Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0175)
| Name |
Juglone
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
juglone; 481-39-0; 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone; 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione; 5-Hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione; Regianin; Nucin; Juglon; Akhnot; Yuglon; C.I. Natural Brown 7; 8-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone; 5-Hydroxynaphthoquinone; 1,4-NAPHTHALENEDIONE, 5-HYDROXY-; 5-Hydroxy-p-naphthoquinone; C.I. 75500; 1,4-Naphthoquinone, 5-hydroxy-; Juglane; Jugnlon; Iuglon; 1,4-Naphthoquinone, 8-hydroxy-; 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthosemiquinone; 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naftochinon; NSC 153189; NSC 622948; 5-hydroxy-1,4-dihydronaphthalene-1,4-dione; JUGLONE CRYSTALLIZED; CHEMBL43612; W6Q80SK9L6; 5-Hydroxy-[1,4]Naphthoquinone; 8-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione; CHEBI:15794; NCI 2323; NSC34266; NSC153189; NSC622948; NSC-153189; NSC-622948; 481-13-0; 1, 8-hydroxy-; WLN: L66 BV EVJ GQ; Caswell No. 515AA; CCRIS 5423; EINECS 207-567-5; 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naftochinon [Czech]; BRN 1909764; UNII-W6Q80SK9L6; Antibiotic PD7; MFCD00001684; Spectrum_000415; 3b7j; JUGLONE [MI]; Spectrum2_000778; Spectrum3_001228; Spectrum4_001769; Spectrum5_000357; 5-HNQ; SCHEMBL34185; BSPBio_001157; BSPBio_002676; KBioGR_000497; KBioGR_002257; KBioGR_002470; KBioSS_000497; KBioSS_000895; KBioSS_002477; SPECTRUM300038; 4-08-00-02368 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); DivK1c_001026; SPBio_000856; -Hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione; DTXSID0031504; BDBM24777; HMS503M13; KBio1_001026; KBio2_000497; KBio2_000895; KBio2_002470; KBio2_003065; KBio2_003463; KBio2_005038; KBio2_005633; KBio2_006031; KBio2_007606; KBio3_000913; KBio3_000914; KBio3_002176; KBio3_002948; 5-hydroxy-naphthalene-1,4-dione; cMAP_000058; NINDS_001026; Bio1_000441; Bio1_000930; Bio1_001419; Bio2_000409; Bio2_000889; HMS1362I19; HMS1792I19; HMS1923G07; HMS1990I19; HMS3403I19; Juglone - CAS 481-39-0; 5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, 4; HY-N6949; CCG-40256; NSC-34266; s5512; ZB1862; 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, 97%; AKOS001576598; 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione, 9CI; CS-W017516; SDCCGMLS-0066542.P001; IDI1_001026; IDI1_002164; SMP1_000168; NCGC00095247-01; NCGC00095247-02; NCGC00095247-03; NCGC00095247-04; NCGC00095247-05; CI 75500; CI-75500; 1,4-dihydro-1,4-dioxo-5-hydroxynaphthalene; AM20040546; FT-0627559; H0286; C03840; EN300-160375; F17689; A827478; A936425; Q900912; SR-05000002406; J-650071; Q-100522; SR-05000002406-1; F0451-0746; InChI=1/C10H6O3/c11-7-4-5-9(13)10-6(7)2-1-3-8(10)12/h1-5,12
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
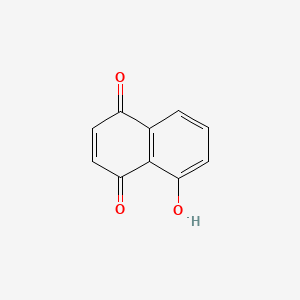 |
||||
| Formula |
C10H6O3
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
5-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC2=C(C(=O)C=CC2=O)C(=C1)O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C10H6O3/c11-7-4-5-9(13)10-6(7)2-1-3-8(10)12/h1-5,12H
|
||||
| InChIKey |
KQPYUDDGWXQXHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver/Suppressor | |||
| Responsed Disease | Corpus uteri cancer | ICD-11: 2C76 | ||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | ||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell autophagy | ||||
| Cell migration | ||||
| In Vitro Model | Ishikawa cells | Endometrial adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2529 |
| Response regulation | Juglone as a natural quinone from C. cathayensisgreen peel could exert its anti-cancer activity by inducing iron dependent autophagy and inhibiting the migration of endometrial cancer (EC) cells. Subsequently, Fe2+ accumulation, lipid peroxidation, GSH depletion, the upregulation of HMOX1, and heme degradation to Fe2+ were reported. Juglone was involved in inducing autophagy and inhibiting cell migration and endoplasmic reticulum stress. | |||
