Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0015)
| Name |
Rotenone
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
rotenone; 83-79-4; Dactinol; Paraderil; Barbasco; Tubatoxin; (-)-Rotenone; (-)-cis-Rotenone; Rotocide; Derrin; Derris; Rotenon; Nicouline; Ronone; Canex; Deril; Liquid Derris; Cube-Pulver; Dri-Kil; Rotessenol; Noxfire; Rotefive; Rotefour; Rotenox; Cubor; Haiari; Mexide; Chem-Mite; Cenol garden dust; Curex flea duster; Tubotoxin; Gerane; Prentox; Ro-Ko; Synpren; Derris (insecticide); Pb-nox; Rotenox 5EC; 5'-beta-Rotenone; Green Cross Warble Powder; Caswell No. 725; Extrax; Rotenone, dehydro; Foliafume E.C.; ENT 133; Rotenone, commercial; CCRIS 895; HSDB 1762; NCI-C55210; 5'beta-Rotenone; EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 071003; AI3-00133; C23H22O6; NSC26258; Rotenona; Derris resins; MLS000738056; CHEMBL429023; 1,2,12,12a-Tetrahydro-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(1-methylethenyl)-(1)benzopyrano(3,4-b)furo(2,3-h)(1)benzopyran-6(6aH)-one; DTXSID6021248; CHEBI:28201; 03L9OT429T; Rotacide E.C.; CUBE; NSC-26258; (1)Benzopyrano(3,4-b)furo(2,3-h)(1)benzopyran-6(6aH)-one, 1,2,12,12a-tetrahydro-2-alpha-isopropenyl-8,9-dimethoxy-; (12aS,6aS,2R)-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(1-methylvinyl)-1,2-dihydrochromano[3,4-b]furano [2,3-h]chroman-6-one; (2R,6aS,12aS)-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1,2,12,12a-tetrahydrochromeno[3,4-b]furo[2,3-h]chromen-6(6aH)-one; (2R-(2alpha,6aalpha,12aalpha))-1,2,12,12a-Tetrahydro-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(1-methylethenyl)(1)benzopyrano(3,4-b)furo(2,3-h)benzopyran-6(6aH)-one; 1,2,12,12aalpha-Tetrahydro-2a-isopropenyl-8,9-dimethoxy(1)benzopyrano(3,4-b)furo(2,3-h)(1)benzopyran-6(6aH)-one; NCGC00017358-05; Nekoe; (1)Benzopyrano(3,4-b)furo(2,3-h)(1)benzopyran-6(6aH)-one, 1,2,12,12a-tetrahydro-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(1-methylethenyl)-, (2R-(2alpha,6aalpha,12aalpha))-; (1S,6R,13S)-16,17-dimethoxy-6-prop-1-en-2-yl-2,7,20-trioxapentacyclo[11.8.0.03,11.04,8.014,19]henicosa-3(11),4(8),9,14,16,18-hexaen-12-one; (2R,6aS,12aS)-1,2,12,12a-Tetrahydro-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(1-methylethenyl)-[1]benzopyrano[3,4-b]furo[2,3-h][1]benzopyran-6(6aH)-one; (2R,6aS,12aS)-1,2,6,6a,12,12a-hexahydro-2-isopropenyl-8,9-dimethoxychromeno(3,4-b)furo(2,3-h)chromen-6-one; [2R-(2alpha,6aalpha,12aalpha)]-1,2,12,12a-tetrahydro-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(1-methylethenyl)[1]benzopyrano[3,4-b]furo[2,3-H][1]benzopyran-6(6aH)-one; Rotenona [Spanish]; DTXCID901248; Rotenone [BSI:ISO]; Protax; 5'.beta.-Rotenone; CAS-83-79-4; (1)Benzopyrano(3,4-b)furo(2,3-h)(1)benzopyran-6(6aH)-one, 1,2,12,12a-tetrahydro-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(1-methylethenyl)-, (2R,6aS,12aS)-; (2R,6aS,12aS)-1,2,6,6a,12,12a- hexahydro-2-isopropenyl-8,9- dimethoxychromeno[3,4-b] furo(2,3-h)chromen-6-one; (2R,6aS,12aS)-1,2,6,6a,12,12a-hexahydro-2-isopropenyl-8,9-dimethoxychromeno[3,4-b]furo[2,3-h]chromen-6-one; (2R,6aS,12aS)-2-isopropenyl-8,9-dimethoxy-1,2,12,12a-tetrahydrochromeno[3,4-b]furo[2,3-h]chromen-6(6aH)-one; (2R,6aS,12aS)-8,9-Dimethoxy-2-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1,2,12,12a-tetrahydrofuro[2',3':7,8][1]benzopyrano[2,3-c][1]benzopyran-6(6aH)-one; [1]Benzopyrano[3,4-b]furo[2,3-h][1]benzopyran-6(6aH)-one, 1,2,12,12a-tetrahydro-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(1-methylethenyl)-, (2R,6aS,12aS)-; SR-01000076110; EINECS 201-501-9; NSC 26258; Rotenoid; Roteonone; UNII-03L9OT429T; WLN: T G5 D6 B666 CV HO MO POT&TT&J IY1&U1 SO1 TO1; 5''beta-rotenone; 5'b-Rotenone; Rotocide E.C.; (1)Benzopyrano[3,3-h](1)benzopyran-6(6aH)-one, 1,2,12,12a-tetrahydro-2-.alpha.