Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0262)
| Name |
Liquiritin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Liquiritin; 551-15-5; Liquiritoside; Likviritin; 7-Hydroxyflavanone 4'-O-glucoside; CHEBI:80845; UNII-T0O79T74CD; T0O79T74CD; 4',7-Dihydroxyflavanone 4'-(beta-D-glucopyranoside); Liquiritigenin-4'-O-glucoside; Liquiritigenin-4'-beta-glucoside; DTXSID40203619; 4',7-Dihydroxyflavanone 4'-(beta-D-glucoside); liquiritigenin-4'-beta-D-glucoside; 4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-7-hydroxyflavan-4-one; 7-hydroxyflavanone 4'-O-beta-D-glucoside; liquiritigenin 4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside; (S)-2-(4-(beta-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)phenyl)-2,3-dihydro-7-hydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one; (2S)-7-hydroxy-2-[4-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydropyran-2-yl]oxyphenyl]chroman-4-one; Likviriton; 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 2-(4-(beta-D-glucopyranosyloxy)phenyl)-2,3-dihydro-7-hydroxy-, (S)-; 4-((2S)-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-2-yl)phenyl beta-D-glucopyranoside; 4-[(2S)-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-2-yl]phenyl beta-D-glucopyranoside; MLS000575018; CHEMBL511995; DTXCID20126110; DEMKZLAVQYISIA-ZRWXNEIDSA-N; GLXC-13392; HMS2214B11; HY-N0376; BDBM50479044; MFCD00210526; s3930; AKOS015897117; CCG-268869; 4H-1-benzopyran-4-one, 2-(4-(beta-D-glucopyranosyloxy)phenyl)-2,3-dihydro-7-hydroxy-, (2S)-; AC-34230; AS-74201; SMR000232362; CS-0008920; L0269; C16989; LIQUIRITIGENIN 4'-beta-D-GLUCOPYRANOSIDE; A870271; LIQUIRITIGENIN 4'-.BETA.-D-GLUCOPYRANOSIDE; Q-100625; Q3242316; 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one,2-[4-(b-D-glucopyranosyloxy)phenyl]-2,3-dihydro-7-hydroxy-, (2S)-; (2S)-7-hydroxy-2-(4-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}phenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-4-one; (S)-7-hydroxy-2-(4-((2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yloxy)phenyl)chroman-4-one; (S)-7-Hydroxy-2-[4-((2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-hydroxymethyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-phenyl]-chroman-4-one; (S)-7-Hydroxy-2-[4-((2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-hydroxymethyltetrahydropyran-2-yloxy)phenyl]chroman-4-one; 4H-1-BENZOPYRAN-4-ONE, 2-(4-(.BETA.-D-GLUCOPYRANOSYLOXY)PHENYL)-2,3-DIHYDRO-7-HYDROXY-, (2S)-; 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 2-[4-(?-D-glucopyranosyloxy)phenyl]-2,3-dihydro-7-hydroxy-, (2S)-
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
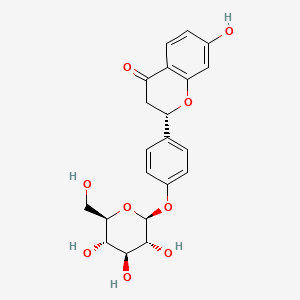 |
||||
| Formula |
C21H22O9
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
(2S)-7-hydroxy-2-[4-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyphenyl]-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1C(OC2=C(C1=O)C=CC(=C2)O)C3=CC=C(C=C3)OC4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H22O9/c22-9-17-18(25)19(26)20(27)21(30-17)28-12-4-1-10(2-5-12)15-8-14(24)13-6-3-11(23)7-16(13)29-15/h1-7,15,17-23,25-27H,8-9H2/t15-,17+,18+,19-,20+,21+/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
DEMKZLAVQYISIA-ZRWXNEIDSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cardiomyopathy | ICD-11: BC43 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | CHO-S/H9C2 cells | Normal | Cricetulus griseus | CVCL_A0TS | |
| In Vivo Model |
The set of animal experiments was designed to evaluate the effectiveness of liquiritin on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity as were as ferroptosis were explored. Mice were randomly divided into 5 groups: (1) the control group; (2) doxorubicin group; (3) the doxorubicin plus liquiritin group (20 mg/kg); (4) the doxorubicin plus liquiritin group (40 mg/kg); (5) the doxorubicin plus liquiritin group (80 mg/kg) (Han et al.2022; Mou et al.2021). The control group and doxorubicin group were given equal volume of 0.5% sodium carboxymethylcellulose; the doxorubicin plus liquiritin groups were given different doses of liquiritin (0.5%) sodium carboxymethylcellulose co-suspension) by intragastric administration 7 days in advance once a daily. On day 8, groups (2), (3), (4), and (5) were given a single intraperitoneal injection of 15 mg/kg of DOX to establish a model of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity; and group (1) was given an equal volume of saline intraperitoneally.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Liquiritin can protect the doxorubicin-induce mice's cardiotoxicity, and its beneficial effect is related to the reduction of ferroptosis through a mechanism involving the regulation of the SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway. | ||||
Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cardiomyopathy | ICD-11: BC43 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | CHO-S/H9C2 cells | Normal | Cricetulus griseus | CVCL_A0TS | |
| In Vivo Model |
The set of animal experiments was designed to evaluate the effectiveness of liquiritin on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity as were as ferroptosis were explored. Mice were randomly divided into 5 groups: (1) the control group; (2) doxorubicin group; (3) the doxorubicin plus liquiritin group (20 mg/kg); (4) the doxorubicin plus liquiritin group (40 mg/kg); (5) the doxorubicin plus liquiritin group (80 mg/kg) (Han et al.2022; Mou et al.2021). The control group and doxorubicin group were given equal volume of 0.5% sodium carboxymethylcellulose; the doxorubicin plus liquiritin groups were given different doses of liquiritin (0.5%) sodium carboxymethylcellulose co-suspension) by intragastric administration 7 days in advance once a daily. On day 8, groups (2), (3), (4), and (5) were given a single intraperitoneal injection of 15 mg/kg of DOX to establish a model of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity; and group (1) was given an equal volume of saline intraperitoneally.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Liquiritin can protect the doxorubicin-induce mice's cardiotoxicity, and its beneficial effect is related to the reduction of ferroptosis through a mechanism involving the regulation of the SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway. | ||||
