Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0066)
| Name |
Paraquat
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
PARAQUAT; 4685-14-7; Paraquat ion; Paraquat dication; 1,1'-Dimethyl-4,4'-bipyridinium; Dimethyl viologen; 4,4'-Bipyridinium, 1,1'-dimethyl-; Methyl viologen (2+); Starfire; Weedol; Spraytop-graze; Dextrone X; Gramoxone; Methyl viologen ion(2+); N,N'-Dimethyl-4,4'-bipyridinium; 1,1'-Dimethyl-4,4'-bipyridyldiylium; CCRIS 7731; 1-methyl-4-(1-methylpyridin-1-ium-4-yl)pyridin-1-ium; HSDB 1668; PRIGLONE; 1,1'-Dimethyl-4,4'-bipyridinium salt; 1,1'-Dimethyl-4,4'-bipyridinium cation; Gramoxone S; PARAQUAT CATION; CHEBI:34905; N,N'-Dimethyl-4,4'-bipyridinium dication; PLG39H7695; DTXSID3034799; 1,1'-dimethyl-4,4'-bipyridium; 1,1'-dimethyl-4,4'-bipyridin-1-ium; PARAQUAT (MART.); PARAQUAT [MART.]; BIPYRIDINIUM, 1,1'-DIMETHYL-4,4'-; MLS001332595; Viologen, Methyl; Paraquat [ANSI:BSI:ISO]; 1,1'-dimethyl-(4,4'-bipyridin)-1,1'-diium; 1,1'-dimethyl-[4,4'-bipyridin]-1,1'-diium; SMR000875209; EINECS 225-141-7; N,N'-Dimethyl-gamma,gamma'-dipyridylium; UNII-PLG39H7695; KHJ; PARAQUAT [HSDB]; PARAQUAT [ISO]; PARAQUAT [MI]; 3240-78-6; ChemDiv3_000231; NCIMech_000502; NCIOpen2_005422; SCHEMBL21652; MLS001304933; BIDD:ER0480; CHEMBL74469; 1,1'-Dimethyl-4,4'-bipyridyldiylium ion (8CI)(9CI); DTXCID1014799; BDBM96275; cid_5351279; 1,1'-Dimethyl,4,4'-bipyridyl; INFDPOAKFNIJBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N; HMS1473K11; 1,1 '-dimethyl-4,4'-bipyridinium; CCG-35984; STK387391; AKOS001483177; IDI1_019549; 1,1'-DIMETHYL-4,4'-BIPYRIDYL; NCGC00166161-02; NCI60_002105; SMR000752910; 1,1'-Dimethyl-4,4'-bipyridyldiylium ion; FT-0606133; FT-0652363; 1,1'-Dimethyl-4,4'-bipyridium bromide (1:2); AC-907/25005209; W-106083; Q26841324; 1,1'-DIMETHYL-[4,4'-BIPYRIDINE]-1,1'-DIIUM; 1-methyl-4-(1-methyl-4-pyridin-1-iumyl)pyridin-1-ium;chloride; 1-methyl-4-(1-methylpyridin-1-ium-4-yl)pyridin-1-ium;chloride
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Investigative
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
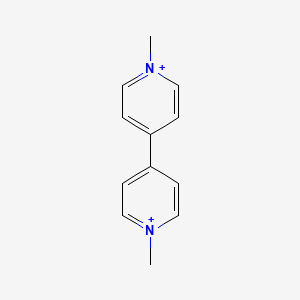 |
||||
| Formula |
C12H14N2+2
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
1-methyl-4-(1-methylpyridin-1-ium-4-yl)pyridin-1-ium
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C[N+]1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=CC=[N+](C=C2)C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C12H14N2/c1-13-7-3-11(4-8-13)12-5-9-14(2)10-6-12/h3-10H,1-2H3/q+2
|
||||
| InChIKey |
INFDPOAKFNIJBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 (PTGS2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease | ICD-11: 8A00 | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| In Vitro Model | SH-SY5Y cells | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0019 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Twenty male C57BL/6 mice at 12 weeks old were purchased from Hebei Medical University Experimental Animal Center. 10 mice of the experimental group were intraperitoneally injected with PQ (10 mg PQ (salt)/kg/dose) three times a week for 3 weeks according to the previous report. Ten mice of the control group were intraperitoneally injected with the same dose of normal saline. Once the experimental schedule was completed, firstly, the animals were used for behavioral tests. Then, the mice were anesthetized with 0.4% pentobarbital sodium (1 mL/100 g) solution and perfused. The substantia nigra tissue was exfoliated for subsequent experiments.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Paraquat (PQ) significantly caused the iron accumulation in cytoplasm and mitochondria through ferritinophagy pathway induced by NCOA4. Iron overload initiated lipid peroxidation through 12Lox, further inducing ferroptosis by producing lipid ROS. PQ downregulated SLC7A11 and GPX4 expression and upregulated Cox2 expression. Bcl2/Bax and P-p38/p38 pathways mediated the cross-talk between ferroptosis and apoptosis induced by PQ. These data further demonstrated the complexity of Parkinson's disease occurrence. | ||||
