Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0092)
| Name |
Ursolic Acid
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ursolic acid; 77-52-1; Prunol; Malol; Urson; 3beta-Hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid; Micromerol; (3beta)-3-Hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid; (+)-Ursolic acid; NSC-4060; CCRIS 7123; CHEBI:9908; NSC 167406; ursolic-acid; EINECS 201-034-0; NSC-167406; UNII-P3M2575F3F; AI3-03109; HSDB 7685; P3M2575F3F; CHEMBL169; Urs-12-en-28-oic acid, 3beta-hydroxy-; NSC 4060; .beta.-Ursolic acid; (1S,2R,4aS,6aR,6aS,6bR,8aR,10S,12aR,14bS)-10-hydroxy-1,2,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyl-2,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,13,14b-tetradecahydro-1H-picene-4a-carboxylic acid; Bungeolic acid; URSOLIC ACID (USP-RS); URSOLIC ACID [USP-RS]; 3beta-Hydroxy-12-ursen-28-ic acid; NSC4060; Prunol;Urson;Malol; MFCD00009621; SMR000445681; SR-01000779684; Urs-12-en-28-oic acid, 3-hydroxy-, (3.beta.)-; TNP00103; (3 beta)-3-hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid; 6Q5; Urs-12-en-28-oic acid, 3-hydroxy-, (3beta)-; 3beta-hydroxy-Urs-12-en-28-oic acid; 3B-HYDROXYURS-12-EN-28-OIC ACID; Prestwick3_000089; Ursolic acid, >=90%; URSOLIC ACID [MI]; URSOLIC ACID [HSDB]; URSOLIC ACID [INCI]; SCHEMBL70205; BSPBio_000018; MLS000728569; MLS002154196; MLS002207073; URSOLIC ACID [WHO-DD]; BPBio1_000020; N-Ethylhydroxylaminehydrochloride; DTXSID70883221; Ursolic acid, analytical standard; WCGUUGGRBIKTOS-GPOJBZKASA-N; 3beta-Hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oate; HMS2095A20; HMS2231P19; (1S,2R,4aS,6aS,6bR,8aR,10S,12aR,12bR,14bS)-10-hydroxy-1,2,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a,12b,13,14b-icosahydropicene-4a-carboxylic acid; 3beta-hydroxy-Urs-12-en-28-oate; HY-N0140; BDBM50148911; 3beta-Hydroxy-12-ursen-28-oic Acid; AKOS005228010; AKOS016023773; 3.beta.-hydroxy-Urs-12-en-28-oate; CCG-208282; CS-3799; DB15588; LMPR0106180007; (3beta)-3-Hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oate; (3beta)-3-hydroxy-Urs-12-en-28-oate; AS-35119; 3.beta.-hydroxy-Urs-12-en-28-oic acid; (3beta)-3-hydroxy-Urs-12-en-28-oic acid; AB00513802; U0065; C08988; A839123; Q416260; Q-201916; SR-01000779684-4; SR-01000779684-5; (3.BETA.)-3-HYDROXYURS-12-EN-28-OIC ACID; BRD-K68185022-001-02-3; BRD-K68185022-001-14-8; URSOLIC ACID (CONSTITUENT OF HOLY BASIL LEAF); Ursolic acid, primary pharmaceutical reference standard; AF479D19-631E-48F1-8ABA-FB2A806046FA; URSOLIC ACID (CONSTITUENT OF HOLY BASIL LEAF) [DSC]; (3beta,5beta,18alpha,20beta)-3-hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid; Ursolic acid, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; '(3beta,5beta,18alpha,20beta)-3-hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid'; Ursolic acid, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; (1S,2R,4aS,6aR,6aS,6bR,8aR,10S,12aR,14bS)-10-hydroxy-1,2,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyl-2,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,13,14b-tetradecahydro-1H-picene-4a-carboxylicacid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
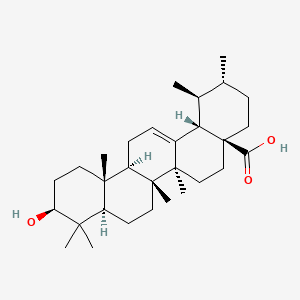 |
||||
| Formula |
C30H48O3
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
(1S,2R,4aS,6aR,6aS,6bR,8aR,10S,12aR,14bS)-10-hydroxy-1,2,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyl-2,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,13,14b-tetradecahydro-1H-picene-4a-carboxylic acid
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1CCC2(CCC3(C(=CCC4C3(CCC5C4(CCC(C5(C)C)O)C)C)C2C1C)C)C(=O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C30H48O3/c1-18-10-15-30(25(32)33)17-16-28(6)20(24(30)19(18)2)8-9-22-27(5)13-12-23(31)26(3,4)21(27)11-14-29(22,28)7/h8,18-19,21-24,31H,9-17H2,1-7H3,(H,32,33)/t18-,19+,21+,22-,23+,24+,27+,28-,29-,30+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
WCGUUGGRBIKTOS-GPOJBZKASA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Ferritin light chain (FTL)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma | ICD-11: 2B51 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| In Vitro Model | HOS cells | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0312 | |
| 143B cells | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2270 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
NU/NU mice (the Fourth Military Medical University, Shaanxi, China) were injected with 143B cells (100 uL, 5 x 107 cells/mL, i.h.). Seven days after the injection, the mice were divided into 6 different groups (n= 3) and intraperitoneally injected with different drugs twice a week. Then, on day 28, the mice were sacrificed, and the tumours in the different groups were weighed. Body weight and tumour size were measured every 3 days from day 7 to day 28. The tumour tissue was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, and cut into 4 um thick sections for haematoxylin-eosin (H&E) and immunofluorescence staining.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Ursolic acid inhibited tumour cell proliferation and promoted the apoptosis of a variety of osteosarcoma cells. Mechanistic studies showed that ursolic acid degraded ferritin by activating autophagy and induced intracellular overload of ferrous ions, leading to ferroptosis. Ferritin, which includes ferritin light peptide 1 (FTL1) and ferritin heavy peptide 1 (FTH1). | ||||
Ferritin heavy chain (FTH1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma | ICD-11: 2B51 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| In Vitro Model | HOS cells | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0312 | |
| 143B cells | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2270 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
NU/NU mice (the Fourth Military Medical University, Shaanxi, China) were injected with 143B cells (100 uL, 5 x 107 cells/mL, i.h.). Seven days after the injection, the mice were divided into 6 different groups (n= 3) and intraperitoneally injected with different drugs twice a week. Then, on day 28, the mice were sacrificed, and the tumours in the different groups were weighed. Body weight and tumour size were measured every 3 days from day 7 to day 28. The tumour tissue was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, and cut into 4 um thick sections for haematoxylin-eosin (H&E) and immunofluorescence staining.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Ursolic acid inhibited tumour cell proliferation and promoted the apoptosis of a variety of osteosarcoma cells. Mechanistic studies showed that ursolic acid degraded ferritin by activating autophagy and induced intracellular overload of ferrous ions, leading to ferroptosis. Ferritin, which includes ferritin light peptide 1 (FTL1) and ferritin heavy peptide 1 (FTH1). | ||||
