Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0316)
| Name |
Curcumenol
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Curcumenol; 19431-84-6; (+)-Curcumenol; 6H-3a,6-Epoxyazulen-6-ol, 1,2,3,4,5,8a-hexahydro-3,8-dimethyl-5-(1-methylethylidene)-, (3S-(3-alpha,3a-alpha,6-alpha,8a-beta))-; 6H-3a,6-Epoxyazulen-6-ol,1,2,3,4,5,8a-hexahydro-3,8-dimethyl-5-(1-methylethylidene)-, (3S,3aS,6R,8aS)-; (1S,2S,5S,8R)-2,6-Dimethyl-9-propan-2-ylidene-11-oxatricyclo[6.2.1.01,5]undec-6-en-8-ol; BRN 3094585; 5-beta-Guiaia-7(11),9-dien-8-alpha-ol, 5,8-epoxy-; DTXSID0058011; HMS3885G10; HY-N2259; s3874; AKOS030529143; CCG-266822; AC-34181; AS-76068; CS-0019588; Q-100237
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
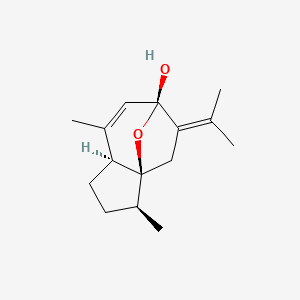
| Structure |
 |
||||
| Formula |
C15H22O2
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
(1S,2S,5S,8R)-2,6-dimethyl-9-propan-2-ylidene-11-oxatricyclo[6.2.1.01,5]undec-6-en-8-ol
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1CCC2C13CC(=C(C)C)C(O3)(C=C2C)O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C15H22O2/c1-9(2)13-8-14-11(4)5-6-12(14)10(3)7-15(13,16)17-14/h7,11-12,16H,5-6,8H2,1-4H3/t11-,12-,14-,15+/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
ISFMXVMWEWLJGJ-NZBPQXDJSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Ferritin heavy chain (FTH1)
| In total 2 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | H19 (IncRNA) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H1299 cells | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 | ||
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| CCD-19Lu cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2382 | ||
| BEAS-2B cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
A subcutaneous tumor-bearing nude mouse model was established by injecting the flank of BALB/c nude mice with 5 x 106 H460 cells. Ten days later, mice were blindly randomized into four groups and intravenously injected with 200 ul ddH2O containing 0.1% CMC-Na and 1% Tween 80, iron chelators DFO (100 mg/kg/day), curcumenol (200 mg/kg/day), and curcumenol combine DFO. Tumor long diameter, short diameter, and body weight were detected every two days after the first drug treatment. The tumor volume calculation formula: (tumor long diameter x tumor short diameter2)/2. Finally, mice were sacrificed. All tumors were collected for immunohistochemical (IHC) staining.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | The natural product curcumenol exerted its antitumor effects on lung cancer by triggering ferroptosis, and the lncRNA H19/miR-19b-3p/FTH1 axis plays an essential role in curcumenol-induced ferroptotic cell death. Mechanistically, we showed that lncRNA H19 functioned as a competing endogenous RNA to bind to miR-19b-3p, thereby enhanced the transcription activity of its endogenous target, ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1), a marker of ferroptosis. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | hsa-miR-19b-3p (miRNA) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H1299 cells | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 | ||
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| CCD-19Lu cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2382 | ||
| BEAS-2B cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
A subcutaneous tumor-bearing nude mouse model was established by injecting the flank of BALB/c nude mice with 5 x 106 H460 cells. Ten days later, mice were blindly randomized into four groups and intravenously injected with 200 ul ddH2O containing 0.1% CMC-Na and 1% Tween 80, iron chelators DFO (100 mg/kg/day), curcumenol (200 mg/kg/day), and curcumenol combine DFO. Tumor long diameter, short diameter, and body weight were detected every two days after the first drug treatment. The tumor volume calculation formula: (tumor long diameter x tumor short diameter2)/2. Finally, mice were sacrificed. All tumors were collected for immunohistochemical (IHC) staining.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | The natural product curcumenol exerted its antitumor effects on lung cancer by triggering ferroptosis, and the lncRNA H19/miR-19b-3p/FTH1 axis plays an essential role in curcumenol-induced ferroptotic cell death. Mechanistically, we showed that lncRNA H19 functioned as a competing endogenous RNA to bind to miR-19b-3p, thereby enhanced the transcription activity of its endogenous target, ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1), a marker of ferroptosis. | ||||
