Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0235)
| Name |
Tiliroside
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Tiliroside; 20316-62-5; Tribuloside; Trans-Tiliroside; 15M04TXR9M; CHEMBL266564; [(2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-6-[5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxochromen-3-yl]oxy-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]methyl (E)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate; CHEBI:80944; 22153-44-2; 2-Propenoic acid, 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-, 6'-ester with 3-(beta-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one; ((2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-6-((5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)oxy)-3,4,5-trihydroxytetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl (E)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acrylate; [(2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-6-[5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-chromen-3-yl]oxy-3,4,5-trihydroxy-tetrahydropyran-2-yl]methyl (E)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate; UNII-15M04TXR9M; Potengriffioside A; RONACARE TILIROSIDE; TILIROSIDE [INCI]; SCHEMBL23597; Tiliroside, analytical standard; MEGxp0_000169; DTXSID601021936; GLXC-13144; 6''-O-trans-p-Coumaroylastragalin; Kaempferol-3-(p-coumaryl)glucoside; HY-N2443; BDBM50241244; MFCD00017454; AKOS015896718; NCGC00163634-01; ASTRAGALIN-6''-TRANS-P-COUMARATE; MS-30569; CS-0022668; kaempferol 3-O-(6'-O-p-coumaroyl)-glucoside; C17140; A814433; Q-100248; KAEMPFEROL 3-O-(6''-O-P-COUMAROYL)GLUCOSIDE; Q23418844; kaempferol-3-beta-D-(6-O-trans-p-coumaroyl)glucopyranoside; Kaempferol-3-O-(6-O-trans-p-coumaroyl)-.beta.-glucopyranoside; kaempferol-3-O-beta-D-(6''-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-glucopyranoside; 3-O-KAEMPFEROL 6-O-(TRANS-P-COUMAROYL)-.BETA.-D-GLUCOPYRANOSIDE; kaempferol 3-O-(6'''' ''''-O-E-p-coumaroyl)-beta-D-glucopyranoside; KAEMPFEROL 3-O-(6''-O-(E)-P-COUMAROYL)-.BETA.-D-GLUCOPYRANOSIDE; KAEMPFEROL 3-O-.BETA.-D-(6-O-TRANS-P-COUMAROYL)GLUCOPYRANOSIDE; KAEMPFEROL-3-O(-6-O-TRANS-P-COUMAROYL-.BETA.-GLUCOPYRANOSIDE; KAEMPFEROL 3-O-(6''-O-(TRANS-P-COUMAROYL))-.BETA.-D-GLUCOPYRANOSIDE; ((2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-6-((5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)oxy)-3,4,5-trihydroxytetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acrylate; (E)-((2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-6-(5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yloxy)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acrylate; (E)-((2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-6-(5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yloxy)-3,4,5-trihydroxytetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acrylate; 2-PROPENOIC ACID, 3-(4-HYDROXYPHENYL)-, 6'-ESTER WITH 3-(.BETA.-D-GLUCOPYRANOSYLOXY)-5,7-DIHYDROXY-2-(4-HYDROXYPHENYL)-4H-1-BENZOPYRAN-4-ONE, (E)-; 4H-1-BENZOPYRAN-4-ONE, 5,7-DIHYDROXY-2-(4-HYDROXYPHENYL)-3-((6-O-((2E)-3-(4-HYDROXYPHENYL)-1-OXO-2-PROPEN-1-YL)-.BETA.-D-GLUCOPYRANOSYL)OXY)-; 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-[[6-O-[(2E)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-oxo-2-propenyl]-.beta.-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy]-; 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4E-1-benzopyran-3-yl 6-O-[(2E)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Investigative
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
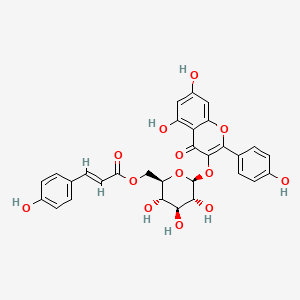 |
||||
| Formula |
C30H26O13
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
[(2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-6-[5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxochromen-3-yl]oxy-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]methyl (E)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC(=CC=C1C=CC(=O)OCC2C(C(C(C(O2)OC3=C(OC4=CC(=CC(=C4C3=O)O)O)C5=CC=C(C=C5)O)O)O)O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C30H26O13/c31-16-6-1-14(2-7-16)3-10-22(35)40-13-21-24(36)26(38)27(39)30(42-21)43-29-25(37)23-19(34)11-18(33)12-20(23)41-28(29)15-4-8-17(32)9-5-15/h1-12,21,24,26-27,30-34,36,38-39H,13H2/b10-3+/t21-,24-,26+,27-,30+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
