Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0126)
| Name |
Idebenone
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
idebenone; 58186-27-9; 2-(10-hydroxydecyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methylcyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione; Idebenona; Idebenonum; Sovrima; hydroxydecyl ubiquinone; CV 2619; CV-2619; Oristar hdu; BRN 2001459; CHEBI:31687; 2-(10-Hydroxydecyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone; 6-(10-Hydroxydecyl)-2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone; NSC-759228; HB6PN45W4J; 2-(10-hydroxydecyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methyl-2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione; 2,5-Cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione, 2-(10-hydroxydecyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methyl-; 2-(10-Hydroxydecyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methyl-p-benzoquinone; DTXSID0040678; Raxone; 5,6-DIMETHOXY-2-(10-HYDROXYDECYL)-3-METHYL-1,4-BENZOQUINONE; MFCD00274552; NCGC00160514-01; 2-(10-hydroxydecyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methylbenzo-1,4-quinone; Idebenone [INN:JAN]; Idebenonum [Latin]; Idebenona [Spanish]; DTXCID8020678; 1189907-75-2; 2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-(10'-hydroxydecyl)-1,4-benzoquinone; 2,3-Dimethoxy-6-(10-hydroxydecyl)-5-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone; SMR000466364; CAS-58186-27-9; SR-01000759378; UNII-HB6PN45W4J; Cerestabon; Catena; Mnesis; Avan; Idebenone- Bio-X; Raxone (TN); IDEBENONE [INN]; IDEBENONE [JAN]; IDEBENONE [MI]; IDEBENONE [USAN]; IDEBENONE [MART.]; IDEBENONE [WHO-DD]; SNT-MC17; SCHEMBL28320; IDEBENONE [EMA EPAR]; Idebenone (JAN/USAN/INN); MLS000759487; MLS001032035; MLS001424002; MLS006011882; Idebenone, analytical standard; CHEMBL252556; QSA-10; Idebenone, >=98% (HPLC); FR114; HMS2051O06; HMS2089D08; HMS3393O06; HMS3656K22; HMS3713A10; HMS3884B12; Pharmakon1600-01505755; BCP09116; HY-N0303; STR09227; Tox21_111864; BBL025842; BDBM50505498; NSC759228; s2605; STK801942; HYDROXYDECYL UBIQUINONE [INCI]; 2,5-Cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione, 5,6-dimethoxy-2-(10-hydroxydecyl)-3-methyl-; AKOS005622577; Tox21_111864_1; AC-4337; CCG-100846; KS-5193; NC00096; NSC 759228; SB19130; NCGC00160514-02; NCGC00160514-03; BI164565; SY051193; SBI-0207024.P001; FT-0617205; I0848; SW219495-1; D01750; H10427; AB00639997-04; AB00639997-06; AB00639997_07; AB00639997_08; EN300-7359600; A-68500; Q4197874; SR-01000759378-4; SR-01000759378-5; SR-01000759378-6; BRD-K37516142-001-01-4; 2,3-Dimethoxy-6-(10-hydroxydecyl)-5-methylbenzoquinone; Z2216898922; 2,3-Dimethoxy-6-(10-hydroxydecyl)-5-methyl-1,4benzoquinone; 2-(10-hydroxydecyl)-6-methoxy-3-methyl-5-(trideuteriomethoxy)cyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
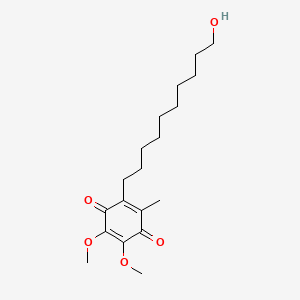 |
||||
| Formula |
C19H30O5
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
2-(10-hydroxydecyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methylcyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(C(=O)C(=C(C1=O)OC)OC)CCCCCCCCCCO
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C19H30O5/c1-14-15(12-10-8-6-4-5-7-9-11-13-20)17(22)19(24-3)18(23-2)16(14)21/h20H,4-13H2,1-3H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
JGPMMRGNQUBGND-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Unspecific Target
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myocardial infarction | ICD-11: BA41 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| In Vitro Model | CHO-S/H9C2 cells | Normal | Cricetulus griseus | CVCL_A0TS | |
| In Vivo Model |
The mice were randomly divided into 3 groups as follows: sham + vehicle (5% DMSO + 10% PEG + 20% Tween80) group; MI + vehicle group; and MI + idebenone group. The 3 groups of mice then received vehicle or idebenone (100 mg/kg) in a final volume of 100 uL by intraperitoneal injections (Lee et al., 2021) 24 h and 2 h prior to surgery. A mouse model of MI was used as previously described (Guo et al., 2022b). In short, mice were placed under general anesthesia by intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital, then endotracheal intubation and artificial respiration were performed. The left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD) of mice was ligated with a 6-0 silk suture, and the color of the LAD wall becoming pale confirmed the occlusion of the vessel. The same procedures were carried out on mice in the sham operation group, but with no LAD occlusion. The 3 groups of mice then received vehicle or idebenone (100 mg/kg/day) in a final volume of 100 uL by intraperitoneal injections once daily for 3 days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | ROS-induced autophagy contributed to the consequent development of ferroptosisin vitro and in vivo. Idebenone alleviated ferroptosis by regulating excessive autophagy via the AMPK-mTOR pathway in myocardial infarction. | ||||
