Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0280)
| Name |
moracin N
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
moracin N; CHEMBL465881; 5-[6-hydroxy-5-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-1-benzofuran-2-yl]benzene-1,3-diol; 135248-05-4; 5-[6-hydroxy-5-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-1-benzofuran-2-yl]benzene-1,3-diol; SCHEMBL6822289; CHEBI:174237; WBSCSIABHGPAMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N; DTXSID501318704; BDBM50251014; HY-N11849; 1,3-benzenediol, 5-[6-hydroxy-5-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-2-benzofuranyl]-; CS-0880943; 2-(3,5-Dihydroxyphenyl)-6-hydroxy-5-prenylbenzofuran; 5-[6-hydroxy-5-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-1-benzouran-2-yl]benzene-1,3-diol; InChI=1/C19H18O4/c1-11(2)3-4-12-5-13-8-18(23-19(13)10-17(12)22)14-6-15(20)9-16(21)7-14/h3,5-10,20-22H,4H2,1-2H
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
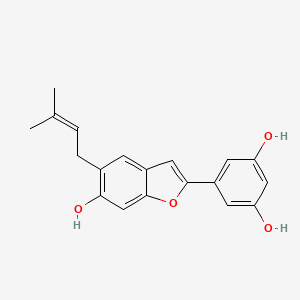 |
||||
| Formula |
C19H18O4
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
5-[6-hydroxy-5-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-1-benzofuran-2-yl]benzene-1,3-diol
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC(=CCC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)C=C(O2)C3=CC(=CC(=C3)O)O)O)C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C19H18O4/c1-11(2)3-4-12-5-13-8-18(23-19(13)10-17(12)22)14-6-15(20)9-16(21)7-14/h3,5-10,20-22H,4H2,1-2H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
WBSCSIABHGPAMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Nervous system disease | ICD-11: 8E7Z | ||
| Pathway Response | Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | ||
| Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | HT22 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0321 |
| Response regulation | Moracin N was a good ferroptosis inhibitor in Neurodegenerative diseases. The neuroprotective mechanisms of moracin N included inhibition of glutathione depletion, glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPx4) inactivation, reactive oxygen species (ROS) overproduction and iron accumulation, as well as improvement of intracellular antioxidant enzyme activities. | |||
