Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0127)
| Name |
Isoliquiritigenin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
isoliquiritigenin; 961-29-5; 2',4,4'-Trihydroxychalcone; (E)-1-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one; 4,2',4'-Trihydroxychalcone; 6'-deoxychalcone; Isoliquiritigen; GU 17; 2',4',4-Trihydroxychalcone; Chalcone, 2',4,4'-trihydroxy-; GU-17; C15H12O4; CCRIS 7676; UNII-B9CTI9GB8F; trihydroxychalcone; B9CTI9GB8F; 42'4'-trihydroxychalcone; 13745-20-5; 2-Propen-1-one, 1-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-, (2E)-; (2E)-1-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one; CHEBI:310312; trans-2',4,4'-trihydroxychalcone; 1-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-propen-1-one; 1-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one; 2-Propen-1-one, 1-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-, (E)-; Acrylophenone, 2',4'-dihydroxy-3-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-; CHEMBL129795; GU17; (E)-1-(2,4-Dihydroxy-phenyl)-3-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-propenone; (2E)-1-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-propen-1-one; (E)-1-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-propen-1-one; 2-PROPEN-1-ONE, 1-(2,4-DIHYDROXYPHENYL)-3-(4-HYDROXYPHENYL)-; (E)-1-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-propene-1-one; 1060-19-1; ILG; SMR000112969; GU17;ISL;Isoliquiritigen; SR-01000075499; EINECS 237-316-5; BRN 1914295; iso-Liquiritigenin; MFCD00075907; ILTG; ISLQ; Isoliquiritigenin, powder; Spectrum5_000612; Lopac0_000681; BSPBio_003411; 1-08-00-00707 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); MLS000438943; MLS002207240; MLS006010045; BIDD:ER0235; SCHEMBL161168; SPECTRUM1504200; cid_638278; MEGxp0_001326; 2',4,4'-Trihydroxy-Chalcone; DTXSID2022466; 2'',4'',4-trihydroxychalcone; 2'',4,4''-trihydroxychalcone; ACon1_000047; CHEBI:94010; TRIHYDROXYCHALCONE [INCI]; BCPP000201; HMS2233H18; HMS3262I03; 2,4''-dihydroxy-4-hydroxychalcone; BCP02312; HY-N0102; Tox21_500681; BDBM50042944; CCG-40334; CMLD3_000056; HB4213; LMPK12120096; s2404; Isoliquiritigenin, analytical standard; AKOS001590146; BCP9000795; CS-1745; DB03285; KS-5256; LP00681; SDCCGMLS-0066751.P001; SDCCGSBI-0050660.P004; NCGC00090504-01; NCGC00090504-02; NCGC00090504-03; NCGC00090504-04; NCGC00090504-05; NCGC00090504-06; NCGC00090504-07; NCGC00090504-08; NCGC00090504-24; NCGC00261366-01; AC-33981; EU-0100681; I0822; SW219658-1; C08650; I 3766; I11575; A845551; 2',4'-Dihydroxy-3-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-Acrylophenone; Q-100904; Q3155537; SR-01000075499-1; SR-01000075499-5; BRD-K33583600-001-03-9; BRD-K33583600-001-04-7; 1-(2,4-Dihydroxy-phenyl)-3-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-propenone; 1-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-prop-2-en-1-one; (E)-1-[2,4-bis(oxidanyl)phenyl]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one; InChI=1/C15H12O4/c16-11-4-1-10(2-5-11)3-8-14(18)13-7-6-12(17)9-15(13)19/h1-9,16-17,19H/b8-3
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Investigative
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
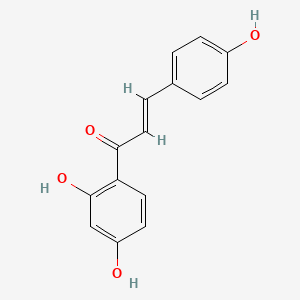 |
||||
| Formula |
C15H12O4
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
(E)-1-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC(=CC=C1C=CC(=O)C2=C(C=C(C=C2)O)O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C15H12O4/c16-11-4-1-10(2-5-11)3-8-14(18)13-7-6-12(17)9-15(13)19/h1-9,16-17,19H/b8-3+
|
||||
| InChIKey |
DXDRHHKMWQZJHT-FPYGCLRLSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Acute kidney failure | ICD-11: GB60 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | High mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HK-2 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0302 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Male C57BL/6 mice (aged 6-8 weeks and weighing 22-25g) were obtained from the Experimental Animal Center, Sichuan Provincial Peoples Hospital, and were fed a standard laboratory diet. LPS and ISL were dissolved in normal saline and 0.5% Tween-20/saline, respectively. AKI mice were developed by intraperitoneal (i.p.) LPS injection. A total of 30 mice were randomly divided into six groups (n = 5): control, ISL, Fer, LPS, LPS plus ISL, and LPS plus Fer. An intraperitoneal injection of LPS (10 mg/kg) was made to induce septic AKI. ISL was administered via gavage at 50 mg/kg 30 min before LPS injection. Mice were dosed intraperitoneally with Fer (Ferrostatin-1, SML0583, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) at 5 mg/kg. Mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation 8 h after LPS injection. Kidney tissue and serum samples were collected concurrently.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Isoliquiritigenin (ISL) attenuates septic acute kidney injury by regulating ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis. ISL inhibited Fe2+ and lipid peroxidation accumulation in LPS-stimulated HK2 cells. It also increased the expression of GPX4 and xCT, reduced the expression of HMGB1 and NCOA4 then attenuated mitochondria injury in renal tubular following LPS stimulation. | ||||
Nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Acute kidney failure | ICD-11: GB60 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HK-2 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0302 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Male C57BL/6 mice (aged 6-8 weeks and weighing 22-25g) were obtained from the Experimental Animal Center, Sichuan Provincial Peoples Hospital, and were fed a standard laboratory diet. LPS and ISL were dissolved in normal saline and 0.5% Tween-20/saline, respectively. AKI mice were developed by intraperitoneal (i.p.) LPS injection. A total of 30 mice were randomly divided into six groups (n = 5): control, ISL, Fer, LPS, LPS plus ISL, and LPS plus Fer. An intraperitoneal injection of LPS (10 mg/kg) was made to induce septic AKI. ISL was administered via gavage at 50 mg/kg 30 min before LPS injection. Mice were dosed intraperitoneally with Fer (Ferrostatin-1, SML0583, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) at 5 mg/kg. Mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation 8 h after LPS injection. Kidney tissue and serum samples were collected concurrently.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Isoliquiritigenin attenuates septic acute kidney injury by regulating ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis. ISL inhibited Fe2+ and lipid peroxidation accumulation in LPS-stimulated HK2 cells. It also increased the expression of GPX4 and xCT, reduced the expression of HMGB1 and NCOA4 then attenuated mitochondria injury in renal tubular following LPS stimulation. | ||||
