Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0365)
| Name |
Punicalin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Punicalin; 65995-64-4; CHEBI:167696; DTXSID301030154; AKOS037514809; Q-100755
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
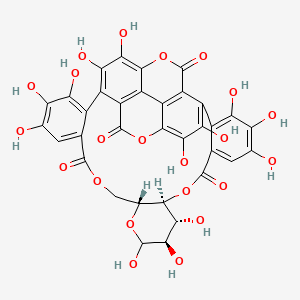 |
||||
|
3D MOL
|
|||||
| Formula |
C34H22O22
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
(10S,11R,12R,15R)-3,4,5,11,12,13,21,22,23,26,27,38,39-tridecahydroxy-9,14,17,29,36-pentaoxaoctacyclo[29.8.0.02,7.010,15.019,24.025,34.028,33.032,37]nonatriaconta-1(39),2,4,6,19,21,23,25,27,31,33,37-dodecaene-8,18,30,35-tetrone
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1C2C(C(C(C(O2)O)O)O)OC(=O)C3=CC(=C(C(=C3C4=C(C(=C5C6=C4C(=O)OC7=C(C(=C(C8=C(C(=C(C=C8C(=O)O1)O)O)O)C(=C67)C(=O)O5)O)O)O)O)O)O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C34H22O22/c35-6-1-4-9(19(39)17(6)37)11-15-13-14-16(33(50)56-28(13)23(43)21(11)41)12(22(42)24(44)29(14)55-32(15)49)10-5(2-7(36)18(38)20(10)40)31(48)54-27-8(3-52-30(4)47)53-34(51)26(46)25(27)45/h1-2,8,25-27,34-46,51H,3H2/t8-,25-,26-,27-,34?/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
IQHIEHIKNWLKFB-OBOTWMKHSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | L-seryl-tRNA(Sec) kinase (PSTK) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | Hep 3B2.1-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | |
| Hep-G2 cells | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | ||
| SK-HEP-1 cells | Liver and intrahepatic bile duct epithelial neoplasm | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0525 | ||
| PLC/PRF/5 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0485 | ||
| SNU-387 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0250 | ||
| SNU-182 cells | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0090 | ||
| SNU-398 cells | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0077 | ||
| WRL 68 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0581 | ||
| HUVECs (Human umbilical vein endothelial cells) | |||||
| JHH-2 cells | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2786 | ||
| JHH-7 cells | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2805 | ||
| Huh-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0336 | ||
| Li-7 cells | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3840 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Female Nod-SCID mice of 6-8 weeks old were purchased from HFK BIOSCIENCE (Beijing). Hep3B-vehicle/Hep3B-PSTK-KO cells were harvested and injected subcutaneously (1 x 107 cells in 200 uL PBS) into Nod-SCID mice (upper flank). Treatments were started when tumor volumes reached around 50 mm3. Included mice were randomly divided into four groups and injected intraperitoneally with Abemaciclib (50 mg/kg, every other day) or vehicle. Mice were sacrificed when the tumor volume exceeded 2000 mm3. PSTK-KO or vehicle Hep3B cells were implanted and treated with Sorafenib (50 mg/kg, every other day) or Erastin (50 mg/kg, every other day) for 42 days. Tumor volumes were monitored and quantified by the modified ellipsoidal formula, tumor volume = (length x width2)/2. To check the efficacities and appraisal the side effects of PSTK inhibitors, Hep3B cells were harvested and in injected subcutaneously (5 x 106 cells in 200 uL PBS) into Nod-SCID mice (upper flank). Treatments were started when tumor volumes reached around 50 mm3. Included mice were randomly divided into six groups and intragastrically treated with Punicalin (100 mg/kg, every day), Geraniin (100 mg/kg, every day), Sorafenib (50 mg/kg, every day) with or without PSTK inhibitors (Punicalin/Geraniin) for 30 days. Tumor volumes and mice weights were measured every three days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | The depletion of PSTK resulted in the inactivation of glutathione peroxidative 4 (GPX4) and the disruption of glutathione (GSH) metabolism owing to the inhibition of selenocysteine and cysteine synthesis, thus enhancing the induction of ferroptosis upon targeted chemotherapeutic treatment. Punicalin, an agent used to treat hepatitis B virus (HBV), was identified as a possible PSTK inhibitor that exhibited synergistic efficacy when applied together with Sorafenib to treat Hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. | ||||
