Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0164)
| Name |
Nobiletin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Nobiletin; 478-01-3; Hexamethoxyflavone; 3',4',5,6,7,8-Hexamethoxyflavone; 5,6,7,8,3',4'-Hexamethoxyflavone; 2-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetramethoxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one; 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetramethoxychromen-4-one; NSC-76751; CCRIS 9012; UNII-D65ILJ7WLY; D65ILJ7WLY; NSC 76751; CHEBI:7602; 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetramethoxy-4H-chromen-4-one; 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetramethoxy-; NSC-618903; CHEMBL76447; Nobiletin (Hexamethoxyflavone); DTXSID30197275; NSC76751; Flavone, 5,6,7,8,3',4'-hexamethoxy; NOBILETIN (USP-RS); NOBILETIN [USP-RS]; FLAVONE, 3',4',5,6,7,8-HEXAMETHOXY-; SMR000156231; MFCD03273560; CPD000156231; Nobiletin, >=97%; NOBILETIN [INCI]; Spectrum2_001697; Spectrum3_000921; Spectrum4_001020; KBioGR_001519; MLS000574877; MLS000759462; MLS000877030; MLS001424129; Nobiletin, analytical standard; SCHEMBL244029; SPECTRUM1505268; SPBio_001654; MEGxp0_000930; ACon1_000921; GTPL12446; KBio3_001922; DTXCID40119766; 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetramethoxy-chromen-4-one; HMS2051D09; HMS2234A09; HMS3373C14; HMS3393D09; HMS3651G20; HEXAMETHOXYFLAVONE [WHO-DD]; HY-N0155; 3'4'5,6,7,8-Hexamethoxyflavone; BDBM50338976; CCG-38781; LMPK12111468; NSC618903; STL565829; AKOS015965334; NOBILETIN, 20% (Technical Grade); AC-1023; CS-5518; NC00186; SDCCGMLS-0066776.P001; NCGC00095703-01; NCGC00095703-02; NCGC00095703-06; NCGC00169228-01; 5,6,7,8,3'',4''-hexamethoxyflavone; AS-17452; NCI60_041691; FT-0686667; N0871; S2333; SW197566-2; A827343; SR-01000712262; Q-100511; Q2402963; SR-01000712262-5; BRD-K06753942-001-02-0; 2-(3,4-Dimethoxy-phenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetramethoxy-chromen-4-one; 4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13-decahydrocyclododeca[d]oxazole; 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetramethoxy-; 2-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetramethoxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one, 9CI
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
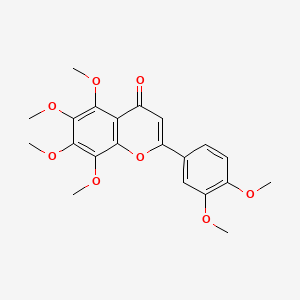 |
||||
| Formula |
C21H22O8
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetramethoxychromen-4-one
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C2=CC(=O)C3=C(O2)C(=C(C(=C3OC)OC)OC)OC)OC
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H22O8/c1-23-13-8-7-11(9-15(13)24-2)14-10-12(22)16-17(25-3)19(26-4)21(28-6)20(27-5)18(16)29-14/h7-10H,1-6H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
MRIAQLRQZPPODS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 2 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma | ICD-11: 2C30 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3B) | Driver | ||
| Pathway Response | Pathways in cancer | hsa05200 | ||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| In Vitro Model | SK-MEL-28 cells | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0526 |
| Response regulation | Nobiletin could induce ferroptosis by regulating the GSK3B-mediated Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signalling pathway in human melanoma cells. Hence, nobiletin stands as a promising drug candidate for melanoma treatment with development prospects. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Melanoma | ICD-11: 2C30 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) | Driver | ||
| Pathway Response | Pathways in cancer | hsa05200 | ||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| In Vitro Model | SK-MEL-28 cells | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0526 |
| Response regulation | Nobiletin could induce ferroptosis by regulating the GSK3B-mediated Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signalling pathway in human melanoma cells. Hence, nobiletin stands as a promising drug candidate for melanoma treatment with development prospects. | |||
Nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Ischemia/reperfusion injury | ICD-11: DB98 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | CHO-S/H9C2 cells | Normal | Cricetulus griseus | CVCL_A0TS | |
| In Vivo Model |
Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (4 weeks old, 90-110 g) were obtained from the Vital River Biological company. Rats were kept in a specific-pathogen-free (SPF) environment, with access to food and tap water at an ambient temperature of 20-22 . All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed. The protocols were reviewed and approved by the Institution of Animal Care and Use Committee of Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University (IACUC, license no. 20200303).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Both ferrostain-1 and nobiletin decreased the expression of ferroptosis-related proteins including Acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4 (ACSL4) and nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4) but not glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) in rats with mature T2DM and cells with HFHG and H/R injury. Nobiletin has therapeutic potential for alleviating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury associated with ACSL4- and NCOA4-related ferroptosis. | ||||
Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 4 (ACSL4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Ischemia/reperfusion injury | ICD-11: DB98 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | CHO-S/H9C2 cells | Normal | Cricetulus griseus | CVCL_A0TS | |
| In Vivo Model |
Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (4 weeks old, 90-110 g) were obtained from the Vital River Biological company. Rats were kept in a specific-pathogen-free (SPF) environment, with access to food and tap water at an ambient temperature of 20-22 . All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed. The protocols were reviewed and approved by the Institution of Animal Care and Use Committee of Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University (IACUC, license no. 20200303).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Both ferrostain-1 and nobiletin decreased the expression of ferroptosis-related proteins including Acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4 (ACSL4) and nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4) but not glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) in rats with mature T2DM and cells with HFHG and H/R injury. Nobiletin has therapeutic potential for alleviating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury associated with ACSL4- and NCOA4-related ferroptosis. | ||||
References
