Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0370)
| Name |
Elabela
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Elabela/Toddler-11; 1784687-32-6; ELA-11; GTPL8526; CHEMBL3809035; BDBM50172365
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
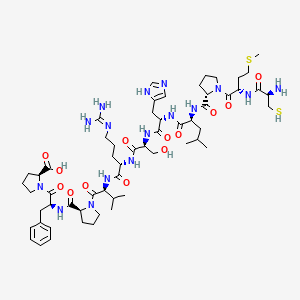 |
||||
|
3D MOL
|
|||||
| Formula |
C58H90N16O13S2
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(2R)-2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoyl]amino]-4-methylsulfanylbutanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)CC(C(=O)NC(CC1=CN=CN1)C(=O)NC(CO)C(=O)NC(CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)NC(C(C)C)C(=O)N2CCCC2C(=O)NC(CC3=CC=CC=C3)C(=O)N4CCCC4C(=O)O)NC(=O)C5CCCN5C(=O)C(CCSC)NC(=O)C(CS)N
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C58H90N16O13S2/c1-32(2)25-39(68-52(81)43-16-10-21-72(43)54(83)38(19-24-89-5)66-47(76)36(59)30-88)49(78)67-40(27-35-28-62-31-64-35)50(79)70-42(29-75)51(80)65-37(15-9-20-63-58(60)61)48(77)71-46(33(3)4)56(85)73-22-11-17-44(73)53(82)69-41(26-34-13-7-6-8-14-34)55(84)74-23-12-18-45(74)57(86)87/h6-8,13-14,28,31-33,36-46,75,88H,9-12,15-27,29-30,59H2,1-5H3,(H,62,64)(H,65,80)(H,66,76)(H,67,78)(H,68,81)(H,69,82)(H,70,79)(H,71,77)(H,86,87)(H4,60,61,63)/t36-,37-,38-,39-,40-,41-,42-,43-,44-,45-,46-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
XXKPNJFJXZBRMX-HDKAIKTRSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cardiomyopathy | ICD-11: BC43 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Krueppel-like factor 15 (KLF15) | Suppressor | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | rAFs (Rat adventitial fibroblasts) | |||
| Response regulation | KLF15 siRNA impeded the beneficial roles of elabela (ELA) in DOX-pretreated rat aortic AFs by suppressing the Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling. In conclusion, ELA prevents DOX-triggered promotion of cytotoxicity, and exerts anti-oxidative and anti-ferroptotic effects in rat aortic AFs via activation of the KLF15/GPX4 signaling, indicating a promising therapeutic value of ELA in antagonizing DOX-mediated cardiovascular abnormality and disorders. | |||
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cardiomyopathy | ICD-11: BC43 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Krueppel-like factor 15 (KLF15) | Suppressor | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | rAFs (Rat adventitial fibroblasts) | |||
| Response regulation | KLF15 siRNA impeded the beneficial roles of elabela (ELA) in DOX-pretreated rat aortic AFs by suppressing the Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling. In conclusion, ELA prevents DOX-triggered promotion of cytotoxicity, and exerts anti-oxidative and anti-ferroptotic effects in rat aortic AFs via activation of the KLF15/GPX4 signaling, indicating a promising therapeutic value of ELA in antagonizing DOX-mediated cardiovascular abnormality and disorders. | |||
Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Cardiomyopathy | ICD-11: BC43 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Krueppel-like factor 15 (KLF15) | Suppressor | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | rAFs (Rat adventitial fibroblasts) | |||
| Response regulation | KLF15 siRNA impeded the beneficial roles of elabela (ELA) in DOX-pretreated rat aortic AFs by suppressing the Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling. In conclusion, ELA prevents DOX-triggered promotion of cytotoxicity, and exerts anti-oxidative and anti-ferroptotic effects in rat aortic AFs via activation of the KLF15/GPX4 signaling, indicating a promising therapeutic value of ELA in antagonizing DOX-mediated cardiovascular abnormality and disorders. | |||
