Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0232)
| Name |
Seratrodast
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
SERATRODAST; 112665-43-7; Bronica; 7-phenyl-7-(2,4,5-trimethyl-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dien-1-yl)heptanoic acid; Abbott 73001; ABT-001; AA-2414; Abbott-73001; AA 2414; (+-)-7-(3,5,6-Trimethyl-1,4-benzoquinon-2-yl)-7-phenylheptanoic acid; 103185-78-0; A-73001; NSC-759640; DTXSID4021397; 4U58JM421N; MFCD00875701; NCGC00181296-01; Seratrodast [USAN:INN]; DTXCID201397; ABT 001; Bronica (TN); CCRIS 8939; CAS-112665-43-7; A 73001; UNII-4U58JM421N; Seratrodast (JAN/USAN/INN); (+/-)-2,4,5-Trimethyl-3,6-dioxo-zeta-phenyl-1,4-cyclohexadiene-1-heptanoic acid; 7-(3,5,6-trimethyl-1,4-benzoquinon-2-yl)-7-phenylheptanoic acid; Seratrodast- Bio-X; SERATRODAST [MI]; SERATRODAST [INN]; SERATRODAST [JAN]; SERATRODAST [USAN]; 7-phenyl-7-(2,4,5-trimethyl-3,6-dioxo-cyclohexa-1,4-dien-1-yl)heptanoic acid; (+-)-2,4,5-Trimethyl-3,6-dioxo-zeta-phenyl-1,4-cyclohexadiene-1-heptanoic acid; Benzeneheptanoic acid, zeta-(2,4,5-trimethyl-3,6-dioxo-1,4-cyclohexadien-1-yl)-, (+-)-; SERATRODAST [MART.]; SCHEMBL98402; SERATRODAST [WHO-DD]; MLS006012011; CHEBI:32126; Seratrodast, >=98% (HPLC); ZBVKEHDGYSLCCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N; HMS3264K16; HMS3748I13; Pharmakon1600-01502336; BCP08860; HY-B0774; Tox21_112774; NSC759640; s2072; STL556121; (+/-)-7-(3,5,6-Trimethyl-1,4-benzoquinon-2-yl)-7-phenylheptanoic Acid; AKOS015911825; Seratrodast(AA-2414, ABT-001); Tox21_112774_1; CCG-207903; DB06739; NSC 759640; 7-phenyl-7-(2,4,5-trimethyl-3,6-dioxo-1-cyclohexa-1,4-dienyl)heptanoic acid; NCGC00181296-02; AS-12945; BS164397; SMR002530529; FT-0631064; D01123; AB01563274_01; A802627; L001973; SR-01000944172; J-002813; Q7452735; SR-01000944172-1; 6-(6-Carboxy-1-phenylhexyl)-2,3,5-trimethylbenzoquinone; 7-(3,5,6-trimethyl-1,4-benzoquinone-2-yl)-7-phenylheptanoic acid; 7-phenyl-7-(2,4,5-trimethyl-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dienyl)heptanoic acid; (+/-)-2,4,5-TRIMETHYL-3,6-DIOXO-.ZETA.-PHENYL-1,4-CYCLOHEXADIENE-1-HEPTANOIC ACID; 7-phenyl-7-[2,4,5-trimethyl-3,6-bis(oxidanylidene)cyclohexa-1,4-dien-1-yl]heptanoic acid; Benzeneoctanoic acid,H-(2,4,5-trimethyl-3,6-dioxo-1,4-cyclohexadien-1-yl)-; 103186-19-2; BENZENEHEPTANOIC ACID, .ZETA.-(2,4,5-TRIMETHYL-3,6-DIOXO-1,4-CYCLOHEXADIEN-1-YL)-, (+/-)-
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Discontinued in Phase 3
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
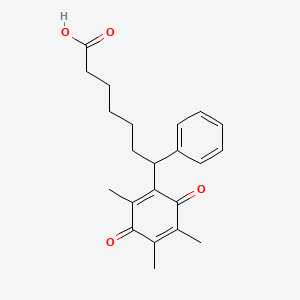 |
||||
| Formula |
C22H26O4
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
7-phenyl-7-(2,4,5-trimethyl-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dien-1-yl)heptanoic acid
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(C(=O)C(=C(C1=O)C)C(CCCCCC(=O)O)C2=CC=CC=C2)C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C22H26O4/c1-14-15(2)22(26)20(16(3)21(14)25)18(17-10-6-4-7-11-17)12-8-5-9-13-19(23)24/h4,6-7,10-11,18H,5,8-9,12-13H2,1-3H3,(H,23,24)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
ZBVKEHDGYSLCCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Status epilepticus | ICD-11: 8A66 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 (MAPK8) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HT22 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0321 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Drugs were dissolved in vehicle (0.1% DMSO + 20% PEG 300 + 0.5% CMC-Na + ddH2O). Mice in Control and PTZ groups were administered for five days with an equivalent volume of vehicle. PTZ-induced seizure model was done for the subsequent 1 h after the last administration of drugs. We performed a preliminary doseresponse trial, the dose of 60 mg/kg was established as being sufficient to trigger seizures with lower mortality and chosen as the optimal dose. One mouse in PTZ group was dead due to a severe seizure. At the end of the experiment, the mice were anesthetized or euthanized. For histopathological studies, the mice were anesthetized and intracardially perfused with 0.9% saline, followed by 0.4% paraformaldehyde for fixation of the brain. For immunoblot analysis, the hippocampus was rapidly isolated.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Seratrodast could reduce lipid ROS production, regulate the system xc-/glutathione (GSH)/glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) axis, and inhibit JNK (MAPK8) phosphorylation and p53 expression. JNK can directly or indirectly modulate the expression and activation of p53, which could regulate ferroptosis through inhibition of SLC7A11 transcription. Seratrodast increased the latency of seizures and reduced seizure duration in pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures. | ||||
Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)
