Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0102)
| Name |
Oleanolic acid
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
OLEANOLIC ACID; 508-02-1; Oleanic acid; Caryophyllin; Astrantiagenin C; Giganteumgenin C; Virgaureagenin B; Oleanol; 3beta-Hydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid; oleonolic acid; CCRIS 6493; NSC-114945; UNII-6SMK8R7TGJ; 6SMK8R7TGJ; Gledigenin 1; EINECS 208-081-6; (3-beta)-3-Hydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid; (4aS,6aR,6aS,6bR,8aR,10S,12aR,14bS)-10-hydroxy-2,2,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyl-1,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,13,14b-tetradecahydropicene-4a-carboxylic acid; CHEBI:37659; NSC114945; 3-beta-Hydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid; Olean-12-en-28-oic acid, 3-hydroxy-, (3beta)-; Olean-12-en-28-oic acid, 3beta-hydroxy-; Olean-12-en-28-oic acid, 3-beta-hydroxy-; DTXSID50858790; NSC 114945; Olean-12-en-28-oic acid, 3-hydroxy-, (3-beta)-; (4aS,6aS,6bR,8aR,10S,12aR,12bR,14bS)-10-hydroxy-2,2,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyl-1,3,4,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a,12b,13,14b-octadecahydropicene-4a(2H)-carboxylic acid; OleanolicAcid; OLEANOLIC ACID (USP-RS); OLEANOLIC ACID [USP-RS]; MFCD00064914; (4aS,5S,6aS,6bR,8R,8aR,10S,12aR,12bR,14bS)-10-Hydroxy-2,2,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyl-1,3,4,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a,12b,13,14b-octadecahydro-2H-picene-4a-carboxylic acid; SMR000445561; OLEANOLIC_ACID; CHEMBL168; (3.beta.)-3-Hydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid; Olean-12-en-28-oic acid, 3-hydroxy-, (3.beta.)-; oleanolic-acid; OleanolsA currencyure; Oleanoic Acid Hydrate; Olean-12-en-28-oic acid, 3.beta.-hydroxy-; Oleanolic acid, >=97%; OLEANOLIC ACID [MI]; SCHEMBL71070; MLS000697656; MLS002207133; OLEANOLIC ACID [INCI]; GTPL3306; OLEANOLIC ACID [WHO-DD]; MIJYXULNPSFWEK-GTOFXWBISA-N; DTXCID701474453; HMS2232D15; Oleanolic acid (OA)(Compound 1); Oleanolic acid, analytical standard; (4aS,6aS,6bR,8aR,10S,12aR,12bR,14bS)-10-hydroxy-2,2,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a,12b,13,14b-icosahydropicene-4a-carboxylic acid; EX-A1991; HY-N0156; BDBM50346601; 3-beta-Hydroxyolean-12-en-28-oate; 3beta-hydroxy-Olean-12-en-28-oate; AKOS015951416; AC-8026; CCG-208530; CS-3800; LMPR0106150004; 3.beta.-hydroxy-Olean-12-en-28-oate; 3beta-hydroxy-Olean-12-en-28-oic acid; NCGC00017222-10; (2S,5S,10S,18S,1R,14R,15R,20R)-18-hydroxy-1,2,8,8,15,19,19-heptamethylpentacyc lo[12.8.0.0<2,11>.0<5,10>.0<15,20>]docos-11-ene-5-carboxylic acid; AS-35338; BP-25410; (3-beta)-3-Hydroxyolean-12-en-28-oate; (3?)-3-Hydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid; 3.beta.-hydroxy-Olean-12-en-28-oic acid; (3beta)-3-hydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid; (3.beta.)-3-hydroxy-Olean-12-en-28-oate; C17148; EN300-342251; (3.beta.)-3-hydroxy-Olean-12-en-28-oic acid; (3.beta.)-3-beta-hydroxy-Olean-12-en-28-oate; 3.BETA.-HYDROXYOLEAN-12-EN-28-OIC ACID; Olean-12-en-28-oic acid, 3-hydroxy-, (3b)-; Q418628; OLEANOLIC ACID (CONSTITUENT OF BANABA LEAF); Q-100572; (3.beta.)-3-beta-hydroxy-Olean-12-en-28-oic acid; OLEANOLIC ACID (CONSTITUENT OF HOLY BASIL LEAF); Oleanolic acid, primary pharmaceutical reference standard; C7EE6ACC-7175-4947-B524-FF8479525DA1; OLEANOLIC ACID (CONSTITUENT OF BANABA LEAF) [DSC]; OLEANOLIC ACID (CONSTITUENT OF HOLY BASIL LEAF) [DSC]; Oleanolic acid, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Oleanolic acid, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; (4aS,6aR,6aS,6bR,8aR,10S,12aR,14bS)-10-hydroxy-2,2,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyl-1,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,13,14b-tetradecahydropicene-4a-carboxylicacid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Investigative
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
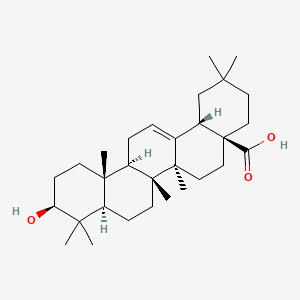 |
||||
| Formula |
C30H48O3
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
(4aS,6aR,6aS,6bR,8aR,10S,12aR,14bS)-10-hydroxy-2,2,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyl-1,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,13,14b-tetradecahydropicene-4a-carboxylic acid
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1(CCC2(CCC3(C(=CCC4C3(CCC5C4(CCC(C5(C)C)O)C)C)C2C1)C)C(=O)O)C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C30H48O3/c1-25(2)14-16-30(24(32)33)17-15-28(6)19(20(30)18-25)8-9-22-27(5)12-11-23(31)26(3,4)21(27)10-13-29(22,28)7/h8,20-23,31H,9-18H2,1-7H3,(H,32,33)/t20-,21-,22+,23-,27-,28+,29+,30-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
MIJYXULNPSFWEK-GTOFXWBISA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 4 (ACSL4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Cervical cancer | ICD-11: 2C77 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | HeLa cells | Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0030 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Male BALB/c Nude mice (20 ± 2g, 5 weeks old) were supplied by Hangzhou Ziyuan Experimental Animal Technology Co. LTD (SYXK-20180049) for this study. The nude mice were kept under specefic pathogen free (SPF) conditions for one week, and 5x107 Hela cells were injected under the left axillary skin after acclimatization. The tumors of Hela cell-inoculated mice were measured every 3 days after modeling, and tumor>=0.5 cm in diameter were considered successful. The tumor-bearing mice were randomly divided into control group (n = 6), 40 mg/kg OA group (n = 6) and 80 mg/kg OA group (n = 6). 40 mg/kg OA group and 80 mg/kg OA group both received subcutaneous injection modeling and control mice received saline intraperitoneal injections. The 40 mg/kg OA group and 80 mg/kg OA group received daily intraperitoneal injections of 40 mg/kg OA and 80 mg/kg OA for 15 days.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Oleanolic acid (OA) significantly reduced the viability and proliferative capacity of Hela cells. OA activated ferroptosis in Hela cells by promoting ACSL4 expression, thereby reducing the survival rate of Hela cells. Therefore, promotion of ACSL4-dependent ferroptosis by OA may be a potential approach for the treatment of cervical cancer. | ||||
