Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0081)
| Name |
Gefitinib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Gefitinib; 184475-35-2; Iressa; ZD1839; N-(3-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)quinazolin-4-amine; Irressat; gefitinib (zd1839); ZD 1839; ZD-1839; N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(morpholin-4-yl)propoxy]quinazolin-4-amine; C22H24ClFN4O3; Gefitinib (GMP); N-(3-Chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholin-4-ylpropoxy)quinazolin-4-amine; 4-(3'-Chloro-4'-fluoroanilino)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)quinazoline; N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholin-4-ylpropoxy)quinazolin-4-amine; MFCD04307832; CHEMBL939; NSC-759856; S65743JHBS; DTXSID8041034; CHEBI:49668; 3-Chloro-4-Fluoro-N-[(4z)-7-Methoxy-6-(3-Morpholin-4-Ylpropoxy)quinazolin-4(1h)-Ylidene]aniline; N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morpholinyl)propoxy]-4-quinazolinamine; Gefitinib [USAN]; NCGC00159455-02; N-(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)quinazolin-4-amine; DTXCID6021034; 4-Quinazolinamine, N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-(4-morpholinyl)propoxy)-; Iressa(TM); IRE; Iressa (TN); CCRIS 9011; CAS-184475-35-2; SR-00000000262; gefitinibum; UNII-S65743JHBS; Gefitinib (JAN/USAN/INN); Gefitinib [USAN:INN:BAN]; Gefitini; Iressa; 4-Quinazolinamine, N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morpholinyl)propoxy]-; N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-(4-morpholinyl)propoxy)-4-quinazolinamine; gefitinib (iressa); Gefitinib - Iressa; Iressa (AstraZeneca); nchembio866-comp14; Kinome_3321; Kinome_3322; GEFITINIB [INN]; GEFITINIB [JAN]; GEFITINIB [MI]; GEFITINIB [VANDF]; GEFITINIB [MART.]; GEFITINIB [WHO-DD]; SCHEMBL7866; Gefitinib,ZD-1839,Iressa; GEFITINIB [EMA EPAR]; KBioSS_002241; MLS003899193; CU-00000000396-1; BDBM5447; cid_123631; GTPL4941; GEFITINIB [ORANGE BOOK]; GEFITINIB [EP MONOGRAPH]; Gefitinib, >=98% (HPLC); BCPP000221; HMS2089B19; HMS3244M21; HMS3244M22; HMS3244N21; HMS3295A21; HMS3413H08; HMS3654A07; HMS3677H08; HMS3714A05; HMS3748E17; Pharmakon1600-01502274; BCP01365; Tox21_111683; HY-50895G; NSC715055; NSC759856; NSC800105; s1025; STK621310; AKOS000280752; Tox21_111683_1; AB20814; AC-1556; BCP9000718; CCG-220642; CS-0124; DB00317; KS-1204; NSC 759856; NSC-715055; NSC-800105; 4-[(3-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)amino]-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)quinazoline; 4-Quinazolinamine, N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-4-morpholin)propoxy)-; 6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)-N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxyquinazolin-4-amine; NCGC00159455-03; NCGC00159455-04; NCGC00159455-05; NCGC00159455-06; NCGC00159455-08; NCGC00159455-09; NCGC00159455-14; BCB03_000781; BG164498; HY-50895; SMR002204119; SY002154; AM20090619; CS-0622782; FT-0602325; G0546; SW199108-4; EC-000.2409; D01977; EN300-123024; G-4408; K00240; AB01273954-01; AB01273954-02; AB01273954-03; AB01273954_04; A812870; Q417824; Q-201149; SR-00000000262-2; SR-00000000262-3; Gefitinib, EuropePharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Z1546610485; 4-(3'-chloro-4'-fluoroanilino)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)-quinazoline; Gefitinib for system suitability, EuropePharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; (3-CHLORO-4-FLUORO-PHENYL)-[7-METHOXY-6-(3-MORPHOLIN-4-YL-PROPOXY)-QUINAZOLIN-4-YL]-AMINE
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
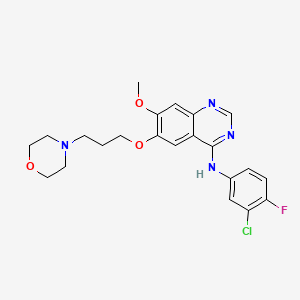 |
||||
| Formula |
C22H24ClFN4O3
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholin-4-ylpropoxy)quinazolin-4-amine
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
COC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)N=CN=C2NC3=CC(=C(C=C3)F)Cl)OCCCN4CCOCC4
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C22H24ClFN4O3/c1-29-20-13-19-16(12-21(20)31-8-2-5-28-6-9-30-10-7-28)22(26-14-25-19)27-15-3-4-18(24)17(23)11-15/h3-4,11-14H,2,5-10H2,1H3,(H,25,26,27)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
XGALLCVXEZPNRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | A-549 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Nude mice (5 weeks) were purchased from SLAC Int. (Shanghai, China). A549 cells (6 x 107 /ml) were collected and mixed with Matrigel (Corning, USA) at a 1:1 ratio by volume. Then, 100 ul cells were injected subcutaneously into the back region of nude mice to generate tumors with a size of 100 mm3 . Mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 5/group): the control group, betulin group (10 mg/kg), gefitinib group (30 mg/kg), and the combined group. The control group was orally administered vehicle, while the betulin group, gefitinib group, and the combined group were orally administered betulin, gefitinib, and betulin plus gefitinib every other day. The tumor size and mice body weight were measured every other day too, and the volume was calculated according to the formula: tumor size (mm3 ) = (length x width2 ) x 0.5.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | The expression of SCL7A11, GPX4, and FTH1, which are negative regulators of ferroptosis, was significantly decreased under the combinative treatment of betulin and gefitinib. Moreover, the positive regulatory protein HO-1 was increased. These findings reiterated that the combination of betulin with gefitinib could trigger ferroptosis in KRASmutant non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. | ||||
Heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | A-549 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Nude mice (5 weeks) were purchased from SLAC Int. (Shanghai, China). A549 cells (6 x 107 /ml) were collected and mixed with Matrigel (Corning, USA) at a 1:1 ratio by volume. Then, 100 ul cells were injected subcutaneously into the back region of nude mice to generate tumors with a size of 100 mm3 . Mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 5/group): the control group, betulin group (10 mg/kg), gefitinib group (30 mg/kg), and the combined group. The control group was orally administered vehicle, while the betulin group, gefitinib group, and the combined group were orally administered betulin, gefitinib, and betulin plus gefitinib every other day. The tumor size and mice body weight were measured every other day too, and the volume was calculated according to the formula: tumor size (mm3 ) = (length x width2 ) x 0.5.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | The expression of SCL7A11, GPX4, and FTH1, which are negative regulators of ferroptosis, was significantly decreased under the combinative treatment of betulin and gefitinib. Moreover, the positive regulatory protein HO-1 was increased. These findings reiterated that the combination of betulin with gefitinib could trigger ferroptosis in KRASmutant non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. | ||||
Ferritin heavy chain (FTH1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | A-549 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Nude mice (5 weeks) were purchased from SLAC Int. (Shanghai, China). A549 cells (6 x 107 /ml) were collected and mixed with Matrigel (Corning, USA) at a 1:1 ratio by volume. Then, 100 ul cells were injected subcutaneously into the back region of nude mice to generate tumors with a size of 100 mm3 . Mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 5/group): the control group, betulin group (10 mg/kg), gefitinib group (30 mg/kg), and the combined group. The control group was orally administered vehicle, while the betulin group, gefitinib group, and the combined group were orally administered betulin, gefitinib, and betulin plus gefitinib every other day. The tumor size and mice body weight were measured every other day too, and the volume was calculated according to the formula: tumor size (mm3 ) = (length x width2 ) x 0.5.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | The expression of SCL7A11, GPX4, and FTH1, which are negative regulators of ferroptosis, was significantly decreased under the combinative treatment of betulin and gefitinib. Moreover, the positive regulatory protein HO-1 was increased. These findings reiterated that the combination of betulin with gefitinib could trigger ferroptosis in KRAS mutant non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. | ||||
