Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0194)
| Name |
Fedratinib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Fedratinib; 936091-26-8; Tg-101348; TG101348; SAR302503; SAR-302503; N-(tert-butyl)-3-((5-methyl-2-((4-(2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethoxy)phenyl)amino)pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)benzenesulfonamide; Inrebic; SAR 302503; TG 101348; Fedratinib (SAR302503, TG101348); N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-3-[[5-methyl-2-[[4-[2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]amino]-4-pyrimidinyl]amino]benzenesulfonamide; TG101348 (SAR302503); CHEMBL1287853; 6L1XP550I6; 936091-26-8 (free base); N-tert-butyl-3-(5-methyl-2-(4-(2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethoxy)phenylamino)pyrimidin-4-ylamino)benzenesulfonamide; Benzenesulfonamide, N-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-3-((5-methyl-2-((4-(2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethoxy)phenyl)amino)-4-pyrimidinyl)amino)-; N-Tert-butyl-3-(5-methyl-2-(4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-yl-ethoxy)-phenylamino)-pyrimidin-4-ylamino)-benzenesulfonamide; N-tert-butyl-3-{[5-methyl-2-({4-[2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethoxy]phenyl}amino)pyrimidin-4-yl]amino}benzenesulfonamide; Fedratinib [USAN]; Fedratinib [USAN:INN]; UNII-6L1XP550I6; 2TA; FEDRATINIB [MI]; FEDRATINIB [INN]; Fedratinib (USAN/INN); TG101348(Fedratinib); FEDRATINIB [WHO-DD]; Fedratinib (TG101348); MLS006011155; N-tert-butyl-3-[[5-methyl-2-[4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethoxy)anilino]pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]benzenesulfonamide; SCHEMBL263741; GTPL5716; CHEBI:91408; DTXSID90239483; EX-A170; HMS3295I03; HMS3656L19; HMS3744G17; HMS3868L03; BCP02300; BDBM50332294; MFCD12922515; NSC767600; NSC800099; s2736; AKOS015842621; CCG-264990; CS-0052; DB12500; EX-5961; NSC-767600; NSC-800099; SB14604; NCGC00244252-01; NCGC00244252-07; AC-30260; AS-16248; HY-10409; SMR004702929; FT-0705969; FT-0763396; FT-0766818; SW218187-2; A25534; D10630; F17372; J-523769; Q7670147; BRD-K12502280-001-01-5; Z2037280076; N-TERT-BUTYL-3-((5-METHYL-2-(4-(2-(PYRROLIDIN-1-YL)ETHOXY)ANILINO(PYRIMIDIN-4-YL)AMINO)BENZENESULFONAMIDE; N-tert-butyl-3-{[5-methyl-2-({4-[2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethoxy]phenyl}amino)pyrimidin-4-yl]amino}benzene-1-sulfonamide; SAR302503, N-tert-butyl-3-(5-methyl-2-(4-(2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethoxy)phenylamino)pyrimidin-4-ylamino)benzenesulfonamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
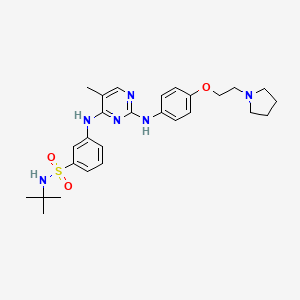 |
||||
| Formula |
C27H36N6O3S
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
N-tert-butyl-3-[[5-methyl-2-[4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethoxy)anilino]pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]benzenesulfonamide
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1=CN=C(N=C1NC2=CC(=CC=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC(C)(C)C)NC3=CC=C(C=C3)OCCN4CCCC4
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C27H36N6O3S/c1-20-19-28-26(30-21-10-12-23(13-11-21)36-17-16-33-14-5-6-15-33)31-25(20)29-22-8-7-9-24(18-22)37(34,35)32-27(2,3)4/h7-13,18-19,32H,5-6,14-17H2,1-4H3,(H2,28,29,30,31)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
JOOXLOJCABQBSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Acute kidney failure | ICD-11: GB60 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM21 (TRIM21) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | HK-2 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0302 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Mice were fasted for 12 h and anesthetized (1% pentobarbital sodium, i.p.) before surgery. Bilateral renal pedicles were clamped for 30 min, then remove the arterial clamps. The sham groups were treated in the same way, except for the clamping of the renal pedicle. Blood samples were collected 24 h after reperfusion, mice were killed, and kidney were collected for follow-up experiments. Fedratinib (5 mg/kg body weight) was injected (i.p.) into mice 24 h once in advance before surgery.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | A JAK2 inhibitor Fedratinib downregulated TRIM21 expression and reduced damage both in vivo and in vitro, which is correlated with the upregulation of GPX4. Our study showed that loss of TRIM21 could alleviate ferroptosis induced by I/R, revealed the mechanism of ubiquitination degradation of GPX4 by TRIM21 and suggested TRIM21 is a potential target for the treatment of acute kidney injury (AKI). | ||||