Polyunsaturated fatty acid lipoxygenase ALOX12 (ALOX12)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease | ICD-11: 8A00 | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| In Vitro Model | SH-SY5Y cells | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0019 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Twenty male C57BL/6 mice at 12 weeks old were purchased from Hebei Medical University Experimental Animal Center. 10 mice of the experimental group were intraperitoneally injected with PQ (10 mg PQ (salt)/kg/dose) three times a week for 3 weeks according to the previous report. Ten mice of the control group were intraperitoneally injected with the same dose of normal saline. Once the experimental schedule was completed, firstly, the animals were used for behavioral tests. Then, the mice were anesthetized with 0.4% pentobarbital sodium (1 mL/100 g) solution and perfused. The substantia nigra tissue was exfoliated for subsequent experiments.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Paraquat (PQ) significantly caused the iron accumulation in cytoplasm and mitochondria through ferritinophagy pathway induced by NCOA4. Iron overload initiated lipid peroxidation through 12Lox, further inducing ferroptosis by producing lipid ROS. PQ downregulated SLC7A11 and GPX4 expression and upregulated Cox2 expression. Bcl2/Bax and P-p38/p38 pathways mediated the cross-talk between ferroptosis and apoptosis induced by PQ. These data further demonstrated the complexity of Parkinson's disease occurrence. | ||||
Nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease | ICD-11: 8A00 | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| In Vitro Model | SH-SY5Y cells | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0019 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Twenty male C57BL/6 mice at 12 weeks old were purchased from Hebei Medical University Experimental Animal Center. 10 mice of the experimental group were intraperitoneally injected with PQ (10 mg PQ (salt)/kg/dose) three times a week for 3 weeks according to the previous report. Ten mice of the control group were intraperitoneally injected with the same dose of normal saline. Once the experimental schedule was completed, firstly, the animals were used for behavioral tests. Then, the mice were anesthetized with 0.4% pentobarbital sodium (1 mL/100 g) solution and perfused. The substantia nigra tissue was exfoliated for subsequent experiments.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Paraquat (PQ) significantly caused the iron accumulation in cytoplasm and mitochondria through ferritinophagy pathway induced by NCOA4. Iron overload initiated lipid peroxidation through 12Lox, further inducing ferroptosis by producing lipid ROS. PQ downregulated SLC7A11 and GPX4 expression and upregulated Cox2 expression. Bcl2/Bax and P-p38/p38 pathways mediated the cross-talk between ferroptosis and apoptosis induced by PQ. These data further demonstrated the complexity of Parkinson's disease occurrence. | ||||
Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease | ICD-11: 8A00 | |||
| Pathway Response | Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| In Vitro Model | SH-SY5Y cells | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0019 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Twenty male C57BL/6 mice at 12 weeks old were purchased from Hebei Medical University Experimental Animal Center. 10 mice of the experimental group were intraperitoneally injected with PQ (10 mg PQ (salt)/kg/dose) three times a week for 3 weeks according to the previous report. Ten mice of the control group were intraperitoneally injected with the same dose of normal saline. Once the experimental schedule was completed, firstly, the animals were used for behavioral tests. Then, the mice were anesthetized with 0.4% pentobarbital sodium (1 mL/100 g) solution and perfused. The substantia nigra tissue was exfoliated for subsequent experiments.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Paraquat (PQ) significantly caused the iron accumulation in cytoplasm and mitochondria through ferritinophagy pathway induced by NCOA4. Iron overload initiated lipid peroxidation through 12Lox, further inducing ferroptosis by producing lipid ROS. PQ downregulated SLC7A11 and GPX4 expression and upregulated Cox2 expression. Bcl2/Bax and P-p38/p38 pathways mediated the cross-talk between ferroptosis and apoptosis induced by PQ. These data further demonstrated the complexity of Parkinson's disease occurrence. | ||||
