Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0042)
| Name |
Chrysophanol
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Chrysophanol; 481-74-3; CHRYSOPHANIC ACID; 3-Methylchrysazin; 1,8-Dihydroxy-3-methylanthraquinone; Turkey rhubarb; 1,8-dihydroxy-3-methylanthracene-9,10-dione; C.I. Natural Yellow 23; NSC 37132; 1,8-Dihydroxy-3-methyl-9,10-anthracenedione; NSC 646567; 4,5-Dihydroxy-2-methylanthraquinone; Crysophanic acid; Crysophanol; 2-Methyl-4,5-dihydroxyanthraquinone; 3-Methyl-1,8-dihydroxyanthraquinone; C.I. 75400; 1,8-Dihydroxy-3-Methyl-Anthraquinone; CCRIS 3525; CHEBI:3687; Chrysophansaeure; UNII-N1ST8V8RR2; EINECS 207-572-2; N1ST8V8RR2; NSC-37132; NSC-646567; Anthraquinone, 1,8-dihydroxy-3-methyl-; DTXSID6024832; 1,8-dihydroxy-3-methyl-9,10-anthraquinone; 9,10-Anthracenedione, 1,8-dihydroxy-3-methyl-; Chrysophanic acid (1,8-dihydroxy-3-methylanthraquinone); DTXCID704832; 1,8-Dihydroxy-3-methylanthra-9,10-quinone; HSDB 8483; NSC646567; Archinin; Rumicin; MFCD00001208; TURKEY-RHUBARB; RHENIC ACID; Spectrum_000792; Chrysophanic Acid,(S); SpecPlus_000321; Spectrum2_000043; Spectrum3_001183; Spectrum4_001477; Spectrum5_000153; 1,8-dihydroxy-3-methyl-anthracene-9,10-dione; BSPBio_002825; KBioGR_002053; KBioSS_001272; SPECTRUM300545; MLS000574888; CHEMBL41092; DivK1c_006417; SCHEMBL308131; SPBio_000165; CHRYSOPHANIC ACID [MI]; 9, 1,8-dihydroxy-3-methyl-; Chrysophanic acid (Chrysophanol); Chrysophanic acid - Chrysophanol; Chrysophanol, analytical standard; KBio1_001361; KBio2_001272; KBio2_003840; KBio2_006408; KBio3_002325; HMS3656G17; CHRYSOPHANIC ACID [WHO-DD]; BCP23439; EX-A6777; NSC37132; Tox21_202499; Anthraquinone,8-dihydroxy-3-methyl-; BDBM50455992; CCG-38348; LMPK13040006; s2406; STL564344; 3-Methyl-1, 8-dihydroxyanthraquinone; 4, 5-Dihydroxy-2-methylanthraquinone; AKOS015905000; AC-7980; BCP9000004; DS-9706; SDCCGMLS-0066504.P001; NCGC00091823-01; NCGC00091823-02; NCGC00091823-03; NCGC00091823-04; NCGC00091823-05; NCGC00260048-01; CAS-481-74-3; HY-13595; SMR000156239; 1,8-Dihydroxy-3-methylanthraquinone, 98%; 8,9-dihydroxy-6-methyl-1,10-anthraquinone; C2505; FT-0623813; SW219732-1; 1,8-Dihydroxy-3-methylanthra-9,10-quinone #; EN300-7401332; A827496; N-(diaminomethylene)formamide;3-METHYLCHRYSAZIN; SR-01000712223; 1,8-Dihydroxy-3-methyl-9,10-anthracenedione, 9CI; Q-100527; SR-01000712223-2; BRD-K59284035-001-02-0; BRD-K59284035-001-03-8; Q15410875; 9,10-Anthracenedione, 1,8-dihydroxy-3-methyl- (9CI); 1,8-DIHYDROXY-3-METHYL-9,10-DIHYDROANTHRACENE-9,10-DIONE
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
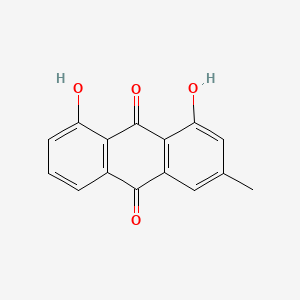 |
||||
| Formula |
C15H10O4
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
1,8-dihydroxy-3-methylanthracene-9,10-dione
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1=CC2=C(C(=C1)O)C(=O)C3=C(C2=O)C=CC=C3O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C15H10O4/c1-7-5-9-13(11(17)6-7)15(19)12-8(14(9)18)3-2-4-10(12)16/h2-6,16-17H,1H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
LQGUBLBATBMXHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver fibrosis | ICD-11: DB93 | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HSC-T6 cells | Normal | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0315 |
| Response regulation | Chrysophanol significantly induced HBx-transfected HSC-T6 death by inducing ferroptosis, as demonstrated by lipid ROS accumulation and upregulation of expression of ER markers, such as Bip, CHOP, and p-IRE1, and ferroptotic markers, such as GPX4 and SLC7A11. Therefore, chrysophanol may exert ferroptotic effects on activated HSCs to prevent liver fibrosis. | |||
Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Liver fibrosis | ICD-11: DB93 | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HSC-T6 cells | Normal | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0315 |
| Response regulation | Chrysophanol significantly induced HBx-transfected HSC-T6 death by inducing ferroptosis, as demonstrated by lipid ROS accumulation and upregulation of expression of ER markers, such as Bip, CHOP, and p-IRE1, and ferroptotic markers, such as GPX4 and SLC7A11. Therefore, chrysophanol may exert ferroptotic effects on activated HSCs to prevent liver fibrosis. | |||
