Ferroptosis Target Information
General Information of the Ferroptosis Target (ID: TAR10043)
| Target Name | Diamine acetyltransferase 1 (SAT1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Polyamine N-acetyltransferase 1; Putrescine acetyltransferase ; Spermidine/spermine N(1)-acetyltransferase 1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene Name | SAT1 | ||||
| Sequence |
MAKFVIRPATAADCSDILRLIKELAKYEYMEEQVILTEKDLLEDGFGEHPFYHCLVAEVP
KEHWTPEGHSIVGFAMYYFTYDPWIGKLLYLEDFFVMSDYRGFGIGSEILKNLSQVAMRC RCSSMHFLVAEWNEPSINFYKRRGASDLSSEEGWRLFKIDKEYLLKMATEE Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Family | Acetyltransferase family | ||||
| Function |
Enzyme which catalyzes the acetylation of polyamines. Substrate specificity: norspermidine = spermidine >> spermine > N(1)- acetylspermine. This highly regulated enzyme allows a fine attenuation of the intracellular concentration of polyamines. Also involved in the regulation of polyamine transport out of cells. Also acts on 1,3- diaminopropane and 1,5-diaminopentane .
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene ID | 6303 | ||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Target Type | Driver Suppressor Marker | ||||
| Mechanism Diagram | Click to View the Original Diagram | ||||
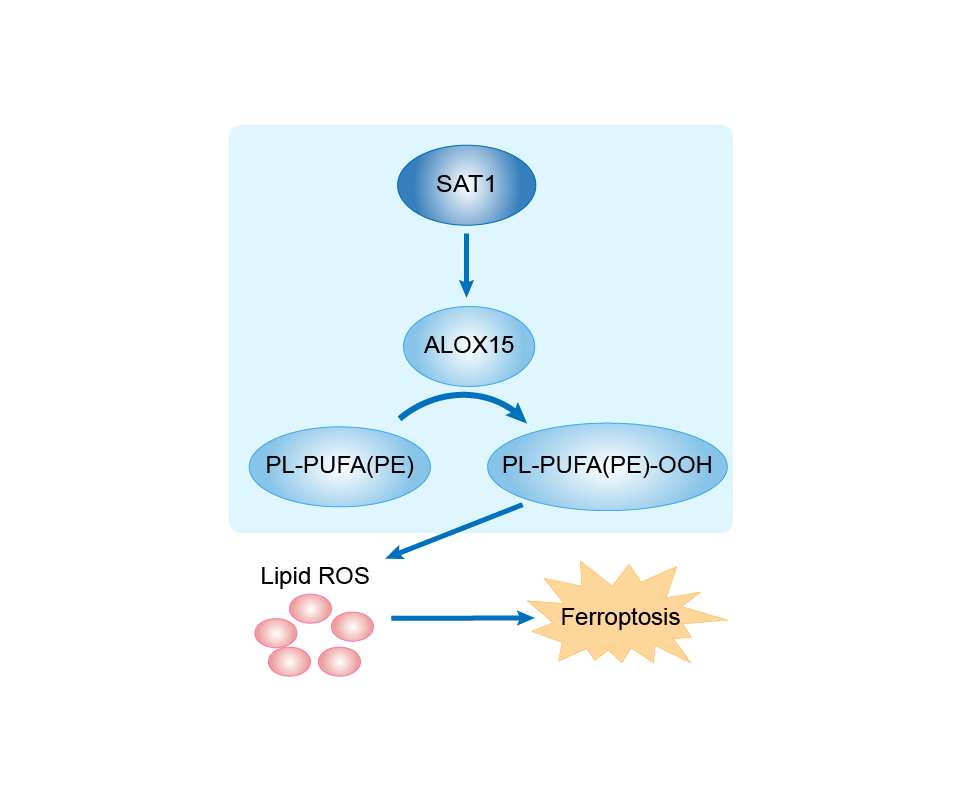
|
|||||
Tissue Relative Abundances of This Target
Full List of Regulator(s) of This Ferroptosis Target and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
SAT1 can be involved in and affect the ferroptosis by the following regulators, and result in corresponding disease/drug response(s). You can browse corresponding disease or drug response(s) resulting from the regulation of certain regulators.
Browse Regulator related Disease
Browse Regulator related Drug
Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53)
Neurotoxicity [ICD-11: NE61]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [1] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Drug | Sevoflurane | Approved | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
In Vitro Model |
hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Pregnant rats were placed in a dedicated plastic chamber with ambient gas at a flow rate of 2L/min. Fer-1 solubilized in saline and 1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and PD146176 (a specific 15LOX inhibitor) dissolved in corn oil containing 1% DMSO were administered intraperitoneally to rats at a dose of 5 mg/kg 1 h before each exposure, respectively. Similarly, 0.5 mg/kg Ku55933 (an ATM inhibitor), which is diluted in saline containing 1% DMSO, was intraperitoneally administered 2 h previously.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Sevoflurane could enhance 15LO2-PEBP1 interaction and activate ATM and its downstream P53/SAT1 pathway, which might be attributed to excessive p-ATM nuclear translocation, indicating a potential therapeutic target for ameliorating sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity. | ||||
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF113A (RNF113A)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [2] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
In Vitro Model |
A-549 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| NCI-H1975 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | ||
| HEK293 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0045 | ||
| PCS-201-012 (Human normal dermal fibroblasts) | |||||
| In Vivo Model |
Five millions of control or RNF113A-depleted Cisplatin-resistant A549 cells were transplanted into immunodeficient NOD/SCID 8 weeks old mice. Tumors were grown up to 0.1-0.2 mm3 and mice were then treated with Cisplatin (1 mg/kg) six times every 3 days. Seven mice were used per experimental conditions. No randomization of mice was used.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | RNF113A, whose loss-of-function causes the X-linked trichothiodystrophy, is overexpressed in lung cancer and protects from Cisplatin-dependent cell death. RNF113A deficiency triggers cell death upon DNA damage through multiple mechanisms, including apoptosis via the destabilization of the prosurvival protein MCL-1, ferroptosis due to enhanced SAT1 expression, and increased production of ROS due to altered Noxa1 expression. | ||||
Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53)
Sevoflurane
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response of This Regulator | [1] | ||||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Neurotoxicity [ICD-11: NE61] | ||||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | hBCs (Brain cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Pregnant rats were placed in a dedicated plastic chamber with ambient gas at a flow rate of 2L/min. Fer-1 solubilized in saline and 1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and PD146176 (a specific 15LOX inhibitor) dissolved in corn oil containing 1% DMSO were administered intraperitoneally to rats at a dose of 5 mg/kg 1 h before each exposure, respectively. Similarly, 0.5 mg/kg Ku55933 (an ATM inhibitor), which is diluted in saline containing 1% DMSO, was intraperitoneally administered 2 h previously.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response Description | Sevoflurane could enhance 15LO2-PEBP1 interaction and activate ATM and its downstream P53/SAT1 pathway, which might be attributed to excessive p-ATM nuclear translocation, indicating a potential therapeutic target for ameliorating sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity. | ||||
References
