Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0107)
| Name |
Abietic acid
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ABIETIC ACID; 514-10-3; Sylvic acid; Abietate; l-Abietic acid; Rosin Acid; 7,13-Abietadien-18-oic acid; Kyselina abietova; 13-Isopropylpodocarpa-7,13-dien-15-oic acid; CCRIS 3183; Abietic acid, technical; Abietinic acid; EINECS 208-178-3; NSC 25149; UNII-V3DHX33184; (-)-Abietic acid; CHEBI:28987; AI3-17273; V3DHX33184; MFCD03423567; NSC-25149; (1R,4aR,4bR,10aR)-1,4a-dimethyl-7-(propan-2-yl)-1,2,3,4,4a,4b,5,6,10,10a-decahydrophenanthrene-1-carboxylic acid; 1-Phenanthrenecarboxylic acid, 1,2,3,4,4a,4b,5,6,10,10a-decahydro-1,4a-dimethyl-7-(1-methylethyl)-, (1R,4aR,4bR,10aR)-; DTXSID7022047; 8050-09-7; NSC25149; Podocarpa-7,13-dien-15-oic acid, 13-isopropyl-; NCGC00166273-01; abieta-7,13-dien-18-oate; Kyselina abietova [Czech]; Abietic acid dimer; (1R,4aR,10aR)-1,4a-dimethyl-7-(propan-2-yl)-1,2,3,4,4a,5,6,10,10a-decahydrophenanthrene-1-carboxylic acid; (1R,4AR,4BR,10AR)-1,2,3,4,4A,4B,5,6,10,10A-DECAHYDRO-1,4A-DIMETHYL-7-(1-METHYLETHYL)-1-PHENANTHRENECARBOXYLIC ACID; (1R,4aR,4bR,10aR)-1,4a-dimethyl-7-propan-2-yl-2,3,4,4b,5,6,10,10a-octahydrophenanthrene-1-carboxylic acid; Colophonium; Kolophonium; Highrosin; Shiragiku rosin; Yellow resin; Rondis R; WW Wood rosin; Rosin WW; Hongkong rosin WW; Levamisole resinate; AbietinsA currencyure; Rosin [USP]; Bandis G100; Abietic acid, 90%; Caswell No. 667; BALS 3A; DSSTox_CID_2047; ABIETIC ACID [MI]; D0UQ6U; ABIETIC ACID [INCI]; DSSTox_RID_82575; DSSTox_GSID_47831; SCHEMBL28888; CHEMBL71893; Podocarpa-7, 13-isopropyl-; DTXCID202047; EM 3; UNII-88S87KL877; RSWGJHLUYNHPMX-ONCXSQPRSA-; RSWGJHLUYNHPMX-ONCXSQPRSA-N; BCP14376; EINECS 232-475-7; Tox21_112386; BDBM50442901; KE 709; NSC154789; Podocarpa-7, 13-isopropyl-, dimer; s5122; AKOS016036412; 88S87KL877; Abietic acid, technical, ~75% (GC); CCG-267495; EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 067205; LMPR0104050001; NSC-154789; (5beta)-abieta-7,13-dien-18-oic acid; 1-Phenanthrenecarboxylic acid, 1,2,3,4,4a,4b,5,6,10,10a-decahydro-1,4a-dimethyl-7-(1-methylethyl- )-; AS-35301; NCI60_002007; 13-isopropyl-podocarpa-13-dien-15-oicacid; 10248-55-2; C06087; EC 232-475-7; EN300-1699654; A871292; Q321068; WLN: L B666 EU GUTJ A1 EY1&1 KVQ K1; C32BF2BB-9F97-4AF5-8F5E-06BC0EA97E83; F8881-8980; Z1954802293; 1-PHENANTHRENECARBOXYLIC ACID, 1,2,3,4,4A,4B,5,6,10,10A-DECAHYDRO-1,4A-DIMETHYL-7-(1-METHYLETHYL)-, (1R-(1ALPHA,4ABETA,4BALPHA,10A.ALPHA)).-; 1-Phenanthrenecarboxylic acid, 1,2,3,4,4a,4b,5,6,10,10a-decahydro-1,4a-dimethyl-7-(1-methylethyl-)-; 1-Phenanthrenecarboxylic acid,2,3,4,4a,4b,5,6,10,10a-decahydro-1,4a-dimethyl-7-(1-methylethyl)-, [1R-(1.alpha.,4a.beta.,4b.alpha.,10a.alpha.)]-; 15522-12-0; A9H; InChI=1/C20H30O2/c1-13(2)14-6-8-16-15(12-14)7-9-17-19(16,3)10-5-11-20(17,4)18(21)22/h7,12-13,16-17H,5-6,8-11H2,1-4H3,(H,21,22)/t16-,17+,19+,20+/m0/s1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Investigative
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
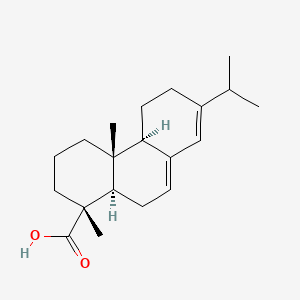 |
||||
| Formula |
C20H30O2
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
(1R,4aR,4bR,10aR)-1,4a-dimethyl-7-propan-2-yl-2,3,4,4b,5,6,10,10a-octahydrophenanthrene-1-carboxylic acid
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)C1=CC2=CCC3C(C2CC1)(CCCC3(C)C(=O)O)C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C20H30O2/c1-13(2)14-6-8-16-15(12-14)7-9-17-19(16,3)10-5-11-20(17,4)18(21)22/h7,12-13,16-17H,5-6,8-11H2,1-4H3,(H,21,22)/t16-,17+,19+,20+/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
RSWGJHLUYNHPMX-ONCXSQPRSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Injury of intra-abdominal organs | ICD-11: NB91 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | AML12 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0140 | |
| In Vivo Model |
APAP-induced liver injury model was induced byintraperitoneal injection 300 mg/kg APAP. The mice of APAP + abietic acid (10, 20, 40 mg/kg) were given abietic acid by intraperitoneal injection 1 h before APAP treatment. The doses of abietic acid used in this study were based on previous studies. Twelve hours later, the mice were sacrificed after anesthesia with 1%pentobarbital (50 mg/kg) injected intraperitoneally and the samples were collected.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | APAP could increase malondialdehyde (MDA) and Fe2+ levels, and decrease ATP and glutathione (GSH) levels, as well as glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) and xCT expression. However, these changes induced by APAP were prevented by abietic acid, indicating abietic acid could inhibit APAP-induced ferroptosis. Furthermore, abietic acid inhibited APAP-induced liver injury, NF-B activation and increased the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1. | ||||
Heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Injury of intra-abdominal organs | ICD-11: NB91 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | AML12 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0140 | |
| In Vivo Model |
APAP-induced liver injury model was induced byintraperitoneal injection 300 mg/kg APAP. The mice of APAP + abietic acid (10, 20, 40 mg/kg) were given abietic acid by intraperitoneal injection 1 h before APAP treatment. The doses of abietic acid used in this study were based on previous studies. Twelve hours later, the mice were sacrificed after anesthesia with 1%pentobarbital (50 mg/kg) injected intraperitoneally and the samples were collected.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | APAP could increase malondialdehyde (MDA) and Fe2+ levels, and decrease ATP and glutathione (GSH) levels, as well as glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) and xCT expression. However, these changes induced by APAP were prevented by abietic acid, indicating abietic acid could inhibit APAP-induced ferroptosis. Furthermore, abietic acid inhibited APAP-induced liver injury, NF-B activation and increased the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1. | ||||