DVGGLGXQSFURLP-VWMSDXGPSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2)
| In total 2 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Serine/threonine-protein kinase TBK1 (TBK1) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | Hep-G2 cells | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | ||
| SMMC-7721 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 | ||
| L-02 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
All animal studies were approved by the Committee on Ethics of Animal Experiments of Binzhou Medical University (approval no: BZMU-IACUC-2021-331, date: 09/10/2021). To generate the ectopic HCC mouse models, HepG2-luciferase cells (HepG2 cells transfected with luciferase gene) were suspended in serum-free media and matrigel (BD Biosciences) at a ratio of 1:1 v/v. A total of 2.5 x 106 HepG2-luciferase cells/100 ul were injected into the left axilla of mice. After reaching a tumor size of 100-150 mm3, all mice were randomly divided into four groups: control (vehicle, intraperitoneal [i.p.]), tiliroside (20 mg/kg,i.p.), sorafenib (30 mg/kg,i.p.), or combination treatment (tiliroside and sorafenib,i.p.). All treatments were administered every 3 d, and the length and width of tumor were measured every 4 d. The formula tumor volume = (length x width2)/2 was used to calculate the tumor volume. Body weight was recorded every 7 d, and the morphology of the tumor was photographed using animal in vivo imaging technology (IVIS Spectrum; PerkinElmer) before the day of sacrifice. The mice were sacrificed 40 d after administration, and the tumors were dissected and weighed. The major organs and xenograft tumors were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Tiliroside directly binds to TBK1 and inhibits its activity, which inhibits the phosphorylation of Ser349 on p62. Consequently, this decreases the affinity of p62 for Keap1, promotes ubiquitination and degradation of Nrf2 and ferroptosis, and eventually increases the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Marker/Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ICD-11: 2C12 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | Hep-G2 cells | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0027 | |
| Hep 3B2.1-7 cells | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0326 | ||
| SMMC-7721 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0534 | ||
| L-02 cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6926 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
All animal studies were approved by the Committee on Ethics of Animal Experiments of Binzhou Medical University (approval no: BZMU-IACUC-2021-331, date: 09/10/2021). To generate the ectopic HCC mouse models, HepG2-luciferase cells (HepG2 cells transfected with luciferase gene) were suspended in serum-free media and matrigel (BD Biosciences) at a ratio of 1:1 v/v. A total of 2.5 x 106 HepG2-luciferase cells/100 ul were injected into the left axilla of mice. After reaching a tumor size of 100-150 mm3, all mice were randomly divided into four groups: control (vehicle, intraperitoneal [i.p.]), tiliroside (20 mg/kg,i.p.), sorafenib (30 mg/kg,i.p.), or combination treatment (tiliroside and sorafenib,i.p.). All treatments were administered every 3 d, and the length and width of tumor were measured every 4 d. The formula tumor volume = (length x width2)/2 was used to calculate the tumor volume. Body weight was recorded every 7 d, and the morphology of the tumor was photographed using animal in vivo imaging technology (IVIS Spectrum; PerkinElmer) before the day of sacrifice. The mice were sacrificed 40 d after administration, and the tumors were dissected and weighed. The major organs and xenograft tumors were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Tiliroside directly binds to TBK1 and inhibits its activity, which inhibits the phosphorylation of Ser349 on p62. Consequently, this decreases the affinity of p62 for Keap1, promotes ubiquitination and degradation of Nrf2 and ferroptosis, and eventually increases the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib. | ||||
