Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0018)
| Name |
Ferulic acid
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ferulic acid; trans-Ferulic Acid; 1135-24-6; 537-98-4; 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid; trans-4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid; 3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)acrylic acid; (E)-Ferulic acid; Coniferic acid; ferulate; 2-Propenoic acid, 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-; Ferulic acid, trans-; 3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-propenoic acid; (E)-3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-propenoic acid; (2E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid; Cinnamic acid, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-; 3-methoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic acid; Fumalic acid; Cinnamic acid, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-, (E)-; (E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid; UNII-AVM951ZWST; (E)-4'-Hydroxy-3'-methoxycinnamic acid; 2-Propenoic acid, 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-, (2E)-; AVM951ZWST; 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy cinnamic acid; EINECS 208-679-7; Cinnamic acid, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-, trans-; MFCD00004400; 2-Propenoic acid, 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-, (E)-; (E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)acrylic acid; CCRIS 3256; CCRIS 7127; CIS-FERULICACID; CHEBI:17620; HSDB 7663; NSC 2821; NSC-2821; EINECS 214-490-0; NSC 51986; NSC-51986; (2E)-3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)acrylic acid; NSC 674320; (E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid; Fumalic acid (Ferulic acid); 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamate; (2E)-3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-propenoic acid; (E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)prop-2-enoic acid; CHEMBL32749; 3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propenoic acid; NSC2821; 3-Methoxy-4-hydroxy-trans-cinnamate; NSC-674320; 97274-61-8; 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy-trans-cinnamic acid; (E)-Ferulate; trans-Ferulic Acid (purified by sublimation); Trans-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)acrylic acid; 4-HYDROXY-3-METHOXY-D3-CINNAMIC ACID; FERULIC ACID (USP-RS); FERULIC ACID [USP-RS]; CINNAMIC ACID,4-HYDROXY,3-METHOXY FERULIC ACID; caffeic acid 3-methyl ether; ferulic acid, (E)-isomer; SMR000112202; 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid; DTXSID5040673; ferulasaure; Ferulicacid; trans-Ferulate; (E)-3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-propenoate; CCRIS 7575; trans-FerulicAcid; Ferulic acid, E-; (E)-Coniferic acid; trans-4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamicacid; Ferulic acid (M5); Ferulic Acid ,(S); FERULIC-ACID; Spectrum5_000554; bmse000459; bmse000587; bmse010211; FERULIC ACID [MI]; trans-Ferulic acid, 99%; FERULIC ACID [HSDB]; FERULIC ACID [INCI]; SCHEMBL15673; BSPBio_003168; MLS001066385; MLS001332483; MLS001332484; MLS002207079; MLS006011435; SPECTRUM1501017; trans-Ferulic acid, >=99%; FERULIC ACID [WHO-DD]; DTXCID3020673; DTXSID70892035; HMS1921D05; HMS2269P04; (E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamate; trans-4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamate; BCP21231; BCP21789; HY-N0060; NSC51986; STR00961; (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-Cinnamate; TRANS-FERULIC ACID [WHO-DD]; (E)4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid; AC7905; BBL010345; BDBM50214744; CCG-38860; s2300; STK801551; AKOS000263735; AC-7965; BCP9000163; DB07767; PS-3435; SDCCGMLS-0066667.P001; trans-3-methoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic acid; (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-Cinnamic acid; 3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propenoate; 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid, trans; NCGC00094889-01; NCGC00094889-02; NCGC00094889-03; NCGC00094889-04; AC-10321; BS-17543; SMR004703246; AM20060784; CS-0007108; F1257; H0267; SW219616-1; EN300-16798; C01494; A829775; FERULIC ACID (CONSTITUENT OF BLACK COHOSH); Q417362; SR-01000765539; (2E)-3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-propenoate; (E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoicacid; J-002980; SR-01000765539-3; Z56782558; (E)-3-(3-methoxy-4-oxidanyl-phenyl)prop-2-enoic acid; FERULIC ACID (CONSTITUENT OF BLACK COHOSH) [DSC]; 055E203F-B305-4B7F-8CE7-F9C0C03AB609; 3986A1BE-A670-4B06-833B-E17253079FD8; Ferulic acid, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; trans-Ferulic acid, certified reference material, TraceCERT(R); Diethyl2-(acetamido)-2-(2-(bromomethyl)-5-nitrobenzyl)malonate; Ferulic acid, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; trans-Ferulic acid, matrix substance for MALDI-MS, >=99.0% (HPLC); Ferulic Acid, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material; 831-85-6; InChI=1/C10H10O4/c1-14-9-6-7(2-4-8(9)11)3-5-10(12)13/h2-6,11H,1H3,(H,12,13
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Patented
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
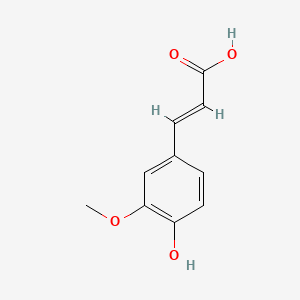 |
||||
| Formula |
C10H10O4
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
(E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
COC1=C(C=CC(=C1)C=CC(=O)O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C10H10O4/c1-14-9-6-7(2-4-8(9)11)3-5-10(12)13/h2-6,11H,1H3,(H,12,13)/b5-3+
|
||||
| InChIKey |
KSEBMYQBYZTDHS-HWKANZROSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Sepsis | ICD-11: 1G40 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | MLE-12 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_3751 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Briefly, female BALB/c mice (6-8 weeks, weighing 20-25 g, purchased from Hunan SJA Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd., Changsha, Hunan, China) were raised in specific pathogen-free conditions under controlled temperature (23-25 ) and humidity (40-80%) as well as a 12 h dark/light cycle for 1 week of acclimation. They were fed a standard chow diet and waterad libitum. Mice were anaesthetised with 2% isoflurane inhalation and underwent moderate caecal ligation and puncture in accordance with a previously reported protocol (Rittirsch etal.2009). Meanwhile, mice in the control groups were subjected to a sham operation. Buprenorphin (0.05 mg/kg) was injected for postoperative analgesia, and all mice were placed in cages immediately after the surgical procedures with free access to water and food (Rittirsch etal. 2009).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Collectively, our data highlighted the alleviatory role of ferulic acid in sepsis-induced ALI by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and inhibiting ferroptosis, offering a new basis for sepsis treatment. | ||||
Heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Sepsis | ICD-11: 1G40 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | MLE-12 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_3751 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Briefly, female BALB/c mice (6-8 weeks, weighing 20-25 g, purchased from Hunan SJA Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd., Changsha, Hunan, China) were raised in specific pathogen-free conditions under controlled temperature (23-25 ) and humidity (40-80%) as well as a 12 h dark/light cycle for 1 week of acclimation. They were fed a standard chow diet and waterad libitum. Mice were anaesthetised with 2% isoflurane inhalation and underwent moderate caecal ligation and puncture in accordance with a previously reported protocol (Rittirsch etal.2009). Meanwhile, mice in the control groups were subjected to a sham operation. Buprenorphin (0.05 mg/kg) was injected for postoperative analgesia, and all mice were placed in cages immediately after the surgical procedures with free access to water and food (Rittirsch etal. 2009).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Collectively, our data highlighted the alleviatory role of ferulic acid in sepsis-induced ALI by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and inhibiting ferroptosis, offering a new basis for sepsis treatment. | ||||
