Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0257)
| Name |
Aristololactam
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Aristololactam; Aristolactam I; 13395-02-3; Aristololactam I; Aristolactam; Aristololactum; NSC 87406; Aristololactam; Aristolactam; 3G8CFM4T9A; CHEMBL479127; NSC-87406; 8-Methoxybenzo[f]-1,3-benzodioxolo[6,5,4-cd]indol-5(6H)-one; Benzo(f)-1,3-benzodioxolo(6,5,4-cd)indol-5(6H)-one, 8-methoxy-; 14-methoxy-3,5-dioxa-10-azapentacyclo[9.7.1.02,6.08,19.013,18]nonadeca-1(18),2(6),7,11(19),12,14,16-heptaen-9-one; Benzo[f]-1,3-benzodioxolo[6,5,4-cd]indol-5(6H)-one, 8-methoxy-; CCRIS 1545; BRN 0307971; Aristolactam-I; UNII-3G8CFM4T9A; 4-27-00-06628 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); DTXSID60158430; HY-N2013; NSC87406; BDBM50306869; MFCD00797313; AKOS028111118; AC-34507; MS-24190; CS-0018333; FT-0697578; Q-100130; 8-methoxy-[1,3]dioxolo[4',5':4,5]benzo[1,2,3-cd]benzo[f]indol-5(6H)-one; 8-Methoxy-6H-benzo[f][1,3]dioxolo[4'',5'':4,5]benzo[1,2,3-cd]indol-5-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Investigative
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
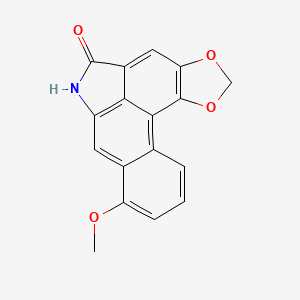 |
||||
| Formula |
C17H11NO4
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
14-methoxy-3,5-dioxa-10-azapentacyclo[9.7.1.02,6.08,19.013,18]nonadeca-1(18),2(6),7,11(19),12,14,16-heptaen-9-one
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
COC1=CC=CC2=C3C4=C(C=C21)NC(=O)C4=CC5=C3OCO5
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C17H11NO4/c1-20-12-4-2-3-8-9(12)5-11-14-10(17(19)18-11)6-13-16(15(8)14)22-7-21-13/h2-6H,7H2,1H3,(H,18,19)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
MXOKGWUJNGEKBH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Aristolochic acid nephropathy | ICD-11: GB55 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group D member 1 (NR1D1) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | mRTECs (Mouse renal tubular epithelial cells) | ||||
| M4100-57 (Mouse renal tubular epithelial cells) | |||||
| In Vivo Model |
Wild-type C57BL/6 mice (eight-week-old, male) were obtained from SPF Biotechnology (Beijing, China). Three sets of animal experiments were performed. In the first set of experiments, male wild-type mice (eight-week-old) were randomly assigned to three groups (n = 6 per group): control group, 2.5 mg/kg AAI group, and 5 mg/kg AAI group. The AAI groups of mice were intraperitoneally injected with AAI (2.5 or 5 mg/kg) once daily for 5 days. The control group of mice were treated with vehicle (corn oil). In the second set of experiments, male Rev-erbfl/fl and Rev-erbkKO mice (eight-week-old) were treated with AAI (5 mg/kg) or vehicle once daily for 5 days by intraperitoneal injection. In the third set of experiments, male wild-type mice (eight-week-old) were randomly divided into the following four groups (n = 6 per group): AAI + SR8278, AAI + DFO, AAI, and vehicle.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Renal REV-ERB protein was significantly increased in aristolochic acid I-treated mice. Furthermore, knockdown of Rev-erb by siRNA or SR8278 (a REV-ERB antagonist) treatment attenuated ALI-induced ferroptosis in mRTECs. SR8278 treatment enhanced the cell survival and GPX4 expression in ALI-treated mRTECs. Taken together, small molecule antagonism of REV-ERB alleviates aristolochic acid I-induced renal injury probably through inhibiting ferroptosis in mice. | ||||
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Aristolochic acid nephropathy | ICD-11: GB55 | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | HK-2 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0302 |
| Response regulation | Long-term administration of medicine-containing Aristolactam I (ALI) was reported to be related to aristolochic acid nephropathy (AAN), which was attributed to ALI-induced nephrotoxicity. ALI dose-dependently inhibited these protein contents of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), which could be partly rescued by Tin-protoporphyrin IX (SnPP) and mitoTEMPO co-treatment. | |||
References
