Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0251)
| Name |
Echinatin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Echinatin; 34221-41-5; Retrochalcone; 4,4'-DIHYDROXY-2-METHOXYCHALCONE; 3-(4-hydroxy-2-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one; (E)-3-(4-hydroxy-2-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one; UNII-3816S4UA9R; CHEMBL141530; 3816S4UA9R; 2-Propen-1-one, 3-(4-hydroxy-2-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-, (2E)-; (E)-3-(4-Hydroxy-2-methoxy-phenyl)-1-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-propenone; Echinantin; SCHEMBL618086; 4'-Dihydroxy-2-methoxychalcone; 4',4-dihydroxy-2-methoxychalcone; DTXSID301019928; HY-N0269; BDBM50068267; LMPK12120431; MFCD00075719; s9437; AKOS016010242; CCG-267154; AC-34080; AS-77068; CS-0008288; A14853; A875066; Q27256724; (E)-3-(4-hydroxy-2-methoxy-phenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
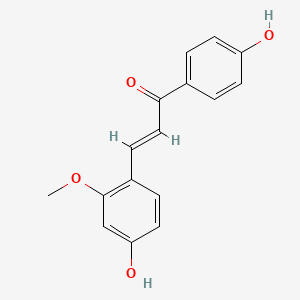 |
||||
| Formula |
C16H14O4
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
(E)-3-(4-hydroxy-2-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
COC1=C(C=CC(=C1)O)C=CC(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C16H14O4/c1-20-16-10-14(18)8-4-12(16)5-9-15(19)11-2-6-13(17)7-3-11/h2-10,17-18H,1H3/b9-5+
|
||||
| InChIKey |
QJKMIJNRNRLQSS-WEVVVXLNSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cognition disorder | ICD-11: MB21 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| In Vitro Model | rPHNs (Rat primary hippocampal neurons) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
The Sprague-Dawley rats (male, 20-month-old, 550-700 g, n = 6 per group) were obtained from the Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijng, China). A total of 78 rats were used in animal experiments. Rats were allocated into the following five experimental groups: control, Sev, Sev + Ech (L), Sev + Ech (M), and Sev + Ech (H). Ech (Sigma-Aldrich; purity 98%) was given to rats by intraperitoneal injection as a single dose of 20 (L), 40 (M), or 80 mg/kg (H) at 1 h before Sev exposure. The injection volume of each rat was 5 mL. For control and Sev groups, an equal volume of vehicle was intraperitoneally injected into rats. Then, rats except for the control group were anaesthetised with 2% Sev (Sigma-Aldrich) for 5 h. The histological and biochemical analysis of the hippocampus was done 48 h later after the rats were sacrificed and the brains were removed.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Echinatin (Ech) could mitigate Sev-induced apoptosis, oxidative stress, and ferroptosis in hippocampal neurons and hippocampus of rats by activating Nrf2 signalling. Moreover, Ech improved Sev-induced cognitive deficits in aged rats. These findings suggested that Ech may be developed as a neuroprotective agent to reduce postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the clinic. | ||||
