
| In Vivo Model |
In vivo, the LIRI model was established as described earlier. All mice were anesthetized with pentobarbital administered intraperitoneally (50 mg/kg, Sigma-Aldrich, MO, USA). After endotracheal intubation, the mice were ventilated using a rodent ventilator (MiniVent, Harvard Apparatus, USA), with the title volume set to 7 ml/kg, the respiratory rate set to 120 times/min, and the inspiratory/expiratory ratio set to 1: 2. A noninvasive clamp was used to interrupt the left pulmonary hilum, causing lung ischemia. The clamp was released after 60 minutes of ischemia, and the left lung was reperfused for 120 minutes. Animals were euthanized via cervical dislocation at the end of the experiment. Following that, lung specimens and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid were harvested for analysis. All procedures except lung ischemia were performed on mice in the sham group.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | As a result, irisin postconditioning may protect against lung I/R damage by suppressing ferroptosis via the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling axis. | ||||
Heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myocardial infarction | ICD-11: BA41 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 (FNDC5) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hCMs (Human cardiomyocytes) | ||||
| Response regulation | Myocardial infarction is characterized by cardiomyocyte death and mitochondrial dysfunction induced by ischemia. FNDC5 overexpression and/or irisin administration elevated cell viability, decreased ferroptosis, and reversed mitochondrial impairments induced by hypoxia. Mechanistically, FNDC5/irisin reduced ferroptosis and reversed mitochondrial impairments by Nrf2/HO-1 axis in hypoxic cardiomyocytes. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [4] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Ischemia/reperfusion injury | ICD-11: DB98 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | MLE-12 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_3751 | |
| In Vivo Model |
In vivo, the LIRI model was established as described earlier. All mice were anesthetized with pentobarbital administered intraperitoneally (50 mg/kg, Sigma-Aldrich, MO, USA). After endotracheal intubation, the mice were ventilated using a rodent ventilator (MiniVent, Harvard Apparatus, USA), with the title volume set to 7 ml/kg, the respiratory rate set to 120 times/min, and the inspiratory/expiratory ratio set to 1: 2. A noninvasive clamp was used to interrupt the left pulmonary hilum, causing lung ischemia. The clamp was released after 60 minutes of ischemia, and the left lung was reperfused for 120 minutes. Animals were euthanized via cervical dislocation at the end of the experiment. Following that, lung specimens and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid were harvested for analysis. All procedures except lung ischemia were performed on mice in the sham group.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | As a result, irisin postconditioning may protect against lung I/R damage by suppressing ferroptosis via the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling axis. | ||||
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [3] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Sepsis | ICD-11: 1G40 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HT22 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0321 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Eight-week-old wild-type (WT) and Nrf2-knockout (Nrf2-/-) littermate male mice on a C57BL/6J background were purchased from Cyagen (Suzhou, China.) and maintained at the Centre for Animals of Wuhan University (Wuhan, China). Before the experiment, the mice were separated and given light and dark cycles for 12 h, 22 ± 0.5 temperature, 60 ± 10% humidity, and free accessed to food and water for at least 1 week. Mice were randomly distributed into sham, CLP, CLP + Irisin (Ir group) and CLP + Irisin + Era (Ir + Era group) groups.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | In conclusion, irisin could ameliorate inflammatory microenvironment in Sepsis-associated encephalopathy by suppressing hippocampus ferroptosis via the Nrf2/GPX4 signaling pathway. | ||||
Unspecific Target
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [5] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer | ICD-11: 2C10 | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| In Vitro Model | PANC-1 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 |
| Response regulation | Irisin Is a positive regulator for ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer. There was a dramatic downregulation of p62 expression, which inhibited NRF2 degradation and enhanced NRF2 nuclear accumulation after 12h of irisin and erastin co-treatment, although irisin or erastin alone did not affect p62 levels. | |||
References
