Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0202)
| Name |
Auranofin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
AURANOFIN; 34031-32-8; (1-Thio-beta-D-glucopyranosato)(triethylphosphine)gold 2,3,4,6-tetraacetate; BCP08217; MFCD00080759; MMV688978; SKF 39162; AKOS026750078; FT-0662343; D78135; A937040; 1-Thio-; A-D-glucopyranosatotriethylphosphine gold-2,3,4,6-tetraacetate; 1-Thio-beta-D-glucopyranosatotriethyl phosphine gold-2,3,4,6-tetraacetate; 3,4,5-Triacetyloxy-6-(acetyloxymethyl) oxane-2-thiolate triethylphosphanium; gold(1+);3,4,5-triacetyloxy-6-(acetyloxymethyl)oxane-2-thiolate;triethylphosphane; SKF-39162; SKF-D-39162; SKF 39162; SKF D 39162; SKFD-39162; SKFD39162
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
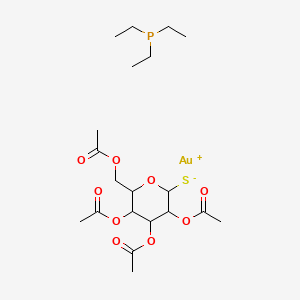 |
||||
|
3D MOL
|
|||||
| Formula |
C20H34AuO9PS
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
gold(1+);3,4,5-triacetyloxy-6-(acetyloxymethyl)oxane-2-thiolate;triethylphosphane
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CCP(CC)CC.CC(=O)OCC1C(C(C(C(O1)[S-])OC(=O)C)OC(=O)C)OC(=O)C.[Au+]
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C14H20O9S.C6H15P.Au/c1-6(15)19-5-10-11(20-7(2)16)12(21-8(3)17)13(14(24)23-10)22-9(4)18;1-4-7(5-2)6-3;/h10-14,24H,5H2,1-4H3;4-6H2,1-3H3;/q;;+1/p-1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
AUJRCFUBUPVWSZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Unspecific Target
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Hemochromatosis | ICD-11: 3B10-3B11 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Thioredoxin reductase 2, mitochondrial (TXNRD2) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | |||
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | ||||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | |
| HEK-293T cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
C57BL/6J mice (7-8 weeks of age, both males and females) were purchased from Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China. Hfe-/-mice were kindly provided by Dr. Nancy C. Andrews. All mice were housed in a specific pathogen-free facility and fed an egg white-based AIN-76A diet containing 50 mg/kg iron (Research Diets, Inc., New Brunswick, NJ).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | High-dose auranofin (AUR) induces ferroptosis and causes lipid peroxidation through inhibition of thioredoxin reductase (TXNRD) activity.In conclusion, TXNRD is a key regulator of ferroptosis, and AUR is a novel activator of hepcidin and ferroptosis via distinct mechanisms, suggesting a promising approach for treating hemochromatosis and hepcidin-deficiency related disorders. | ||||
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12 | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 |
| Hep-G2 cells | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Response regulation | Auranofin/buthionine sulfoxime (BSO) and Erastin/BSO cotreatment alters redox homeostasis by increasing levels of Nrf2 and HO-1 and decreasing GPX4 levels. Targeting these two main ferroptotic pathways simultaneously can overcome chemotherapy resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). | |||
References
