Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0068)
| Name |
Borneol
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(+)-Borneol; 464-43-7; Borneol; Camphol; d-Borneol; Hechenglongnao; Bingpian; Malayan camphor; Baros camphor; endo-Borneol; Bhimsaim camphor; Isoborneol; 2-Hydroxybornane; 2-Camphanol; 507-70-0; 2-borneol; 2-Hydroxycamphane; FEMA No. 2157; DL-Isoborneol; Borneol, dl-; Dryobalanops camphor; (1R,2S,4R)-Borneol; Borneolum syntheticum; 2-Bornanol, endo-; 2-endo-Bornyl alcohol; Camphane, 2-hydroxy-; Borneol, (+)-; (1R,2S,4R)-1,7,7-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ol; (1R,2S,4R)-rel-1,7,7-Trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ol; UNII-M89NIB437X; Bornyl alcohol; CCRIS 7300; HSDB 946; M89NIB437X; EINECS 208-080-0; NSC-60223; Bicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ol, 1,7,7-trimethyl-, (1R,2S,4R)-; 8D24LWT4FK; Borneocamphor; Borneo camphor; endo-(1R)-1,7,7-Trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ol; Sumatra camphor; AI3-00116; 2-Hydroxy-1,7,7-trimethylnorbornane, endo-; BORNEOL, (+/-)-; BICYCLO(2.2.1)HEPTAN-2-OL, 1,7,7-TRIMETHYL-, endo-; CHEBI:15393; DL-Borneol; Bicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ol, 1,7,7-trimethyl-, (1R,2S,4R)-rel-; NSC 60223; 1,7,7-Trimethyl-bicyclo(2.2.1)heptan-2-ol, endo-; 124-76-5; BORNEOL (MART.); BORNEOL [MART.]; (1R-endo)-1,7,7-Trimethylbicyclo(2.2.1)heptan-2-ol; Endo-2-camphanol; trans-Borneol; Endo-2-hydroxycamphane; (+-)-borneol; BORNEOL, D-; UNII-8D24LWT4FK; (1R-endo)-1,7,7-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ol; Bicyclo(2.2.1)heptan-2-ol, 1,7,7-trimethyl-, (1R,2S,4R)-rel-; CCRIS 6550; Borneol (contains ca. 20% Isoborneol); (+)-Borneol 100 microg/mL in Methanol; EINECS 207-352-6; endo-2-Hydroxy-1,7,7-trimethylnorbornane; UN1312; (-) Borneol; D-CAMPHANOL; BRN 2038056; BORNEOL D-FORM; BORNEOL [FHFI]; BORNEOL [HSDB]; BORNEOL [INCI]; BORNEOL [FCC]; BORNEOL [MI]; BORNEOL [WHO-DD]; (+)-Borneol, 97%; D-BORNEOL [WHO-DD]; SCHEMBL56713; BORNEOL D-FORM [MI]; 4-06-00-00281 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); endo-1,7,7-Trimethylbicyclo; CHEMBL486208; GTPL6413; DTXSID2058700; DTXSID3052143; REL-(1S,2R,4S)-1,7,7-TRIMETHYLBICYCLO(2.2.1)HEPTAN-2-OL; BDBM36265; HY-N1368A; (+)-Borneol, analytical standard; BORNEOLUM SYNTHETICUM [CHP]; ENDO-(+-)-BORNAN-2-OL; Bicyclo(2.2.1)heptan-2-ol, 1,7,7-trimethyl-, (1R-endo)-; CCG-36088; MFCD00066427; AKOS016004136; CS-7758; Borneol [UN1312] [Flammable solid]; BS-42578; FEMA NO. 2157, (+)-; BORNEOL (CONSTITUENT OF BLACK PEPPER); EN300-84951; A14485; D96054; Q412435; BORNEOL (CONSTITUENT OF BLACK PEPPER) [DSC]; Q-100570; F0001-1255; Z1255372631; (1R,3S,4R)-4,7,7-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-3-ol; (1R,4R,6S)-1,7,7-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-6-ol; Flavor and Extract Manufacturers' Association Number 2157
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
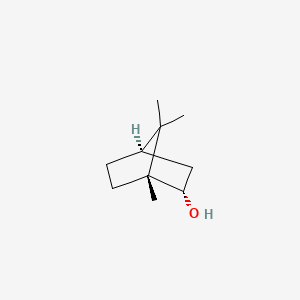 |
||||
| Formula |
C10H18O
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
(1R,2S,4R)-1,7,7-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ol
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1(C2CCC1(C(C2)O)C)C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C10H18O/c1-9(2)7-4-5-10(9,3)8(11)6-7/h7-8,11H,4-6H2,1-3H3/t7-,8+,10+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
DTGKSKDOIYIVQL-WEDXCCLWSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Unspecific Target
| In total 2 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Poly(rC)-binding protein 2 (PCBP2) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||||
| Cell adhesion molecules | hsa04514 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| In Vitro Model | H460/CisR cells | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C5S1 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Male Balb/c nude mice (4-week-old) were purchased from SPF (Beijing) biotechnology co., LTD and maintained in the Experimental Animal Research Center of Chengdu University of TCM. After 1 week of adaptable feeding, H460/CDDP cells (5 x 106 cells in 0.1 ml phosphate-buffered saline) were subcutaneously injected into the right dorsal flank to establish tumor model. When the tumor volume grows to 100 mm3, the tumor-bearing mice were randomly divided into the following four treatment groups: a control group (Con, n = 6): intraperitoneal injection of saline once a day; vehicle group (Vehicle, n = 6): intragastric administration of 2% tween and intraperitoneal injection of saline; d-borneol low-dose group (Bor-L, n = 6): intragastric administration of d-borneol (30 mg/kg) once a day; d-borneol high-dose group (Bor-H, n = 6): intragastric administration of d-borneol (60 mg/kg) once a day; CDDP group (CDDP, n = 6): intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin (3 mg/kg) every two days; a low-dose combination treatment group (C+B-L, n = 6): intragastric administration of d-borneol (30 mg/kg) once a day and intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin (3 mg/kg) every two days; a high-dose combination treatment group (C+B-H, n = 6): intragastric administration of d-borneol (60 mg/kg) once a day and intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin (3 mg/kg) every two days. We usually first orally gavage d-borneol, and then inject cisplatin intraperitoneally half an hour later. After 14 days treatment, the samples were obtained from the mice for the further experiments.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | d-borneol in combination with cisplatin induced ferroptosisviaNCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy and also increased the expression levels of ACSL4, regulated PCBP2 and PRNP to promote the conversion of Fe3+to Fe2+, reduced the activity or expression of antioxidants enzymes (GSH and HO-1), and induced ROS accumulation and thereby promoted ferroptosis. In addition, activation of autophagy inhibited progression of the EMT and increased sensitivity to cisplatin in cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Major prion protein (PRNP) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||||