| In total 2 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Status epilepticus | ICD-11: 8A66 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 (MAPK8) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HT22 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0321 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Drugs were dissolved in vehicle (0.1% DMSO + 20% PEG 300 + 0.5% CMC-Na + ddH2O). Mice in Control and PTZ groups were administered for five days with an equivalent volume of vehicle. PTZ-induced seizure model was done for the subsequent 1 h after the last administration of drugs. We performed a preliminary doseresponse trial, the dose of 60 mg/kg was established as being sufficient to trigger seizures with lower mortality and chosen as the optimal dose. One mouse in PTZ group was dead due to a severe seizure. At the end of the experiment, the mice were anesthetized or euthanized. For histopathological studies, the mice were anesthetized and intracardially perfused with 0.9% saline, followed by 0.4% paraformaldehyde for fixation of the brain. For immunoblot analysis, the hippocampus was rapidly isolated.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Seratrodast could reduce lipid ROS production, regulate the system xc-/glutathione (GSH)/glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) axis, and inhibit JNK (MAPK8) phosphorylation and p53 expression. JNK can directly or indirectly modulate the expression and activation of p53, which could regulate ferroptosis through inhibition of SLC7A11 transcription. Seratrodast increased the latency of seizures and reduced seizure duration in pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Status epilepticus | ICD-11: 8A66 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HT22 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0321 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Drugs were dissolved in vehicle (0.1% DMSO + 20% PEG 300 + 0.5% CMC-Na + ddH2O). Mice in Control and PTZ groups were administered for five days with an equivalent volume of vehicle. PTZ-induced seizure model was done for the subsequent 1 h after the last administration of drugs. We performed a preliminary doseresponse trial, the dose of 60 mg/kg was established as being sufficient to trigger seizures with lower mortality and chosen as the optimal dose. One mouse in PTZ group was dead due to a severe seizure. At the end of the experiment, the mice were anesthetized or euthanized. For histopathological studies, the mice were anesthetized and intracardially perfused with 0.9% saline, followed by 0.4% paraformaldehyde for fixation of the brain. For immunoblot analysis, the hippocampus was rapidly isolated.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Seratrodast could reduce lipid ROS production, regulate the system xc-/glutathione (GSH)/glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) axis, and inhibit JNK (MAPK8) phosphorylation and p53 expression. JNK can directly or indirectly modulate the expression and activation of p53, which could regulate ferroptosis through inhibition of SLC7A11 transcription. Seratrodast increased the latency of seizures and reduced seizure duration in pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures in Epilepsy. | ||||
Unspecific Target
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Status epilepticus | ICD-11: 8A66 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 (MAPK8) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HT22 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0321 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Drugs were dissolved in vehicle (0.1% DMSO + 20% PEG 300 + 0.5% CMC-Na + ddH2O). Mice in Control and PTZ groups were administered for five days with an equivalent volume of vehicle. PTZ-induced seizure model was done for the subsequent 1 h after the last administration of drugs. We performed a preliminary doseresponse trial, the dose of 60 mg/kg was established as being sufficient to trigger seizures with lower mortality and chosen as the optimal dose. One mouse in PTZ group was dead due to a severe seizure. At the end of the experiment, the mice were anesthetized or euthanized. For histopathological studies, the mice were anesthetized and intracardially perfused with 0.9% saline, followed by 0.4% paraformaldehyde for fixation of the brain. For immunoblot analysis, the hippocampus was rapidly isolated.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Seratrodast could reduce lipid ROS production, regulate the system xc-/glutathione (GSH)/glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) axis, and inhibit JNK (MAPK8) phosphorylation and p53 expression. JNK can directly or indirectly modulate the expression and activation of p53, which could regulate ferroptosis through inhibition of SLC7A11 transcription. Seratrodast increased the latency of seizures and reduced seizure duration in pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures in Epilepsy. | ||||
