Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0293)
| Name |
Quisinostat
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
QUISINOSTAT; 875320-29-9; JNJ-26481585; N-Hydroxy-2-(4-((((1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methyl)amino)methyl)piperidin-1-yl)pyrimidine-5-carboxamide; JNJ26481585; JNJ 26481585; N-hydroxy-2-[4-[[(1-methylindol-3-yl)methylamino]methyl]piperidin-1-yl]pyrimidine-5-carboxamide; 9BJ85K1J8S; Quisinostat (JNJ-26481585); 5-Pyrimidinecarboxamide, N-hydroxy-2-(4-((((1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methyl)amino)methyl)-1-piperidinyl)-; N-Hydroxy-2-(4-((((1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methyl)amino)-methyl)piperidin-1-yl)pyrimidine-5-carboxamide; 2-[4-[[(1-methylindol-3-yl)methylamino]methyl]piperidin-1-yl]-~{N}-oxidanyl-pyrimidine-5-carboxamide; Quisinostat [USAN]; Quisinostat [USAN:INN]; UNII-9BJ85K1J8S; GOK; N-Hydroxy-2-[4-({[(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methyl]amino}methyl)piperidin-1-yl]pyrimidine-5-carboxamide; QUISINOSTAT [INN]; Quisinostat (USAN/INN); QUISINOSTAT [WHO-DD]; MLS006011096; GTPL7503; SCHEMBL2360460; CHEMBL2105763; CHEBI:94771; DTXSID90236376; JNJ 26481585 dihydrochloride; HMS3654M19; HMS3747E21; BCP01811; BDBM50105327; MFCD17010272; NSC759657; AKOS016004011; BCP9000803; CS-5065; DB12985; NSC-759657; SB16528; NCGC00346487-01; NCGC00346487-04; AC-27415; AS-16361; HY-15433; N-Hydroxy-2-(4-((((1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methyl)amino)methyl)piperidin-1-yl)pyrimidine-5-carboxamid; N-hydroxy-2-(4-(((1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methylamino)methyl)piperidin-1-yl)pyrimidine-5-carboxamide; SMR004702884; FT-0700499; SW219796-1; EC-000.2337; D10321; A862539; Q7272620; BRD-K83837640-001-01-4; N-hydroxy-2-(4-(((1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methylamino)methyl)piperidin-1-yl)pyrimidine-5-carboxamide dihydrochloride; N-Hydroxy-2-[4-[[[(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methyl]amino]methyl]-1-piperidinyl]-5-pyrimidinecarboxamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
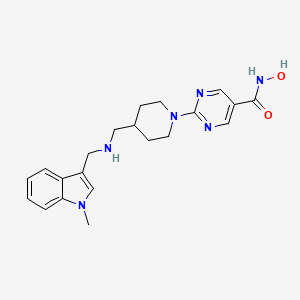 |
||||
| Formula |
C21H26N6O2
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
N-hydroxy-2-[4-[[(1-methylindol-3-yl)methylamino]methyl]piperidin-1-yl]pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CN1C=C(C2=CC=CC=C21)CNCC3CCN(CC3)C4=NC=C(C=N4)C(=O)NO
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H26N6O2/c1-26-14-17(18-4-2-3-5-19(18)26)11-22-10-15-6-8-27(9-7-15)21-23-12-16(13-24-21)20(28)25-29/h2-5,12-15,22,29H,6-11H2,1H3,(H,25,28)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
PAWIYAYFNXQGAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | ICD-11: 2B6E | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||||
| Necroptosis | hsa04217 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| Cell pyroptosis | |||||
| In Vitro Model | CAL-27 cells | Tongue adenosquamous carcinom | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1107 | |
| Tca8113 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6851 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Adult male athymic BALB/c nude mice (20-22 g of 5-week-old mice) were housed in a controlled environment at 23 ± 2 and 40%-70% humidity under a 12 h dark/light cycle with free access to irradiated food and sterile water. A suspension of 6 x 106/100 uL TCA-8113 cells was inoculated subcutaneously into the hind flank region of each nude mouse. The average tumor volume in nude mice reached 100 mm3, and mice were randomly divided into three groups. Quisinostat was formulated in normal saline and administered at 3 and 10 mg/kg/day byintraperitoneal injection. Control mice were given equal volume saline intraperitoneally. The tumor volume and the bodyweight of mice were monitored every three days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Quisinostat could increase the apoptosis rate in the tumor tissues of nude mice. Up-regulation of the expression of p53 and down-regulated expression of GPX4 in cell lines were observed by immunofluorescent staining, and the expression locations of p53 and GPX4 proteins in TSCC cells were observed. Quisinostat may be a potential drug for the treatment of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. | ||||
