Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0168)
| Name |
Olaparib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Olaparib; 763113-22-0; Lynparza; AZD2281; KU-0059436; AZD-2281; AZD 2281; 1-(Cyclopropylcarbonyl)-4-[5-[(3,4-dihydro-4-oxo-1-phthalazinyl)methyl]-2-fluorobenzoyl]piperazine; 4-(3-(4-(Cyclopropanecarbonyl)piperazine-1-carbonyl)-4-fluorobenzyl)phthalazin-1(2H)-one; OLAPARIB cpd; Olaparib (AZD-2281); KU-59436; Olaparib (AZD2281, Ku-0059436); Olaparib [USAN:INN]; UNII-WOH1JD9AR8; WOH1JD9AR8; C24H23FN4O3; 4-[[3-[4-(Cyclopropanecarbonyl)piperazine-1-carbonyl]-4-fluorophenyl]methyl]-2H-phthalazin-1-one; AZ2281; MFCD13185161; NSC-747856; CHEBI:83766; 4-(3-{[4-(Cyclopropylcarbonyl)piperazin-1-Yl]carbonyl}-4-Fluorobenzyl)phthalazin-1(2h)-One; 4-[3-(4-Cyclopropanecarbonyl-piperazine-1-carbonyl)-4-fluoro-benzyl]-2H-phthalazin-1-one; AZ-2281; KEYLYNK-010 COMPONENT OLAPARIB; KU59436; OLAPARIB COMPONENT OF KEYLYNK-010; Olaparib [INN]; 4-[(3-{[4-(Cyclopropylcarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]carbonyl}-4-fluorophenyl)methyl]phthalazin-1(2H)-one; Olaparib (AZD2281; Ku-0059436); Olaparib (AZD2281); Olaparibum; AZD221; 4-[3-[4-(Cyclopropanecarbonyl)piperazine-1-carbonyl]-4-fluorobenzyl]phthalazin-1(2H)-one; Olaparib- Bio-X; Lynparza (TN); 09L; 4-((3-{(4-(cyclopropylcarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl)carbonyl}-4-fluorophenyl)methyl)phthalazin-1(2H)-one; OLAPARIB [USAN]; OLAPARIB [JAN]; KU0059436; OLAPARIB [MI]; OLAPARIB [VANDF]; Olaparib - AZD2281; OLAPARIB [MART.]; OLAPARIB [WHO-DD]; AZD-2281 (Olaparib); Olaparib (JAN/USAN/INN); MLS006010185; SCHEMBL426568; OLAPARIB [ORANGE BOOK]; CHEMBL521686; GTPL7519; BDBM27566; DTXSID60917988; EX-A002; FDLYAMZZIXQODN-UHFFFAOYSA-N; BCPP000360; HMS3295I09; HMS3426C03; HMS3654G13; HMS3746K07; HMS3870H03; AMY10295; BCP01872; 763113-22-0, Lynparza,; NSC747856; NSC753686; s1060; AKOS005145764; AC-7939; BCP9000363; CCG-264799; CS-0075; DB09074; EX-7210; NSC 747856; NSC-753686; SB14617; SS-4573; AZD2281,Olaparib, KU-0059436; NCGC00238451-01; NCGC00238451-02; NCGC00238451-08; NCGC00238451-09; NCGC00238451-11; 1(2H)-Phthalazinone, 4-[[3-[[4-(cyclopropylcarbonyl)-1-piperazinyl]carbonyl]-4-fluorophenyl]methyl]-; 4-[(3-{[4-Cyclopropylcarbonyl)piperazin-4-yl]carbonyl}-4-fluorophenyl)methyl]phtalazin-1(2H)-one; 4-{[3-(4-cyclopropanecarbonylpiperazine-1-carbonyl)-4-fluorophenyl]methyl}-1,2-dihydrophthalazin-1-one; BO164169; HY-10162; SMR004701291; SY040527; Olaparib(AZD2281,KuDOSKU-0059436); A9666; BB 0260909; FT-0651458; SW218142-2; EC-000.2324; D09730; EN300-7542225; J-503540; Q7083106; BRD-K02113016-001-08-9; BRD-K02113016-001-09-7; Z2227698469; 1-(cyclopropylcarbonyl)-4-[5-[(3,4-dihydro-4-oxo-1-phthalazine; 4-(3-(1-(cyclopropanecarbonyl)piperazine-4-carbonyl)-4-fluorobenzyl)phthalazin-1(2H)-one; (2H)-Phthalazinone, 4-((3-((4-(cyclopropylcarbonyl)-1-piperazinyl)carbonyl)-4-fluorophenyl)methyl)-; 1021843-02-6; 4-({3-[(4-cyclopropanecarbonylpiperazin-1-yl)carbonyl]-4-fluorophenyl}methyl)-1,2-dihydrophthalazin-1-one; PIPERAZINE, 1-(CYCLOPROPYLCARBONYL)-4-(5-((3,4-DIHYDRO-4-OXO-1-PHTHALAZINYL)METHYL)-2-FLUOROBENZOYL)-
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
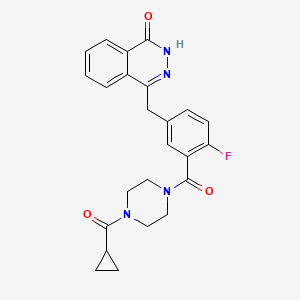 |
||||
| Formula |
C24H23FN4O3
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
4-[[3-[4-(cyclopropanecarbonyl)piperazine-1-carbonyl]-4-fluorophenyl]methyl]-2H-phthalazin-1-one
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1CC1C(=O)N2CCN(CC2)C(=O)C3=C(C=CC(=C3)CC4=NNC(=O)C5=CC=CC=C54)F
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C24H23FN4O3/c25-20-8-5-15(14-21-17-3-1-2-4-18(17)22(30)27-26-21)13-19(20)24(32)29-11-9-28(10-12-29)23(31)16-6-7-16/h1-5,8,13,16H,6-7,9-12,14H2,(H,27,30)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
FDLYAMZZIXQODN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Unspecific Target
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer | ICD-11: 2C73 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53) | Driver | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 |
| OVCAR-3 cells | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| Response regulation | Apatinib combined with olaparib-induced ferroptosis via a p53-dependent manner in ovarian cancer. Further studies showed that apatinib combined with olaparib-induced ferroptosis by inhibiting the expression of Nrf2 and autophagy, thereby inhibiting the expression of GPX4. The Nrf2 activator RTA408 and the autophagy activator rapamycin rescued the combination drug-induced ferroptosis. | |||
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer | ICD-11: 2C73 | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 |
| OVCAR-3 cells | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| Response regulation | Apatinib combined with olaparib-induced ferroptosis via a p53-dependent manner in ovarian cancer. Further studies showed that apatinib combined with olaparib-induced ferroptosis by inhibiting the expression of Nrf2 and autophagy, thereby inhibiting the expression of GPX4. The Nrf2 activator RTA408 and the autophagy activator rapamycin rescued the combination drug-induced ferroptosis. | |||
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer | ICD-11: 2C73 | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0134 |
| OVCAR-3 cells | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0465 | |
| Response regulation | Apatinib combined with olaparib-induced ferroptosis via a p53-dependent manner in ovarian cancer. Further studies showed that apatinib combined with olaparib-induced ferroptosis by inhibiting the expression of Nrf2 and autophagy, thereby inhibiting the expression of GPX4. The Nrf2 activator RTA408 and the autophagy activator rapamycin rescued the combination drug-induced ferroptosis. | |||
