Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0044)
| Name |
Lidocaine
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
lidocaine; 137-58-6; Lignocaine; Xylocaine; 2-(Diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide; Lidoderm; Alphacaine; Duncaine; Esracaine; Xylestesin; Cappicaine; Gravocain; Leostesin; Maricaine; Isicaina; Solcain; Xylocain; L-Caine; Isicaine; Xylocitin; Rucaina; Xilina; Xycaine; Cito optadren; Anestacon; Lida-Mantle; Dentipatch; Xylotox; 2-(Diethylamino)-2',6'-acetoxylidide; Lidocainum; Lignocainum; Cuivasil; Jetocaine; Octocaine; Remicaine; Xilocaina; Xyloneural (free base); Dalcaine; 2-Diethylamino-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide; Lidocaina; ELA-Max; Acetamide, 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-; ZTlido; Diethylaminoaceto-2,6-xylidide; 2',6'-Acetoxylidide, 2-(diethylamino)-; alpha-Diethylamino-2,6-dimethylacetanilide; Dilocaine; Versatis; Ztilido; CHEBI:6456; alfa-Dietilamino-2,6-dimetilacetanilide; HSDB 3350; EINECS 205-302-8; NSC 40030; NSC-40030; Lidocaton; Xylocard; Zingo; BRN 2215784; ALGRX 3268; ALGRX-3268; DTXSID1045166; Xylocaine Viscous; UNII-98PI200987; Xylocaine (TN); CHEMBL79; LIDOPEN; N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N(2),N(2)-diethylglycinamide; Diethylaminoacet-2,6-xylidide; MLS000069724; EMLA COMPONENT LIDOCAINE; 98PI200987; DTXCID9025166; ORAQIX COMPONENT LIDOCAINE; SYNERA COMPONENT LIDOCAINE; Xllina; FORTACIN COMPONENT LIDOCAINE; LIDOCAINE COMPONENT OF EMLA; 4-12-00-02538 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); NSC40030; LIDOCAINE COMPONENT OF ORAQIX; LIDOCAINE COMPONENT OF SYNERA; 2-diethylamino-2',6'-acetoxylidide; LANABIOTIC COMPONENT LIDOCAINE; LIDOCAIN COMPONENT OF FORTACINE; N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N~2~,N~2~-diethylglycinamide; Lidocaine (VAN); ROCEPHIN KIT COMPONENT LIDOCAINE; .alpha.-Diethylaminoaceto-2,6-xylidide; LIDOCAINE COMPONENT OF LANABIOTIC; NCGC00015611-10; Xilocaina [Italian]; Lanabiotic; SMR000058189; .alpha.-(Diethylamino)-2,6-acetoxylidide; LIDOCAINE COMPONENT OF ROCEPHIN KIT; DIETHYLAMINO-2,6-DIMETHYLACETANILIDE; Rocephin Kit; .alpha.-Diethylamino-2,6-dimethylacetanilide; .omega.-Diethylamino-2,6-dimethylacetanilide; LIDOCAINE (MART.); LIDOCAINE [MART.]; Lidocainum [INN-Latin]; Lidocaina [INN-Spanish]; N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-N2,N2-diethylglycinamide; 2-(Diethylamino)-N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)ethanamide; EMBOLEX; LIDOCAINE (EP MONOGRAPH); LIDOCAINE [EP MONOGRAPH]; LIDOCAINE (USP MONOGRAPH); LIDOCAINE [USP MONOGRAPH]; DermaFlex; Anestacon Jelly; Xylocaine-Mpf; Zilactin-L; 2-(Diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-acetamide; After Burn Gel; Lidoject-1; Lidoject-2; After Burn Spray; Dentipatch (TN); Octocaine-50; 91484-71-8; CAS-137-58-6; LQZ; Octocaine-100; Xylocaine Test Dose; Xylocaine Endotracheal; Norwood Sunburn Spray; Xylocaine 5% Spinal; 2-2EtN-2MePhAcN; Xylocaine Dental Ointment; MFCD00026733; Xylocaine-Mpf with Glucose; alfa-Dietilamino-2,6-dimetilacetanilide [Italian]; Lidocain; Qualigens; Xyline; Lignocaine base; After Burn Double Strength Gel; LidocaineHClH2O; After Burn Double Strength Spray; Lidocaine [USP:INN:BAN:JAN]; Lidocaine, powder; N1-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N2,N2-diethylglycinamide; Zingo (Salt/Mix); CDS1_000283; Lidocaine (Alphacaine); Spectrum_001118; Lidothesin (Salt/Mix); Xyloneural (Salt/Mix); LIDOCAINE [INN]; LIDOCAINE [JAN]; Opera_ID_385; LIDOCAINE [MI]; LIDOCAINE [HSDB]; LIDOCAINE [INCI]; Maybridge1_002571; Prestwick0_000050; Prestwick1_000050; Prestwick2_000050; Prestwick3_000050; Spectrum2_001343; Spectrum3_001392; Spectrum4_000070; Spectrum5_001549; LIDOCAINE [VANDF]; Lopac-L-5647; Lidaform HC (Salt/Mix); Epitope ID:116205; Lidamantle HC (Salt/Mix); 2', 2-(diethylamino)-; LIDOCAINE [USP-RS]; LIDOCAINE [WHO-DD]; LIDOCAINE [WHO-IP]; Neosporin Plus (Salt/Mix); Lopac0_000669; SCHEMBL15689; BSPBio_000179; BSPBio_001359; BSPBio_003004; KBioGR_000079; KBioGR_000599; KBioSS_000079; KBioSS_001598; 2-Diethylamino-N-(2,6-dimethyl-phenyl)-acetamide; MLS000758263; MLS001074177; MLS001423964; BIDD:GT0342; DivK1c_000174; DivK1c_001323; Lidocaine, analytical standard; SPBio_001525; SPBio_002100; Lidocaine (JP17/USP/INN); LIDOCAINE [GREEN BOOK]; Lidocaine, 1mg/ml in Methanol; BPBio1_000197; GTPL2623; LIDOCAINE [ORANGE BOOK]; SCHEMBL17967359; HMS548M19; KBio1_000174; KBio2_000079; KBio2_001598; KBio2_002647; KBio2_004166; KBio2_005215; KBio2_006734; KBio3_000157; KBio3_000158; KBio3_002224; C01BB01; C05AD01; D04AB01; N01BB02; R02AD02; S01HA07; S02DA01; Lidocaine 1.0 mg/ml in Methanol; LIDOCAINUM [WHO-IP LATIN]; NINDS_000174; Bio1_000379; Bio1_000868; Bio1_001357; Bio2_000079; Bio2_000559; HMS1791D21; HMS1989D21; HMS2051C21; HMS2089E15; HMS2235O14; HMS3371J04; HMS3393C21; HMS3428O07; HMS3651G09; AMY25560; BCP09081; HY-B0185; Tox21_110183; BDBM50017662; NSC789222; s1357; STK552033; AKOS001026768; Tox21_110183_1; CCG-100824; CS-2070; DB00281; NC00074; NSC-789222; SB19118; SDCCGSBI-0050648.P005; WLN: 2N2 & 1VMR B1 F1; .alpha.-Diethylamino-2,6-acetoxylidide; CAS-73-78-9; IDI1_000174; IDI1_033829; NCGC00015611-01; NCGC00015611-02; NCGC00015611-03; NCGC00015611-04; NCGC00015611-05; NCGC00015611-06; NCGC00015611-07; NCGC00015611-08; NCGC00015611-09; NCGC00015611-11; NCGC00015611-12; NCGC00015611-13; NCGC00015611-14; NCGC00015611-15; NCGC00015611-16; NCGC00015611-18; NCGC00015611-31; NCGC00022176-05; NCGC00022176-06; NCGC00022176-07; NCGC00022176-08; NCGC00022176-09; AC-10282; AS-13718; SY052029; 2-(Diethylamino)-2'',6''-acetoxylidide; SBI-0050648.P004; AB00053581; L0156; SW196598-4; A18187; C07073; D00358; M06299; AB00053581-27; AB00053581-28; AB00053581_29; AB00053581_30; EN300-6472705; A833036; Q216935; W-108233; 2-(Diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide #; BRD-K52662033-001-02-6; BRD-K52662033-003-05-5; BRD-K52662033-003-14-7; Z55135799; Lidocaine, British Pharmacopoeia (BP) Reference Standard; Lidocaine, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; N~1~-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N~2~,N~2~-diethylglycinamide; Lidocaine, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide hydrate hydrochloride; Lidocaine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
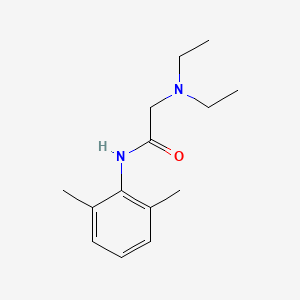 |
||||
| Formula |
C14H22N2O
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CCN(CC)CC(=O)NC1=C(C=CC=C1C)C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C14H22N2O/c1-5-16(6-2)10-13(17)15-14-11(3)8-7-9-12(14)4/h7-9H,5-6,10H2,1-4H3,(H,15,17)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
NNJVILVZKWQKPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)
| In total 2 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | hsa-miR-382-5p (miRNA) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| Cell migration | |||||
| Cell invasion | |||||
| In Vitro Model | SK-OV-3 cells | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 | |
| T-47D cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
SPF-level male nude mice aged 56weeks and weighted around 20 g were purchased from Vitalriver (China). All mice were maintained in a 12-hour circadian rhythm, and had free access to water and food. Cancer cells were subcutaneously injected into the right flank of mice. Lidocaine was administrated to mice at a dose of 1.5 mg per kg injected through the vail tails. For control group, the mice were treated with saline. Tumor volume and mice body weight were monitored every 5 days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | The ovarian and breast cancer cell proliferation was suppressed while cell apoptosis was induced by lidocaine in vitro. Lidocaine attenuated invasion and migration of ovarian and breast cancer cells as well. Regarding the mechanism, lidocaine downregulated solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) expression by enhancing microRNA-382-5p (miR-382-5p) in the cells. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer | ICD-11: 2C73 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | hsa-miR-382-5p (miRNA) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| Cell migration | |||||
| Cell invasion | |||||
| In Vitro Model | SK-OV-3 cells | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0532 | |
| T-47D cells | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0553 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
SPF-level male nude mice aged 56weeks and weighted around 20 g were purchased from Vitalriver (China). All mice were maintained in a 12-hour circadian rhythm, and had free access to water and food. Cancer cells were subcutaneously injected into the right flank of mice. Lidocaine was administrated to mice at a dose of 1.5 mg per kg injected through the vail tails. For control group, the mice were treated with saline. Tumor volume and mice body weight were monitored every 5 days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | The ovarian and breast cancer cell proliferation was suppressed while cell apoptosis was induced by lidocaine in vitro. Lidocaine attenuated invasion and migration of ovarian and breast cancer cells as well. Regarding the mechanism, lidocaine downregulated solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) expression by enhancing microRNA-382-5p (miR-382-5p) in the cells. | ||||
Unspecific Target
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ischemia/reperfusion injury | ICD-11: DB98 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 (MAPK14) | Driver | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | A-549 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 |
| Response regulation | Lidocaine could regulate inflammation, oxidative stress and ferroptosis by blocking the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Thus, lidocaine could act as a novel therapeutic treatment of patients with Lung Ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. | |||
References
