Ferroptosis Target Information
General Information of the Ferroptosis Target (ID: TAR10018)
| Target Name | CDGSH iron-sulfur domain-containing protein 1 (CISD1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cysteine transaminase CISD1 ; MitoNEET
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene Name | CISD1 | ||||
| Sequence |
MSLTSSSSVRVEWIAAVTIAAGTAAIGYLAYKRFYVKDHRNKAMINLHIQKDNPKIVHAF
DMEDLGDKAVYCRCWRSKKFPFCDGAHTKHNEETGDNVGPLIIKKKET Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Family | CISD protein family | ||||
| Function |
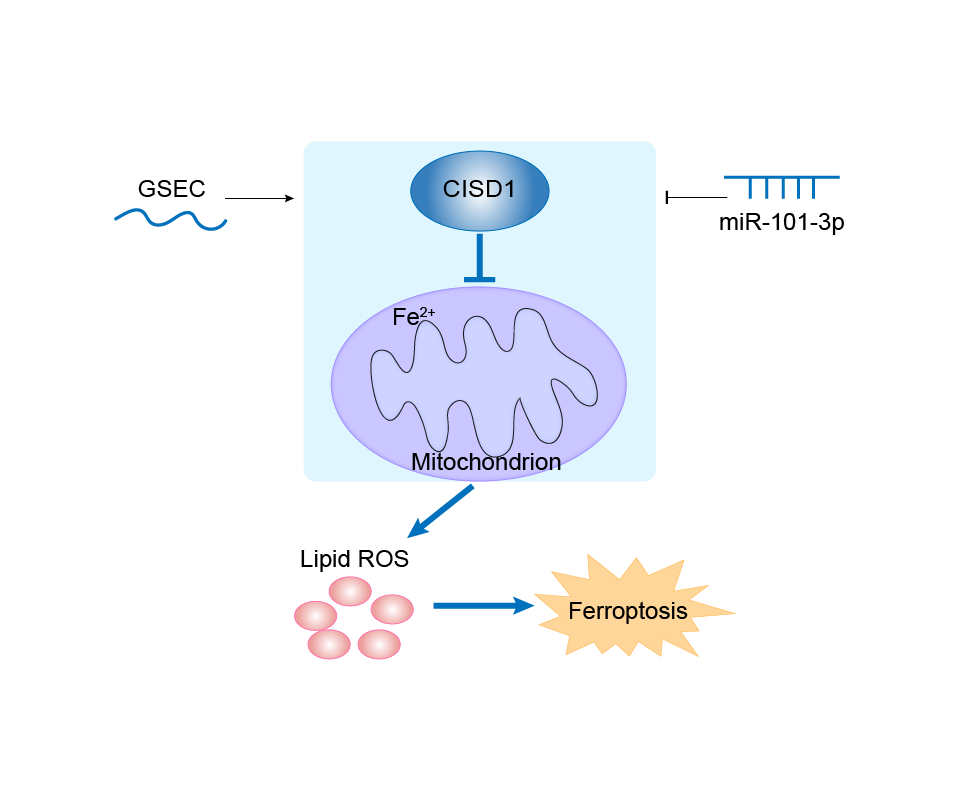
L-cysteine transaminase that catalyzes the reversible transfer of the amino group from L-cysteine to the alpha-keto acid 2- oxoglutarate to respectively form 2-oxo-3-sulfanylpropanoate and L- glutamate. The catalytic cycle occurs in the presence of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) cofactor that facilitates transamination by initially forming an internal aldimine with the epsilon-amino group of active site Lys-55 residue on the enzyme (PLP- enzyme aldimine), subsequently displaced by formation of an external aldimine with the substrate amino group (PLP-L-cysteine aldimine). The external aldimine is further deprotonated to form a carbanion intermediate, which in the presence of 2-oxoglutarate regenerates PLP yielding final products 2-oxo-3-sulfanylpropanoate and L-glutamate. The proton transfer in carbanion intermediate is suggested to be controlled by the active site lysine residue, whereas PLP stabilizes carbanion structure through electron delocalization, also known as the electron sink effect. Plays a key role in regulating maximal capacity for electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation. May be involved in iron-sulfur cluster shuttling and/or in redox reactions. Can transfer the [2Fe-2S] cluster to an apo-acceptor protein only when in the oxidation state, likely serving as a redox sensor that regulates mitochondrial iron-sulfur cluster assembly and iron trafficking upon oxidative stress.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene ID | 55847 | ||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Target Type | Driver Suppressor Marker | ||||
| Mechanism Diagram | Click to View the Original Diagram | ||||
|
|||||
Tissue Relative Abundances of This Target
Full List of Regulator(s) of This Ferroptosis Target and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
CISD1 can be involved in and affect the ferroptosis by the following regulators, and result in corresponding disease/drug response(s). You can browse corresponding disease or drug response(s) resulting from the regulation of certain regulators.
Browse Regulator related Disease
hsa-miR-101-3p (miRNA)
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Disease Response of This Regulator | [1] | |||
| Regulator for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell proliferation | ||||
| Cell migration | ||||
| Cell infiltration | ||||
In Vitro Model |
BEAS-2B cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0168 |
| A-549 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0023 | |
| NCI-H1975 cells | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1511 | |
| Response Description | The study found GSEC, CISD1, ATP5MC3, and PGD to be upregulated, with miRNA-101-3p downregulated, in the setting of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). Immunohistochemical analysis revealed CISD1, ATP5MC3, and PGD overexpression in LUAD tissue samples; CISD1 knockdown was noted to significantly inhibit LUAD proliferation and migration. | |||