-iospropenyl-8,9-dimethoxy-; [1]Benzopyrano[3,3-h][1]benzopyran-6(6a.alpha.H)-one, 1,2,12,12a.alpha.-tetrahydro-2.alpha.-isopropenyl-8,9-dimethoxy-; [1]Benzopyrano[3,3-h][1]benzopyran-6(6aH)-one, 1,2,12,12a-tetrahydro-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(1-methylethenyl)-, [2R-(2.alpha.,6a.alpha.,12a.alpha.)]-; [1]Benzopyrano[3,4-b]furo[2,3-h][1]benzopyran-6(6aH)-one, 1,2,12,12a-tetrahydro-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(1-methylethenyl)-, [2R-(2alpha,6aalpha,12aalpha)]-; Derris, JMAF; Prestwick_542; Rotenone (7CI); Rotenone, >=95%; Spectrum_000065; ROTENONE [HSDB]; ROTENONE [ISO]; ROTENONE [MI]; Spectrum2_000457; Spectrum3_000158; Spectrum4_001638; Spectrum5_000455; ROTENONE [MART.]; Lopac0_001112; SCHEMBL42253; BSPBio_001896; isopropenyl(dimethoxy)[?]one; KBioGR_002075; KBioSS_000465; SPECTRUM200013; (2R-(6aalpha,12aalpha)-1,2-Dihydro-2-isopropenyl-8,9-dimethoxychromano(3,4-b)furo(2,3-h)chroman-6-on; DivK1c_000947; ROTENONE [GREEN BOOK]; SPBio_000534; HMS502P09; KBio1_000947; KBio2_000465; KBio2_003033; KBio2_005601; KBio3_001116; inhibits NADH2 oxidation to NAD; NSC8505; JUVIOZPCNVVQFO-HBGVWJBISA-N; NINDS_000947; HMS3263O06; BCP07278; HY-B1756; NSC-8505; TNP00301; Tox21_110819; Tox21_201904; Tox21_300695; Tox21_501112; BDBM50135527; CCG-39886; HB5398; LMPK12060007; AKOS004910398; Tox21_110819_1; CS-6067; DB11457; LP01112; SDCCGMLS-0066415.P001; SDCCGSBI-0051081.P003; IDI1_000947; Rotenone 100 microg/mL in Acetonitrile; NCGC00017358-01; NCGC00017358-02; NCGC00017358-03; NCGC00017358-04; NCGC00017358-06; NCGC00017358-07; NCGC00017358-08; NCGC00017358-09; NCGC00017358-10; NCGC00017358-11; NCGC00017358-14; NCGC00017358-15; NCGC00017358-22; NCGC00094382-01; NCGC00094382-02; NCGC00094382-03; NCGC00094382-04; NCGC00094382-05; NCGC00254603-01; NCGC00259453-01; NCGC00261797-01; AC-31290; AS-10183; NCI60_002093; SMR000393729; EU-0101112; R0090; Rotenone, PESTANAL(R), analytical standard; C07593; R 8875; Q412388; SR-01000076110-2; SR-01000076110-5; SR-01000076110-6; W-104134; BRD-K08316444-001-01-9; BRD-K08316444-001-05-0; (2R,6AS,12AS)-1,2,12,12A-TETRAHYDRO-8,9-DIMETHOXY-2-(1-METHYLETHENYL)(1)BENZOPYRANO(3,4-B)FURO(2,3-H)(1)BENZOPYRAN-6(6AH)-ONE; (2R-(6aalpha,12aalpha)-1,2-Dihydro-2-isopropenyl-8,9-dimethoxychromano(3,4-b)furo(2,3-h)chroman-6-one; [1]Benzopyrano[3,3-h][1]benzopyran-6(6aH)-one, 1,2,12,12a-tetrahydro-2-.alpha.-isopropenyl-8,9-dimethoxy-; [1]Benzopyrano[3,3-h][1]benzopyran-6(6aH)-one, 1,2,12,12a-tetrahydro-2-isopropenyl-8,9-dimethoxy-; [1]Benzopyrano[3,4-b]furo[2,3-h][1]benzopyran-6(6aalphaH)-one, 1,2,12,12aalpha-tetrahydro-2alpha-isopropenyl-8,9-dimethoxy- (8CI); [1]Benzopyrano[3,4-b]furo[2,3-h][1]benzopyran-6(6aH)-one, 1,2,12,12a-tetrahydro-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(1-methylethenyl)-, (2R,6aS,12aS)- (9CI); 1,2,12,12a-Tetrahydro-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(1-methylethenyl)-[1]benzopyrano[3,4-b]furo[2,3-h][1]benzopyran-6(6aH)-one, 9CI; Tubatoxin 1,2,12,12a,-Tetrahydro-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(1-methylethenyl)-[1]benzopyrano[3,4-b]furo[2,3-h][1]-benzopyran-6(6aH)-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Approved
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
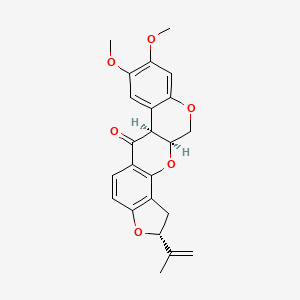 |
||||
| Formula |
C23H22O6
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
(1S,6R,13S)-16,17-dimethoxy-6-prop-1-en-2-yl-2,7,20-trioxapentacyclo[11.8.0.03,11.04,8.014,19]henicosa-3(11),4(8),9,14,16,18-hexaen-12-one
