Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0253)
| Name |
Bisindolylmaleimide i
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
bisindolylmaleimide i; 133052-90-1; GF 109203X; GF109203X; GF-109203X; Go 6850; Go-6850; 3-(1-(3-(Dimethylamino)propyl)-1H-indol-3-yl)-4-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione; 3-[1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]indol-3-yl]-4-(1H-indol-3-yl)pyrrole-2,5-dione; Bisindolylmaleimide I (GF 109203X); 2-[1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)indol-3-yl]-3-(indol-3-yl)maleimide; CHEMBL7463; 3-{1-[3-(DIMETHYLAMINO)PROPYL]-1H-INDOL-3-YL}-4-(1H-INDOL-3-YL)-1H-PYRROLE-2,5-DIONE; L79H6N0V6C; 2-(1-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)indol-3-yl)-3-(indol-3-yl)maleimide; 1H-Pyrrole-2,5-dione, 3-(1-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-1H-indol-3-yl)-4-(1H-indol-3-yl)-; Bisindolylmaleimide I (GF109203X); 3-{1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-1H-indol-3-yl}-4-(1H-indol-3-yl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione; 3-[1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-1h-indol-3-yl]-4-(1h-indol-3-yl)-1h-pyrrole-2,5-dione; BI1; UNII-L79H6N0V6C; 1zrz; 1H-Pyrrole-2,5-dione, 3-[1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-1H-indol-3-yl]-4-(1H-indol-3-yl)-; bisin-dolylmaleimide; BisindolylmaleimideI; Bisindolylmaleimide 1; Gouml6850; Tocris-0741; 1uu8; BIM I; GF-109203; BiomolKI_000031; BiomolKI2_000039; BIM-1; SCHEMBL78990; BMK1-D7; BSPBio_001160; KBioGR_000500; KBioSS_000500; JMC526193 Compound 2; SCHEMBL338086; BDBM2683; GTPL5193; KBio2_000500; KBio2_003068; KBio2_005636; KBio3_000919; KBio3_000920; DTXSID50157932; Bio2_000420; Bio2_000900; HMS1362J21; HMS1792J21; HMS1990J21; HMS3229A21; HMS3266P07; HMS3403J21; HMS3411F13; HMS3653O17; HMS3675F13; BCP08311; EX-A1223; EI-246; HSCI1_000290; MFCD00236428; s7208; AKOS024458625; CCG-100635; CS-6154; DB03777; SB19439; IDI1_002175; NCGC00024760-01; NCGC00024760-02; NCGC00024760-03; NCGC00024760-04; NCGC00024760-07; AC-32872; AS-74139; HY-13867; B5781; FT-0623120; SW219715-1; EC-000.2373; A13197; C72321; GF 109203X, synthetic, >=90% (HPLC); A888223; Q866357; SR-01000597689; J-006293; SR-01000597689-1; BRD-K31342827-001-05-4; 2-[1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-indol-3-yl]-3-(indol-3-yl)maleimide; 2-[1-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)indol-3-yl]-3-(indol-3-yl) maleimide; 2-(1H-Indol-3-yl)-3-[1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]-maleinimide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Investigative
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
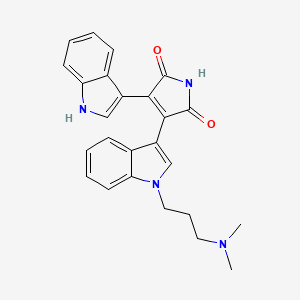 |
||||
| Formula |
C25H24N4O2
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
3-[1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]indol-3-yl]-4-(1H-indol-3-yl)pyrrole-2,5-dione
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CN(C)CCCN1C=C(C2=CC=CC=C21)C3=C(C(=O)NC3=O)C4=CNC5=CC=CC=C54
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C25H24N4O2/c1-28(2)12-7-13-29-15-19(17-9-4-6-11-21(17)29)23-22(24(30)27-25(23)31)18-14-26-20-10-5-3-8-16(18)20/h3-6,8-11,14-15,26H,7,12-13H2,1-2H3,(H,27,30,31)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
QMGUOJYZJKLOLH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Unspecific Target
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Rhabdomyosarcoma | ICD-11: 2B55 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Protein kinase C alpha type (PRKCA) | Driver | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | RD cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1649 |
| Rh18 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1659 | |
| Rh30 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0041 | |
| Rh36 cells | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_M599 | |
| Rh41 cells | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2176 | |
| T 174 cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_U955 | |
| TE 381.T cells | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1751 | |
| KYM-1 cells | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3007 | |
| Response regulation | Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) cells might be vulnerable to oxidative stress-induced cell death. The broad-spectrum protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor Bisindolylmaleimide I as well as the PKC-a (PRKCA) and b-selective inhibitor G6976 significantly reduced Erastin-induced cell death. Furthermore, the broad-spectrum nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-oxidase (NOX) inhibitor Diphenyleneiodonium and the selective NOX1/4 isoform inhibitor GKT137831 significantly decreased Erastin-stimulated ROS, lipid ROS and cell death. | |||