| Cell adhesion molecules | hsa04514 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| In Vitro Model | H460/CisR cells | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C5S1 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Male Balb/c nude mice (4-week-old) were purchased from SPF (Beijing) biotechnology co., LTD and maintained in the Experimental Animal Research Center of Chengdu University of TCM. After 1 week of adaptable feeding, H460/CDDP cells (5 x 106 cells in 0.1 ml phosphate-buffered saline) were subcutaneously injected into the right dorsal flank to establish tumor model. When the tumor volume grows to 100 mm3, the tumor-bearing mice were randomly divided into the following four treatment groups: a control group (Con, n = 6): intraperitoneal injection of saline once a day; vehicle group (Vehicle, n = 6): intragastric administration of 2% tween and intraperitoneal injection of saline; d-borneol low-dose group (Bor-L, n = 6): intragastric administration of d-borneol (30 mg/kg) once a day; d-borneol high-dose group (Bor-H, n = 6): intragastric administration of d-borneol (60 mg/kg) once a day; CDDP group (CDDP, n = 6): intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin (3 mg/kg) every two days; a low-dose combination treatment group (C+B-L, n = 6): intragastric administration of d-borneol (30 mg/kg) once a day and intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin (3 mg/kg) every two days; a high-dose combination treatment group (C+B-H, n = 6): intragastric administration of d-borneol (60 mg/kg) once a day and intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin (3 mg/kg) every two days. We usually first orally gavage d-borneol, and then inject cisplatin intraperitoneally half an hour later. After 14 days treatment, the samples were obtained from the mice for the further experiments.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | d-borneol in combination with cisplatin induced ferroptosisvia NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy and also increased the expression levels of ACSL4, regulated PCBP2 and PRNP to promote the conversion of Fe3+ to Fe2+, reduced the activity or expression of antioxidants enzymes (GSH and HO-1), and induced ROS accumulation and thereby promoted ferroptosis. In addition, activation of autophagy inhibited progression of the EMT and increased sensitivity to cisplatin in cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells. | ||||
Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 4 (ACSL4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Target for Ferroptosis | Driver | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||||
| Cell adhesion molecules | hsa04514 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| In Vitro Model | H460/CisR cells | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_C5S1 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Male Balb/c nude mice (4-week-old) were purchased from SPF (Beijing) biotechnology co., LTD and maintained in the Experimental Animal Research Center of Chengdu University of TCM. After 1 week of adaptable feeding, H460/CDDP cells (5 x 106 cells in 0.1 ml phosphate-buffered saline) were subcutaneously injected into the right dorsal flank to establish tumor model. When the tumor volume grows to 100 mm3, the tumor-bearing mice were randomly divided into the following four treatment groups: a control group (Con, n = 6): intraperitoneal injection of saline once a day; vehicle group (Vehicle, n = 6): intragastric administration of 2% tween and intraperitoneal injection of saline; d-borneol low-dose group (Bor-L, n = 6): intragastric administration of d-borneol (30 mg/kg) once a day; d-borneol high-dose group (Bor-H, n = 6): intragastric administration of d-borneol (60 mg/kg) once a day; CDDP group (CDDP, n = 6): intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin (3 mg/kg) every two days; a low-dose combination treatment group (C+B-L, n = 6): intragastric administration of d-borneol (30 mg/kg) once a day and intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin (3 mg/kg) every two days; a high-dose combination treatment group (C+B-H, n = 6): intragastric administration of d-borneol (60 mg/kg) once a day and intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin (3 mg/kg) every two days. We usually first orally gavage d-borneol, and then inject cisplatin intraperitoneally half an hour later. After 14 days treatment, the samples were obtained from the mice for the further experiments.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | d-borneol in combination with cisplatin induced ferroptosisviaNCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy and also increased the expression levels of ACSL4, regulated PCBP2 and PRNP to promote the conversion of Fe3+to Fe2+, reduced the activity or expression of antioxidants enzymes (GSH and HO-1), and induced ROS accumulation and thereby promoted ferroptosis. In addition, activation of autophagy inhibited progression of the EMT and increased sensitivity to cisplatin in cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells. | ||||