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC(=C)C1CC2=C(O1)C=CC3=C2OC4COC5=CC(=C(C=C5C4C3=O)OC)OC
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C23H22O6/c1-11(2)16-8-14-15(28-16)6-5-12-22(24)21-13-7-18(25-3)19(26-4)9-17(13)27-10-20(21)29-23(12)14/h5-7,9,16,20-21H,1,8,10H2,2-4H3/t16-,20-,21+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
JUVIOZPCNVVQFO-HBGVWJBISA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Unspecific Target
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Intracerebral hemorrhage | ICD-11: 8B00 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | 60S ribosomal protein L8 (RPL8) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Six-to-eight week old male ICR mice were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). All animal procedures have been approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Ruijin hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Shanghai, China). Efforts were made as much as possible to reduce the number of mice used and to minimize suffering. Herein, a total of 51 mice were randomly divided into 3 groups: (i) sham group (n = 15), (ii) ICH group (n = 18), and (iii) ICH + Rot group (n = 18). To be specific, the current study was divided into two parts of the experimental design. Part 1: to observe the effects of Rot on the mitochondria-related genes, iron levels, MDA levels, SOD activity, hematoma volume, brain edema, and ultrastructural changes of mitochondria, animals were randomly divided into the sham group (n = 9), ICH group (n = 12), and ICH + Rot group (n = 12). All mice were euthanized at 3 d after operation and brain samples were harvested, as per our previously described reports. Part 2: to observe the effect of Rot on neurological deficits following ICH, 18 mice were randomly divided into additional 3 groups (sham group, ICH group, and ICH + Rot group). We evaluated mNSS scores at 1, 3, 7, and 14 days after ICH. We also assessed the memory function with the MWM test at 14 days after ICH.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Intracerebral hemorrhage induced significant mitochondrial dysfunction and that mitochondrial inhibitor rotenone can trigger and enhance neuronal ferroptosis. The ferroptosis protein markers ACSL4, COX-2, xCT, RPL8, and GPX4 were significantly upregulated in the hemin group. Rot treatment further enhanced hemin-induced upregulation of ACSL4, COX-2, xCT, RPL8, and GPX4 levels. | ||||
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Intracerebral hemorrhage | ICD-11: 8B00 | |||
| Pathway Response | Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | |||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | rPCNs (Rat primary cortical neurons) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Six-to-eight week old male ICR mice were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). Herein, a total of 51 mice were randomly divided into 3 groups: (i) sham group (n = 15), (ii) ICH group (n = 18), and (iii) ICH + Rot group (n = 18). All mice were euthanized at 3 d after operation and brain samples were harvested, as per our previously described reports.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Single rotenone administration markedly inhibited neuronal viability, promoted iron accumulation, increased malondialdehyde (MDA) contents, decreased total superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, and downregulated ferroptosis-related proteins RPL8, COX-2, xCT, ASCL4, and GPX4 in primary neurons. Together, our data revealed that intracerebral hemorrhage induced significant mitochondrial dysfunction and that mitochondrial inhibitor rotenone can trigger and enhance neuronal ferroptosis. | ||||
