Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0190)
| Name |
Niraparib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Niraparib; 1038915-60-4; MK-4827; (S)-2-(4-(piperidin-3-yl)phenyl)-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide; MK4827; Niraparib [USAN]; 2-{4-[(3s)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2h-indazole-7-carboxamide; MK 4827; HMC2H89N35; 2-[4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl]indazole-7-carboxamide; CHEMBL1094636; Niraparib (USAN); ZL-2306; JNJ-64091742; (S)-2-(4-(piperidin-3-yl)phenyl)-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide;MK-4827; Niraparib [USAN:INN]; 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}indazole-7-carboxamide; UNII-HMC2H89N35; MK 4827 (Base); 3JD; Zejula (TN); NIRAPARIB [INN]; NIRAPARIB [MI]; MK-4827(Niraparib); NIRAPARIB [WHO-DD]; GTPL8275; SCHEMBL1421875; AMY4192; DTXSID50146129; EX-A290; CHEBI:176844; MK-4827 (PARP-1); BDBM50316226; MFCD17779309; NSC754355; NSC800020; s2741; AKOS016004869; BCP9000940; CCG-267709; compound 56 [PMID 19873981]; CS-0780; DB11793; MK-4827/MK4827; NSC-754355; NSC-800020; NCGC00346435-01; NCGC00346435-04; AC-28447; AS-35248; HY-10619; BCP0726000077; D10140; EN300-7364833; A857972; Q25326660; 2-[4-(3S)-3-Piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide; 2H-Indazole-7-carboxamide, 2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]; 2H-INDAZOLE-7-CARBOXAMIDE, 2-(4-(3S)-3-PIPERIDINYLPHENYL)-; 2H-Indazole-7-carboxamide, 2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-; 2-[4-(3S)-3-Piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide; Niraparib; Zejula; MK-4827
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
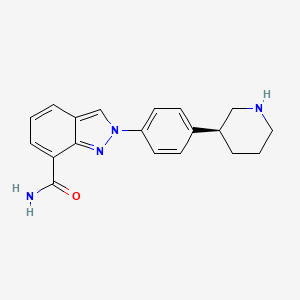 |
||||
| Formula |
C19H20N4O
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
2-[4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl]indazole-7-carboxamide
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1CC(CNC1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)N3C=C4C=CC=C(C4=N3)C(=O)N
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C19H20N4O/c20-19(24)17-5-1-3-15-12-23(22-18(15)17)16-8-6-13(7-9-16)14-4-2-10-21-11-14/h1,3,5-9,12,14,21H,2,4,10-11H2,(H2,20,24)/t14-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
PCHKPVIQAHNQLW-CQSZACIVSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Suppressor | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (CGAS) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | hsa04623 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HT29 cells | Colon cancer | Mus musculus | CVCL_A8EZ | |
| CT26 cells | Colon adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_7254 | ||
| MC-38 cells | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_B288 | ||
| In Vivo Model |
Six-week-old male BALB/c athymic nude mice were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of Peking (Beijing, China). Stable cells (5 x 106) were seeded into the right flanks of the mice. After the xenografts had grown to 200 mm3, saline as a vehicle or sorafenib (30 mg/kg) was administered by gavage every day, and the mice were euthanized by the cervical dislocation method five weeks later. Before sacrifice, the tumor sizes and body weights were measured twice per week. The tumor volume (V) was calculated as follows: (L x W2)/2 (length, L, and width, W). The xenografts were excised and further assessed.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Niraparib, a widely used PARPi, augmented cGAS-mediated ferroptosis and immune activation. In colorectal cancer models, cGAS signaling exerts tumor control via ATF3SLC7A11GPX4-mediated ferroptosis and IFNCD8 T cell-mediated antitumor immune response. | ||||
