Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0289)
| Name |
Forsythoside A
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Forsythoside A; Forsythiaside; 79916-77-1; Forsythiaside A; CHEMBL504363; OUH5BQ893P; CHEBI:5160; MEGxp0_001187; NSC-729638; [(2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-6-[2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy]-4,5-dihydroxy-2-[[(2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxan-3-yl] (E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate; (E)-(2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-6-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenethoxy)-4,5-dihydroxy-2-((((2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)methyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)acrylate; AC1NQZ1W; UNII-OUH5BQ893P; Forsythoside-A; SureCN3318896; SCHEMBL3318896; ACon1_001402; DTXSID801317212; HY-N0028; BDBM50269517; MFCD08460220; NSC729638; s9317; AKOS015897128; CCG-270267; NSC 729638; NCGC00180544-01; [(2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-6-[2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy]-4,5-dihydroxy-2-[[(2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydropyran-2-yl]oxymethyl]tetrahydropyran-3-yl] (E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate; beta-D-Glucopyranoside, 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl 6-O-(6-deoxy-alpha-L-mannopyranosyl)-, 4-(3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-propenoate), (E)-; CS-0007097; A854587; Q-100834; BRD-K62073009-001-01-6; Q27106670; (2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-6-(3,4-dihydroxyphenethoxy)-4,5-dihydroxy-2-((((2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)methyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl (E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)acrylate; .BETA.-D-GLUCOPYRANOSIDE, 2-(3,4-DIHYDROXYPHENYL)ETHYL 6-O-(6-DEOXY-.ALPHA.-L-MANNOPYRANOSYL)-, 4-((2E)-3-(3,4-DIHYDROXYPHENYL)-2-PROPENOATE); .BETA.-D-GLUCOPYRANOSIDE, 2-(3,4-DIHYDROXYPHENYL)ETHYL 6-O-(6-DEOXY-.ALPHA.-L-MANNOPYRANOSYL)-, 4-(3-(3,4-DIHYDROXYPHENYL)-2-PROPENOATE), (E)-
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Investigative
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
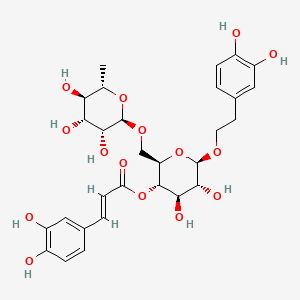 |
||||
| Formula |
C29H36O15
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
[(2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-6-[2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy]-4,5-dihydroxy-2-[[(2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxan-3-yl] (E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OCC2C(C(C(C(O2)OCCC3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)O)O)O)OC(=O)C=CC4=CC(=C(C=C4)O)O)O)O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C29H36O15/c1-13-22(35)23(36)25(38)29(42-13)41-12-20-27(44-21(34)7-4-14-2-5-16(30)18(32)10-14)24(37)26(39)28(43-20)40-9-8-15-3-6-17(31)19(33)11-15/h2-7,10-11,13,20,22-33,35-39H,8-9,12H2,1H3/b7-4+/t13-,20+,22-,23+,24+,25+,26+,27+,28+,29+/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
DTOUWTJYUCZJQD-UJERWXFOSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Alzheimer disease | ICD-11: 8A20 | |||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HT22 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0321 | |
| Neuro-2a cells | Neuroblastoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0470 | ||
| BV-2 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0182 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (permit No. SY201905013) and were conducted in compliance with the ARRIVE guidelines. Eight-month-old B6C3-Tg (APPswePSEN1dE9)/Nju double transgenic male mice (APP/PS1) (genotype: (Appswe) T, (Psen1) T) and age-matched wild-type (WT) (genotype: (Appswe) W, (Psen1) W) male mice were purchased from Nanjing Biomedical Research Institute of Nanjing University. All mice were individually housed at 24 with food and drinking water availablead libitum. After 1 week of adaption in the new environment, WT mice received oral administration of normal saline (10 mL/kg) and were designated as the control group (n = 12). APP/PS1 mice were randomly divided into two groups: the model group (n = 12) received oral administration of normal saline (10 mL/kg) and the agent-treated group (n = 12) received oral treatment with 30 mg/kg FA (L-012-171216, 98.83% purity, Chengdu Herbpurify Co., Ltd., Chengdu, China) beginning on day 8. After 30-day treatment, behavioral experiments were serially performed. The entire treatment protocol lasted for 42 days. Blood samples were collected from the caudal vein. After euthanasia via CO2 inhalation, organs including the brain, liver, spleen, and kidney were collected for further analysis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Forsythoside A treatment exerted anti-ferroptosis and anti-neuroinflammatory effects in erastin-stimulated HT22 cells, and the Nrf2/GPX4 axis played a key role in these effects. Collectively, these results demonstrate the protective effects of FA and highlight its therapeutic potential as a drug component for AD ( Alzheimer's disease) treatment. | ||||
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Alzheimer disease | ICD-11: 8A20 | |||
| Pathway Response | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HT22 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0321 | |
| Neuro-2a cells | Neuroblastoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_0470 | ||
| BV-2 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0182 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (permit No. SY201905013) and were conducted in compliance with the ARRIVE guidelines. Eight-month-old B6C3-Tg (APPswePSEN1dE9)/Nju double transgenic male mice (APP/PS1) (genotype: (Appswe) T, (Psen1) T) and age-matched wild-type (WT) (genotype: (Appswe) W, (Psen1) W) male mice were purchased from Nanjing Biomedical Research Institute of Nanjing University. All mice were individually housed at 24 with food and drinking water availablead libitum. After 1 week of adaption in the new environment, WT mice received oral administration of normal saline (10 mL/kg) and were designated as the control group (n = 12). APP/PS1 mice were randomly divided into two groups: the model group (n = 12) received oral administration of normal saline (10 mL/kg) and the agent-treated group (n = 12) received oral treatment with 30 mg/kg FA (L-012-171216, 98.83% purity, Chengdu Herbpurify Co., Ltd., Chengdu, China) beginning on day 8. After 30-day treatment, behavioral experiments were serially performed. The entire treatment protocol lasted for 42 days. Blood samples were collected from the caudal vein. After euthanasia via CO2 inhalation, organs including the brain, liver, spleen, and kidney were collected for further analysis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Forsythoside A treatment exerted anti-ferroptosis and anti-neuroinflammatory effects in erastin-stimulated HT22 cells, and the Nrf2/GPX4 axis played a key role in these effects. Collectively, these results demonstrate the protective effects of FA and highlight its therapeutic potential as a drug component for AD ( Alzheimer's disease) treatment. | ||||
