Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0115)
| Name |
5-aminolevulinic acid
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
5-Aminolevulinic acid; Aminolevulinic acid; 106-60-5; 5-Amino-4-oxopentanoic acid; 5-Aminolevulinate; Pentanoic acid, 5-amino-4-oxo-; delta-aminolevulinic acid; Aladerm; 5-Amino-4-oxovaleric acid; Aminolevulinate; Kerastick; 5-amino-4-oxo-pentanoic acid; 5-ALA; delta-ALA; 5-amino-levulinate; 5-amino-levulinic acid; 5-Amino-4-oxopentanoate; Levulinic acid, 5-amino-; DALA; CHEMBL601; .delta.-aminolevulinic acid; 4-oxo-5-amino-pentanoic acid; CHEBI:17549; 88755TAZ87; 5-azanyl-4-oxidanylidene-pentanoic acid; delta-aminolevulinate; 5-Aminolaevulinic acid; Aminolevulinic; 5-Aminolaevulinate; SMR000857229; CCRIS 8958; D-aminolevulinic acid; EINECS 203-414-1; BF-200 ALA; UNII-88755TAZ87; FVT; Amino-levulinic acid; 5-aminolevulinic-acid; Spectrum_001582; 5-Amino-4-oxovalerate; SpecPlus_000858; Spectrum2_001662; Spectrum3_001654; Spectrum4_000618; Spectrum5_001505; 5-amino-4-oxo-Pentanoate; SCHEMBL8243; BSPBio_003407; KBioGR_001176; KBioSS_002062; MLS001333097; MLS001333098; BIDD:GT0260; DivK1c_006954; SPBio_001843; GTPL4784; DTXSID8048490; KBio1_001898; KBio2_002062; KBio2_004630; KBio2_007198; KBio3_002627; HMS2231I19; HMS3259E22; HMS3369O14; AMINOLEVULINIC ACID [VANDF]; Levulinic acid, 5-amino- (8CI); BCP23830; AC-054; AMINOLEVULINIC ACID [WHO-DD]; BDBM50240386; LMFA01100055; MFCD00044485; AKOS003587520; 5-AMINOLEVULINIC ACID [MART.]; CS-W000450; DB00855; HY-W000450; NC00601; NCGC00178086-01; NCGC00178086-06; .DELTA.-AMINOLEVULINIC ACID [MI]; AS-30950; Pentanoic acid, 5-amino-4-oxo- (9CI); SBI-0206721.P001; FT-0620021; C00430; D07567; EN300-101562; AB00053763-07; AB00053763-08; AB00053763_09; AB00053763_10; A801471; Q238474; 35BEC718-C970-426A-9859-BF58284C60B4; METHYLAMINOLEVULINATE HYDROCHLORIDE IMPURITY B [EP IMPURITY]; Aminolevulinic Acid;ALA;5-Amino-4-oxopentanoic acid;5-amino-4-oxo-pentanoic acid;5-amino-4-keto-valeric acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Approved
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
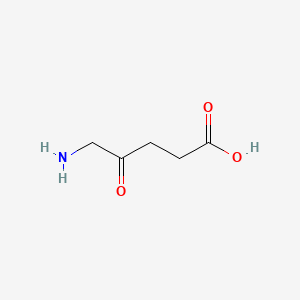 |
||||
| Formula |
C5H9NO3
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
5-amino-4-oxopentanoic acid
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C(CC(=O)O)C(=O)CN
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C5H9NO3/c6-3-4(7)1-2-5(8)9/h1-3,6H2,(H,8,9)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
ZGXJTSGNIOSYLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Oesophageal cancer | ICD-11: 2B70 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | KYSE30 cells | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1351 | |
| KYSE-510 cells | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1354 | ||
| MKN45 cells | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0434 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
KYSE30 cells were subcutaneously inoculated with 5 x 106 cells per site into both flanks on day 0. At 1 week after transplantation, tumor-bearing mice were randomly assigned to one of the following three groups: (1) saline as a control, (2) 10 mg/kg/day of 5-ALA, or (3) 30 mg/kg/day of 5-ALA. The treatment groups were orally administered 5-ALA once daily for 4 weeks, and the control group was orally administered saline during the same period.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Modulation of GPX4 and HMOX1 by 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) induced ferroptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Furthermore, 5-ALA led to an increase in lipid peroxidation and exerted an antitumor effect in various cancer cell lines, which was inhibited by ferrostatin-1. Thus, 5-ALA could be a promising new therapeutic agent for ESCC. | ||||
Heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Oesophageal cancer | ICD-11: 2B70 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | KYSE30 cells | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1351 | |
| KYSE-510 cells | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1354 | ||
| MKN45 cells | Gastric adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0434 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
KYSE30 cells were subcutaneously inoculated with 5 x 106 cells per site into both flanks on day 0. At 1 week after transplantation, tumor-bearing mice were randomly assigned to one of the following three groups: (1) saline as a control, (2) 10 mg/kg/day of 5-ALA, or (3) 30 mg/kg/day of 5-ALA. The treatment groups were orally administered 5-ALA once daily for 4 weeks, and the control group was orally administered saline during the same period.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Modulation of GPX4 and HMOX1 by 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) induced ferroptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Furthermore, 5-ALA led to an increase in lipid peroxidation and exerted an antitumor effect in various cancer cell lines, which was inhibited by ferrostatin-1. Thus, 5-ALA could be a promising new therapeutic agent for ESCC. | ||||
